Green steel production utilizes hydrogen and renewable energy to reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional scrap-based steel, which relies on melting recycled steel scrap in electric arc furnaces. Green steel offers a sustainable alternative by minimizing environmental impact through direct reduction processes, while scrap-based steel depends on the availability and quality of scrap materials. Explore the advantages and challenges of each method to better understand their roles in sustainable manufacturing.
Why it is important
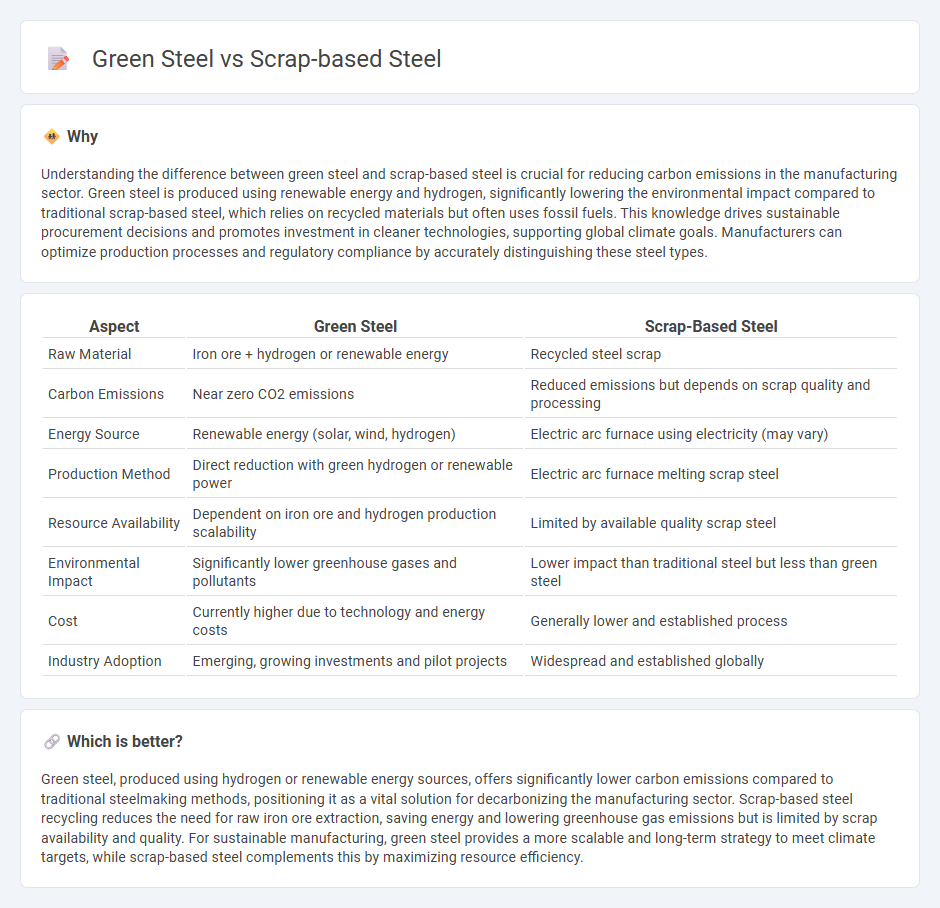
Understanding the difference between green steel and scrap-based steel is crucial for reducing carbon emissions in the manufacturing sector. Green steel is produced using renewable energy and hydrogen, significantly lowering the environmental impact compared to traditional scrap-based steel, which relies on recycled materials but often uses fossil fuels. This knowledge drives sustainable procurement decisions and promotes investment in cleaner technologies, supporting global climate goals. Manufacturers can optimize production processes and regulatory compliance by accurately distinguishing these steel types.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Steel | Scrap-Based Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Iron ore + hydrogen or renewable energy | Recycled steel scrap |
| Carbon Emissions | Near zero CO2 emissions | Reduced emissions but depends on scrap quality and processing |
| Energy Source | Renewable energy (solar, wind, hydrogen) | Electric arc furnace using electricity (may vary) |
| Production Method | Direct reduction with green hydrogen or renewable power | Electric arc furnace melting scrap steel |
| Resource Availability | Dependent on iron ore and hydrogen production scalability | Limited by available quality scrap steel |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly lower greenhouse gases and pollutants | Lower impact than traditional steel but less than green steel |
| Cost | Currently higher due to technology and energy costs | Generally lower and established process |
| Industry Adoption | Emerging, growing investments and pilot projects | Widespread and established globally |
Which is better?
Green steel, produced using hydrogen or renewable energy sources, offers significantly lower carbon emissions compared to traditional steelmaking methods, positioning it as a vital solution for decarbonizing the manufacturing sector. Scrap-based steel recycling reduces the need for raw iron ore extraction, saving energy and lowering greenhouse gas emissions but is limited by scrap availability and quality. For sustainable manufacturing, green steel provides a more scalable and long-term strategy to meet climate targets, while scrap-based steel complements this by maximizing resource efficiency.
Connection
Green steel production significantly reduces carbon emissions by using hydrogen or renewable energy in place of traditional coal-based methods, while scrap-based steel relies on recycling steel scrap to lower raw material usage and energy consumption. Both approaches contribute to sustainable manufacturing by minimizing environmental impact and conserving natural resources. Integrating green steel technology with scrap-based recycling enhances overall efficiency and supports the steel industry's transition to a circular economy.
Key Terms
Recycled Scrap
Recycled scrap steel is a key component in scrap-based steel production, using domestically sourced steel scrap to reduce reliance on raw iron ore and decrease carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnace methods. Scrap-based steel typically accounts for around 60-70% of global steel production, offering significant environmental benefits by lowering energy consumption up to 75% and minimizing waste. Explore further insights into recycled scrap's role in transforming the steel industry towards sustainability and green steel advancements.
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI)
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) plays a crucial role in green steel production by using natural gas or hydrogen to reduce iron ore, significantly lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional scrap-based steelmaking which relies heavily on electric arc furnaces recycling scrap metal. DRI offers a cleaner alternative that supports decarbonization goals by minimizing dependence on recycled scrap while enhancing steel quality through consistent iron content. Explore more about how DRI transforms the steel industry toward sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
Hydrogen Reduction
Hydrogen reduction steelmaking revolutionizes green steel production by using hydrogen gas to reduce iron ore, significantly cutting CO2 emissions compared to traditional scrap-based steel processes that rely on electric arc furnaces. This innovative method enables direct reduction of iron pellets, promoting sustainability and aligning with global decarbonization goals for the steel industry. Discover how hydrogen-based steelmaking paves the way for eco-friendly manufacturing and the future of steel production.
Source and External Links
New Study: Enough Scrap to Meet Rising U.S. Demand for Recycled Steel - Scrap-based steel production, primarily through electric arc furnaces (EAFs), can meet nearly all U.S. steel demand and significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnaces, with scrap availability growing to support this transition.
Scrap use in the steel industry - Scrap steel, sourced from end-of-life products and manufacturing waste, is a valuable raw material that is continuously recycled to produce new steel, maintaining quality and enabling adjustments in composition, and is used in all steelmaking processes including blast furnaces and EAFs.
What Is Steel Scrap? - Worthington Steel - Steel scrap consists of discarded steel from various sources such as old vehicles and manufacturing offcuts and is essential in steel recycling, allowing for energy-efficient production of new steel and reducing environmental impact by conserving natural resources.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com