Industrial symbiosis involves the collaboration of diverse industries to share resources, by-products, and energy streams, reducing waste and enhancing overall efficiency. Closed-loop supply chains focus on recycling, reusing, and refurbishing materials within a single company, aiming to minimize environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. Explore the distinctions between industrial symbiosis and closed-loop supply chains to optimize sustainable manufacturing practices.
Why it is important
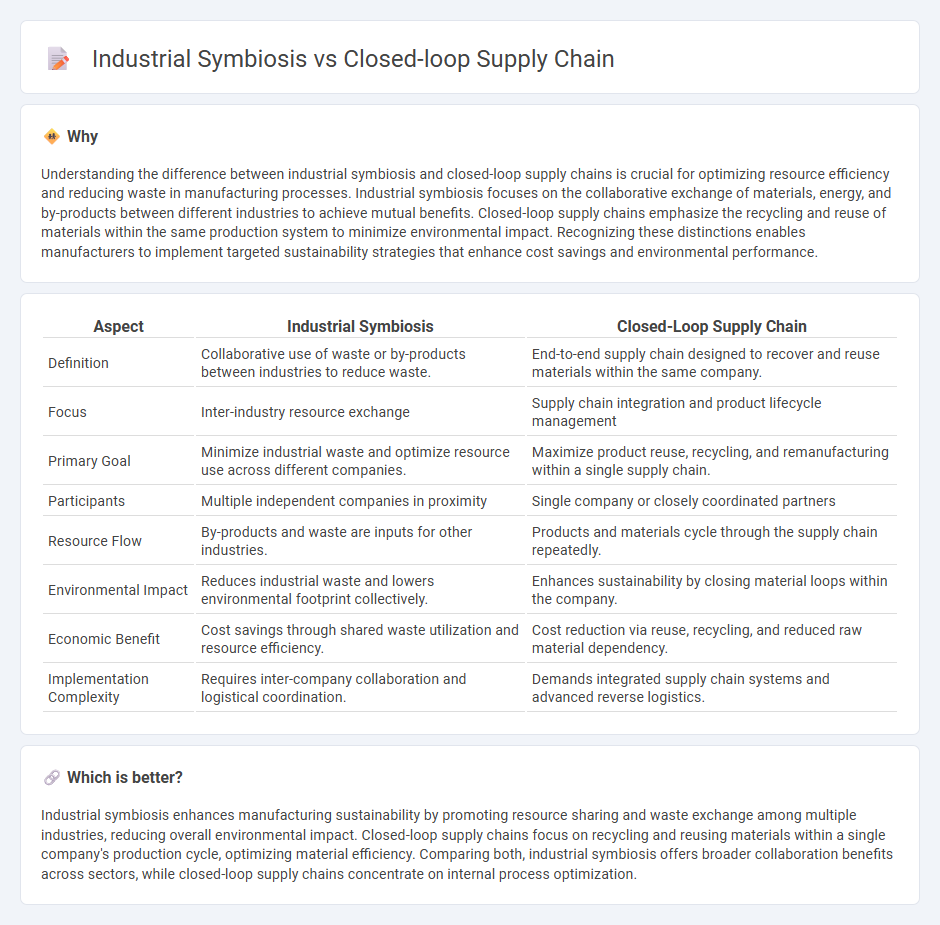
Understanding the difference between industrial symbiosis and closed-loop supply chains is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and reducing waste in manufacturing processes. Industrial symbiosis focuses on the collaborative exchange of materials, energy, and by-products between different industries to achieve mutual benefits. Closed-loop supply chains emphasize the recycling and reuse of materials within the same production system to minimize environmental impact. Recognizing these distinctions enables manufacturers to implement targeted sustainability strategies that enhance cost savings and environmental performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Symbiosis | Closed-Loop Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative use of waste or by-products between industries to reduce waste. | End-to-end supply chain designed to recover and reuse materials within the same company. |
| Focus | Inter-industry resource exchange | Supply chain integration and product lifecycle management |
| Primary Goal | Minimize industrial waste and optimize resource use across different companies. | Maximize product reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing within a single supply chain. |
| Participants | Multiple independent companies in proximity | Single company or closely coordinated partners |
| Resource Flow | By-products and waste are inputs for other industries. | Products and materials cycle through the supply chain repeatedly. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces industrial waste and lowers environmental footprint collectively. | Enhances sustainability by closing material loops within the company. |
| Economic Benefit | Cost savings through shared waste utilization and resource efficiency. | Cost reduction via reuse, recycling, and reduced raw material dependency. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires inter-company collaboration and logistical coordination. | Demands integrated supply chain systems and advanced reverse logistics. |
Which is better?
Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing sustainability by promoting resource sharing and waste exchange among multiple industries, reducing overall environmental impact. Closed-loop supply chains focus on recycling and reusing materials within a single company's production cycle, optimizing material efficiency. Comparing both, industrial symbiosis offers broader collaboration benefits across sectors, while closed-loop supply chains concentrate on internal process optimization.
Connection
Industrial symbiosis and closed-loop supply chains are interconnected through their shared goal of minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency within manufacturing systems. Industrial symbiosis facilitates the exchange of by-products and energy between different industries, creating a network where waste from one process becomes input for another. Closed-loop supply chains complement this by ensuring products and materials are continually reused, remanufactured, or recycled, thus supporting sustainable production and reducing environmental impact.
Key Terms
Reverse Logistics
Closed-loop supply chain integrates reverse logistics to recapture value by recycling, refurbishing, and remanufacturing products, enhancing sustainability and reducing waste. Industrial symbiosis focuses on inter-organizational resource sharing, where byproducts or waste from one company serve as inputs for another within a network, optimizing overall efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. Explore the distinct roles of reverse logistics in these sustainable systems to improve resource management and competitive advantage.
By-product Exchange
Closed-loop supply chains emphasize the recovery and reuse of materials within a single organization or supply chain to minimize waste and enhance sustainability. Industrial symbiosis involves collaboration between different industries to exchange by-products, converting one industry's waste into another's resource, thus creating economic and environmental benefits. Explore more to understand the critical differences and synergies in optimizing by-product exchange strategies.
Material Flow Optimization
Closed-loop supply chains prioritize recycling and remanufacturing within a company's own network to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. Industrial symbiosis enhances material flow optimization by facilitating resource sharing across different industries, promoting collective waste reduction, and improving overall environmental sustainability. Explore how these strategies transform material flow optimization for competitive advantage and sustainability gains.
Source and External Links
What is Closed-Loop Supply Chain - A closed-loop supply chain integrates the forward and reverse flows of products and materials to maximize value and minimize waste through activities like repair, remanufacturing, recycling, and refurbishing.
What is a Closed-Loop Supply Chain? - Closed-loop supply chains use reverse logistics to return used products to the manufacturing process for repair, resale, or component reuse, reducing waste and supporting circular economy principles.
Closed Loop Supply Chain (CLSC): Meaning & Examples - Closed-loop supply chain management involves managing a product's entire lifecycle, including the return of used products for reuse or recycling, to minimize waste, reduce costs, and lessen environmental impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com