Human augmentation involves integrating advanced technologies directly with the human body to enhance physical and cognitive capabilities, often through implants or bioengineering. Wearable technology, in contrast, consists of external devices like smartwatches or fitness trackers that monitor and support health or performance without invasive integration. Explore how these innovations are transforming manufacturing processes and workforce efficiency.
Why it is important
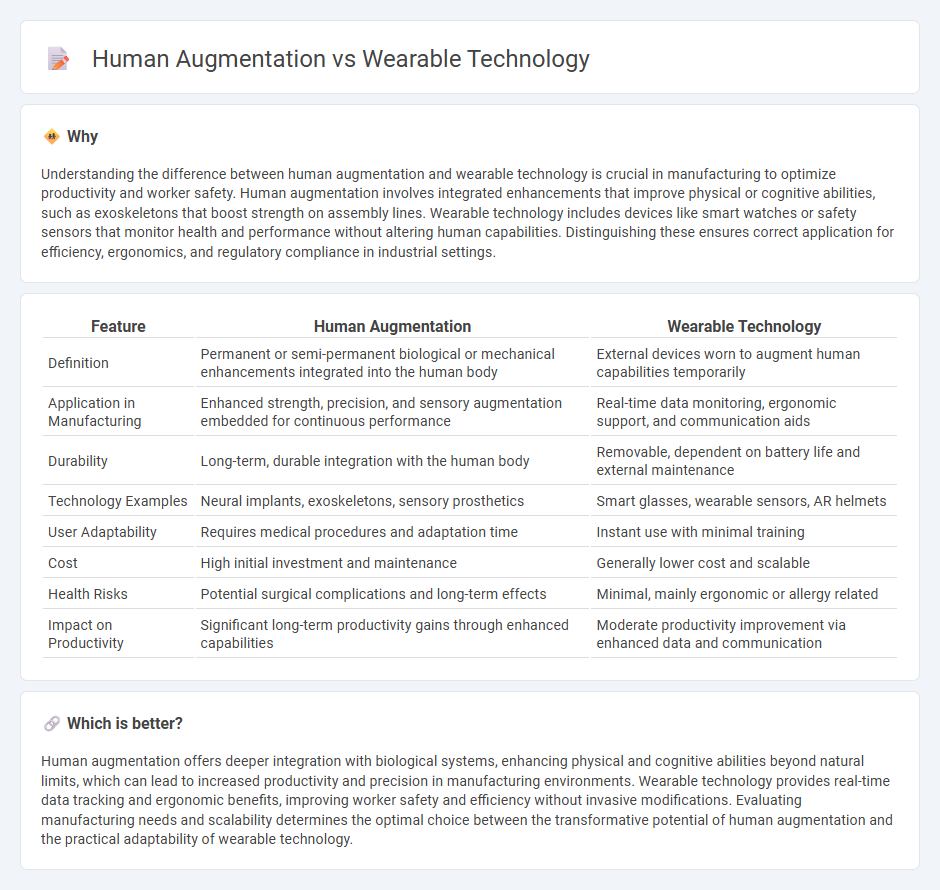
Understanding the difference between human augmentation and wearable technology is crucial in manufacturing to optimize productivity and worker safety. Human augmentation involves integrated enhancements that improve physical or cognitive abilities, such as exoskeletons that boost strength on assembly lines. Wearable technology includes devices like smart watches or safety sensors that monitor health and performance without altering human capabilities. Distinguishing these ensures correct application for efficiency, ergonomics, and regulatory compliance in industrial settings.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Human Augmentation | Wearable Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent or semi-permanent biological or mechanical enhancements integrated into the human body | External devices worn to augment human capabilities temporarily |
| Application in Manufacturing | Enhanced strength, precision, and sensory augmentation embedded for continuous performance | Real-time data monitoring, ergonomic support, and communication aids |
| Durability | Long-term, durable integration with the human body | Removable, dependent on battery life and external maintenance |
| Technology Examples | Neural implants, exoskeletons, sensory prosthetics | Smart glasses, wearable sensors, AR helmets |
| User Adaptability | Requires medical procedures and adaptation time | Instant use with minimal training |
| Cost | High initial investment and maintenance | Generally lower cost and scalable |
| Health Risks | Potential surgical complications and long-term effects | Minimal, mainly ergonomic or allergy related |
| Impact on Productivity | Significant long-term productivity gains through enhanced capabilities | Moderate productivity improvement via enhanced data and communication |
Which is better?
Human augmentation offers deeper integration with biological systems, enhancing physical and cognitive abilities beyond natural limits, which can lead to increased productivity and precision in manufacturing environments. Wearable technology provides real-time data tracking and ergonomic benefits, improving worker safety and efficiency without invasive modifications. Evaluating manufacturing needs and scalability determines the optimal choice between the transformative potential of human augmentation and the practical adaptability of wearable technology.
Connection
Human augmentation and wearable technology are transforming manufacturing by enhancing worker capabilities through real-time data monitoring and ergonomic support. These innovations improve precision, reduce fatigue, and increase safety on production lines by integrating sensors, exoskeletons, and augmented reality devices. The synergy between augmented workers and wearable tech drives higher productivity and efficiency in industrial operations.
Key Terms
Sensors integration
Wearable technology primarily uses sensors to monitor physiological signals such as heart rate, temperature, and motion, enabling real-time health tracking and fitness optimization. Human augmentation integrates advanced sensors directly into the body or exoskeletons to enhance sensory perception, strength, or cognitive abilities, providing extended functionality beyond natural limits. Explore the latest innovations in sensor integration to discover how these technologies are shaping the future of human-machine interaction.
Exoskeletons
Exoskeletons serve as a key intersection between wearable technology and human augmentation, enhancing physical capabilities by providing external support and strength. These devices are utilized in medical rehabilitation, industrial work, and military applications to reduce fatigue and prevent injuries. Explore the advancements and impacts of exoskeletons to understand their transformative role in human augmentation.
Ergonomic enhancement
Ergonomic enhancement in wearable technology centers on improving user comfort and reducing physical strain, using devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers that monitor posture and movement. Human augmentation advances this concept by integrating biomechanical exoskeletons and neural interfaces, directly enhancing physical capabilities and reducing fatigue in demanding tasks. Explore how ergonomic innovations in both fields are reshaping productivity and wellbeing.
Source and External Links
What is Wearable Technology? Definition, Uses and Examples - Wearable technology refers to electronic devices designed to be worn on the body in forms such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, VR headsets, and smart clothing, which monitor bodily functions and sync data wirelessly for health, fitness, or entertainment purposes.
Wearable technology - Wikipedia - Wearable technology includes devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers that collect physiological and behavioral data in real time to aid health monitoring, communication, and lifestyle improvement, while raising concerns about data privacy and security.
7 ways wearable technology can help you reach your health goals - Wearables can increase physical activity, help maintain healthy eating habits through meal tracking, and monitor important health metrics like heart rate and sleep patterns to support personalized health management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com