Dark pool activity involves private, non-transparent trading venues where large blocks of shares are executed away from public exchanges, reducing market impact and information leakage. Algorithmic trading employs sophisticated computer algorithms to execute trades at high speed based on predefined strategies, optimizing order execution and minimizing transaction costs. Explore the differences and implications of dark pool trading versus algorithmic approaches to enhance your market understanding.
Why it is important
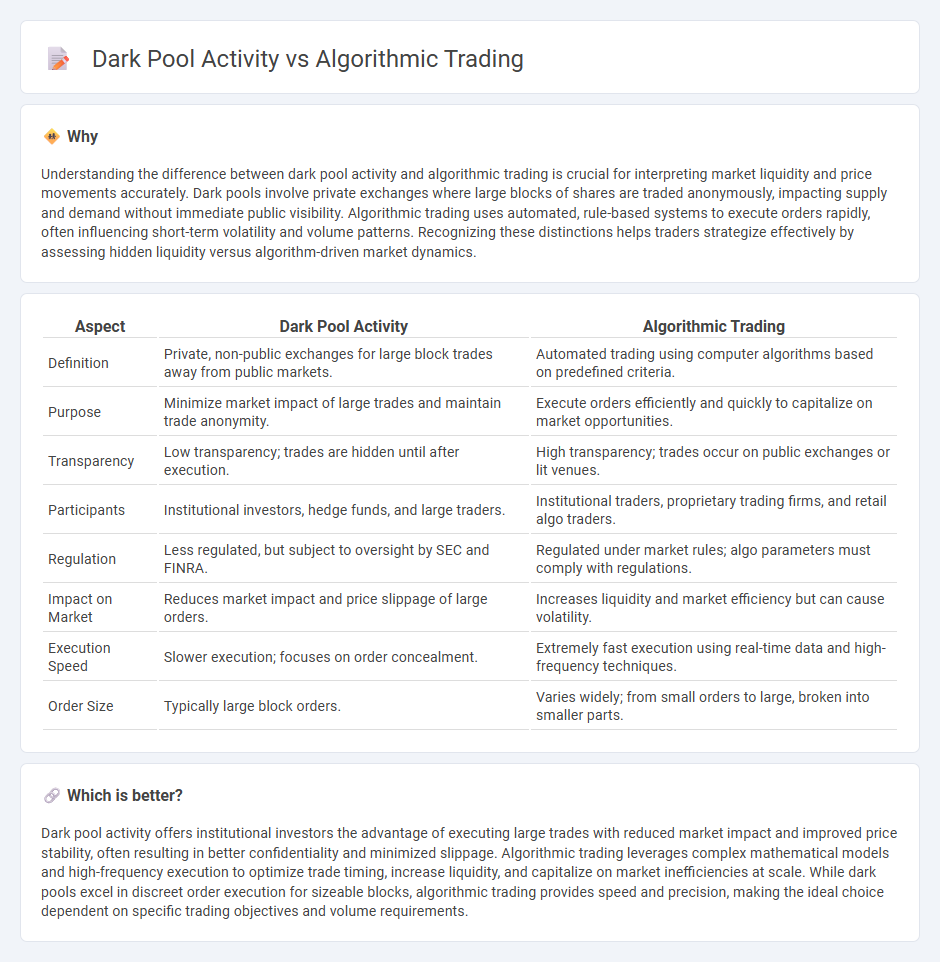
Understanding the difference between dark pool activity and algorithmic trading is crucial for interpreting market liquidity and price movements accurately. Dark pools involve private exchanges where large blocks of shares are traded anonymously, impacting supply and demand without immediate public visibility. Algorithmic trading uses automated, rule-based systems to execute orders rapidly, often influencing short-term volatility and volume patterns. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders strategize effectively by assessing hidden liquidity versus algorithm-driven market dynamics.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pool Activity | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private, non-public exchanges for large block trades away from public markets. | Automated trading using computer algorithms based on predefined criteria. |
| Purpose | Minimize market impact of large trades and maintain trade anonymity. | Execute orders efficiently and quickly to capitalize on market opportunities. |
| Transparency | Low transparency; trades are hidden until after execution. | High transparency; trades occur on public exchanges or lit venues. |
| Participants | Institutional investors, hedge funds, and large traders. | Institutional traders, proprietary trading firms, and retail algo traders. |
| Regulation | Less regulated, but subject to oversight by SEC and FINRA. | Regulated under market rules; algo parameters must comply with regulations. |
| Impact on Market | Reduces market impact and price slippage of large orders. | Increases liquidity and market efficiency but can cause volatility. |
| Execution Speed | Slower execution; focuses on order concealment. | Extremely fast execution using real-time data and high-frequency techniques. |
| Order Size | Typically large block orders. | Varies widely; from small orders to large, broken into smaller parts. |
Which is better?
Dark pool activity offers institutional investors the advantage of executing large trades with reduced market impact and improved price stability, often resulting in better confidentiality and minimized slippage. Algorithmic trading leverages complex mathematical models and high-frequency execution to optimize trade timing, increase liquidity, and capitalize on market inefficiencies at scale. While dark pools excel in discreet order execution for sizeable blocks, algorithmic trading provides speed and precision, making the ideal choice dependent on specific trading objectives and volume requirements.
Connection
Dark pool activity and algorithmic trading are interconnected through the use of high-frequency algorithms designed to execute large trades anonymously within private trading venues, minimizing market impact and avoiding price slippage. Dark pools provide the liquidity necessary for algorithmic traders to strategically place orders without revealing intent to the broader market, enhancing execution efficiency. The integration of advanced algorithms with dark pools accelerates trade matching and optimizes order flow, crucial for institutional investors managing significant portfolios.
Key Terms
Execution Algorithms
Execution algorithms play a critical role in algorithmic trading by optimizing trade execution to minimize market impact and reduce transaction costs while dark pool activity provides an alternative venue for trading large blocks of shares anonymously, thereby enhancing price discovery and liquidity. The interaction between execution algorithms and dark pools is pivotal, with algorithms often designed to intelligently route orders between lit markets and dark pools to achieve best execution. Explore how innovative execution algorithms leverage dark pool activity to maximize trading efficiency and confidentiality.
Liquidity
Algorithmic trading enhances market liquidity by executing high-frequency trades that narrow bid-ask spreads and increase order flow transparency. Dark pool activity, however, provides liquidity off-exchange by enabling large block trades without immediate market impact, reducing information leakage and minimizing price volatility. Explore how these liquidity sources differ and influence market efficiency in greater detail.
Transparency
Algorithmic trading uses computer algorithms to execute high-speed, data-driven trades, often contributing to market liquidity but sometimes increasing volatility. Dark pool activity occurs within private exchanges that conceal order sizes and prices, limiting transparency and complicating price discovery for public markets. Explore how transparency differences impact market fairness and trading efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading uses computer codes to open and close trades based on set rules such as price movement, and it includes strategies like price action, technical analysis, and combinations; for example, scalpers use high-frequency trading to capitalize on small price moves.
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - Algorithmic trading involves pre-set programmed rules executing trades automatically when conditions are met, commonly employing strategies like moving averages to buy or sell securities based on price versus average price trends.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading automates order execution using programmed instructions and has evolved significantly with machine learning methods like deep reinforcement learning and directional change algorithms to adapt to volatile markets and improve trade timing and profitability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com