Dark factories leverage automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Batch manufacturing involves producing goods in specific quantities or lots, allowing flexibility for customization and quality control. Explore the key differences and advantages of dark factory and batch manufacturing to optimize production strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark factory and batch manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing labor costs. Dark factories operate fully automated processes without human intervention, enabling 24/7 operation and minimizing errors. Batch manufacturing involves producing goods in specific quantities, allowing customization but requiring more manual control and downtime. Knowing these distinctions helps manufacturers select the right system for scalability, cost management, and product quality.
Comparison Table
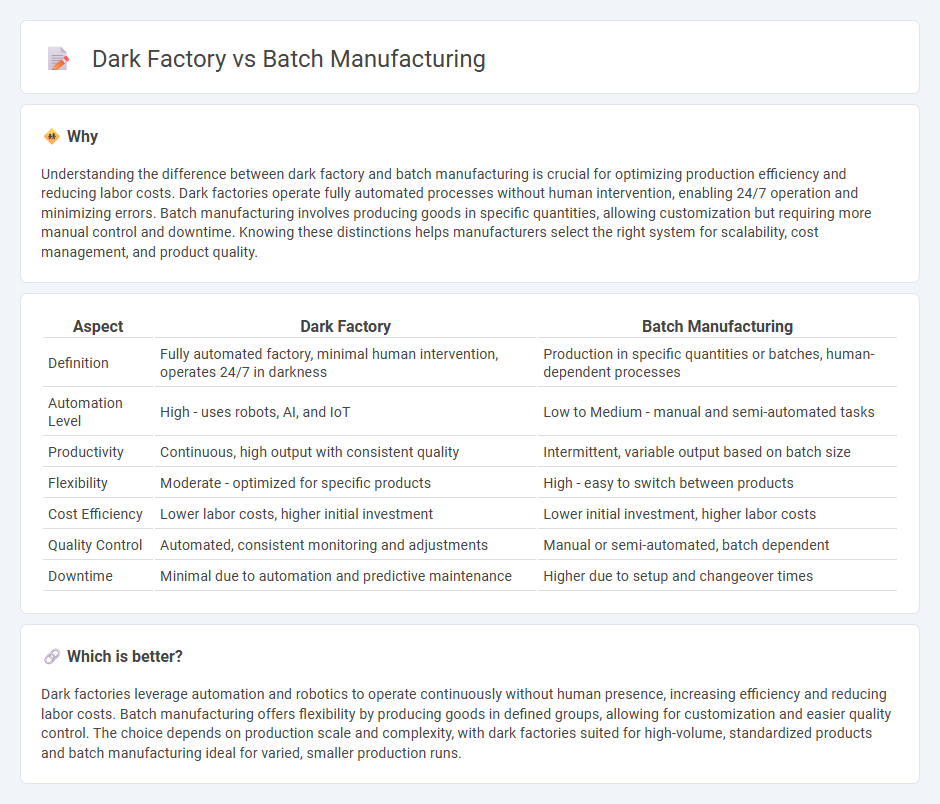
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Batch Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory, minimal human intervention, operates 24/7 in darkness | Production in specific quantities or batches, human-dependent processes |
| Automation Level | High - uses robots, AI, and IoT | Low to Medium - manual and semi-automated tasks |
| Productivity | Continuous, high output with consistent quality | Intermittent, variable output based on batch size |
| Flexibility | Moderate - optimized for specific products | High - easy to switch between products |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower labor costs, higher initial investment | Lower initial investment, higher labor costs |
| Quality Control | Automated, consistent monitoring and adjustments | Manual or semi-automated, batch dependent |
| Downtime | Minimal due to automation and predictive maintenance | Higher due to setup and changeover times |
Which is better?
Dark factories leverage automation and robotics to operate continuously without human presence, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Batch manufacturing offers flexibility by producing goods in defined groups, allowing for customization and easier quality control. The choice depends on production scale and complexity, with dark factories suited for high-volume, standardized products and batch manufacturing ideal for varied, smaller production runs.
Connection
Dark factories utilize automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, optimizing batch manufacturing processes by enabling continuous, high-precision production runs. Batch manufacturing benefits from dark factory environments through increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and consistent quality control. This integration supports scalable production while minimizing labor costs and errors.
Key Terms
Human Labor Involvement
Batch manufacturing relies heavily on human labor for tasks such as machine operation, quality checks, and material handling, which can increase labor costs and introduce variability. Dark factories utilize advanced automation and robotics to minimize human intervention, enhancing productivity, consistency, and operational efficiency. Explore deeper insights on how human labor involvement impacts manufacturing processes and cost-effectiveness.
Automation Level
Batch manufacturing typically involves partial automation with human oversight during production cycles, optimizing flexibility for varying product types. Dark factories operate with full automation and zero human presence, leveraging robotics and AI for continuous, high-efficiency output in controlled environments. Explore how automation levels impact manufacturing strategies and operational efficiencies in dark factories versus batch processes.
Production Flexibility
Batch manufacturing offers moderate production flexibility by producing goods in predefined quantities, allowing adjustments between batches but limited customization within each batch. Dark factories leverage automation and AI to enable continuous, high-precision production with rapid reprogramming for diverse product variations, significantly increasing production flexibility. Explore how these manufacturing approaches impact operational efficiency and adaptability in dynamic markets.
Source and External Links
What is Batch Production in Manufacturing? - Batch manufacturing is the process where a group of identical products is produced as a batch, passing through production stages together for efficient quality control and flexibility in product variations within a given timeframe.
What is batch production in manufacturing? - Batch production involves making a set of identical products simultaneously, with each batch completing manufacturing steps before the next begins, allowing quality checks after each stage and flexibility to alter the product specifications between batches.
Batch Production: Examples, Advantages and Disadvantages - Batch production is commonly used in industries like food, apparel, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, offering advantages such as producing smaller quantities, lowering costs by spreading expenses across products, reducing lead times, and enabling better quality control through stage-wise inspections.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com