Atomic swaps enable direct cryptocurrency exchanges between parties without relying on intermediaries, using smart contracts to ensure simultaneous transaction completion and prevent fraud. Trustless escrow, on the other hand, involves a decentralized third-party service that holds funds securely until both sides fulfill agreed conditions, minimizing counterparty risk. Explore these innovative trading mechanisms to understand their impact on secure, efficient digital asset exchanges.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between atomic swaps and trustless escrow is crucial for secure and efficient cryptocurrency trading. Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer asset exchange across different blockchains without intermediaries, minimizing counterparty risk. Trustless escrow involves a neutral third party smart contract that holds funds until transaction conditions are met, reducing the chance of fraud. Knowing these mechanisms enhances trader confidence, reduces costs, and improves transaction speed in decentralized finance.
Comparison Table
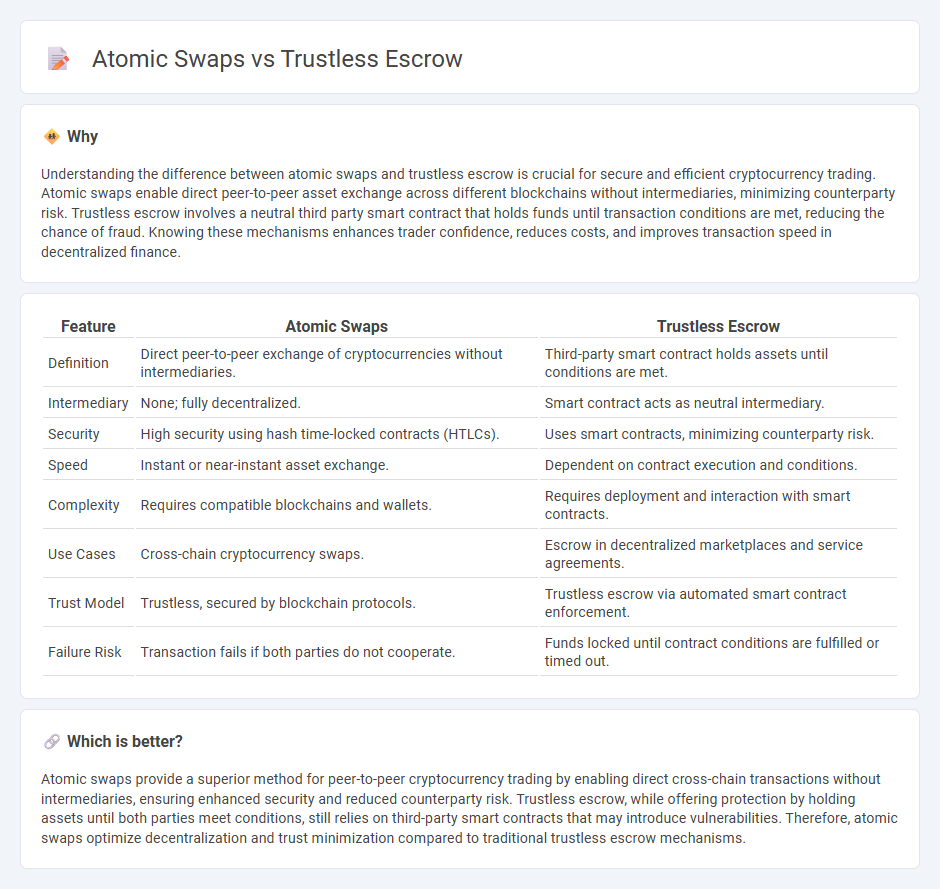
| Feature | Atomic Swaps | Trustless Escrow |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct peer-to-peer exchange of cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. | Third-party smart contract holds assets until conditions are met. |
| Intermediary | None; fully decentralized. | Smart contract acts as neutral intermediary. |
| Security | High security using hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs). | Uses smart contracts, minimizing counterparty risk. |
| Speed | Instant or near-instant asset exchange. | Dependent on contract execution and conditions. |
| Complexity | Requires compatible blockchains and wallets. | Requires deployment and interaction with smart contracts. |
| Use Cases | Cross-chain cryptocurrency swaps. | Escrow in decentralized marketplaces and service agreements. |
| Trust Model | Trustless, secured by blockchain protocols. | Trustless escrow via automated smart contract enforcement. |
| Failure Risk | Transaction fails if both parties do not cooperate. | Funds locked until contract conditions are fulfilled or timed out. |
Which is better?
Atomic swaps provide a superior method for peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading by enabling direct cross-chain transactions without intermediaries, ensuring enhanced security and reduced counterparty risk. Trustless escrow, while offering protection by holding assets until both parties meet conditions, still relies on third-party smart contracts that may introduce vulnerabilities. Therefore, atomic swaps optimize decentralization and trust minimization compared to traditional trustless escrow mechanisms.
Connection
Atomic swaps enable direct cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, ensuring trustless transactions. Trustless escrow mechanisms complement atomic swaps by securely holding funds until all transaction conditions are met, eliminating counterparty risk. Together, they create a decentralized, secure environment for peer-to-peer trading without reliance on centralized exchanges.
Key Terms
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts facilitate trustless escrow by automatically executing fund releases based on predefined conditions without intermediaries, ensuring secure and transparent transactions. Atomic swaps utilize smart contracts to enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains, eliminating counterparty risk and enhancing interoperability. Explore the benefits of smart contract-powered trustless escrow and atomic swaps to understand their impact on decentralized finance.
Decentralization
Trustless escrow utilizes smart contracts to hold funds securely until specific conditions are met, ensuring no centralized intermediary controls the assets. Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without relying on third-party services, emphasizing a higher degree of decentralization. Explore how these mechanisms transform decentralized finance by delving deeper into their operational frameworks.
Counterparty Risk
Trustless escrow eliminates counterparty risk by using smart contracts to hold funds until predefined conditions are met, ensuring neither party can unilaterally access the assets. Atomic swaps further reduce counterparty risk by enabling direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains, without intermediaries or third-party custody. Explore how these technologies enhance security and trust in decentralized transactions.
Source and External Links
Trustless Escrow Services: Ensuring Safety with Hashed Timelock Contracts - Trustless escrow services use smart contracts and cryptographic tools like Hashed Timelock Contracts (HTLCs) to automate financial transactions without intermediaries, ensuring funds are released only when predefined conditions are met, thus reducing fraud and increasing security and transparency.
Trustless Swap - Sui Documentation - Trustless swaps operate like escrows but remove the need for trusted third parties by using blockchain-based mechanisms that lock assets with single-use keys, guaranteeing atomic swaps and preventing tampering before trades complete.
Escrow Types - Trustless Work - Trustless escrow implementations include single-release and multi-release escrow types, supporting automated, condition-based fund releases ideal for freelance jobs, staged projects, and digital goods, all enabling trust without relying on third-party intermediaries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com