Smart dust consists of tiny, networked sensors capable of real-time data collection and environmental monitoring in manufacturing processes, enabling precise control and predictive maintenance. Wearable devices enhance worker safety and productivity by providing health monitoring, location tracking, and communication tools on the factory floor. Explore how these innovative technologies are transforming manufacturing efficiency and safety.
Why it is important
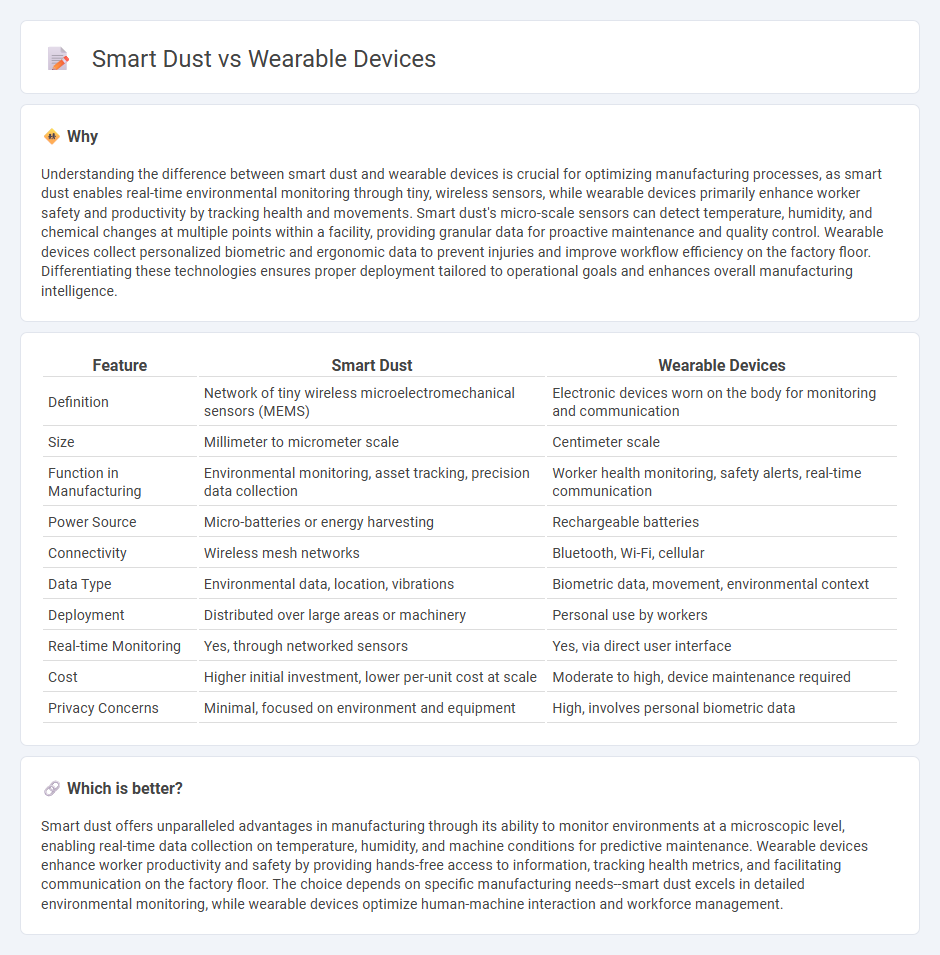
Understanding the difference between smart dust and wearable devices is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as smart dust enables real-time environmental monitoring through tiny, wireless sensors, while wearable devices primarily enhance worker safety and productivity by tracking health and movements. Smart dust's micro-scale sensors can detect temperature, humidity, and chemical changes at multiple points within a facility, providing granular data for proactive maintenance and quality control. Wearable devices collect personalized biometric and ergonomic data to prevent injuries and improve workflow efficiency on the factory floor. Differentiating these technologies ensures proper deployment tailored to operational goals and enhances overall manufacturing intelligence.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Dust | Wearable Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of tiny wireless microelectromechanical sensors (MEMS) | Electronic devices worn on the body for monitoring and communication |
| Size | Millimeter to micrometer scale | Centimeter scale |
| Function in Manufacturing | Environmental monitoring, asset tracking, precision data collection | Worker health monitoring, safety alerts, real-time communication |
| Power Source | Micro-batteries or energy harvesting | Rechargeable batteries |
| Connectivity | Wireless mesh networks | Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, cellular |
| Data Type | Environmental data, location, vibrations | Biometric data, movement, environmental context |
| Deployment | Distributed over large areas or machinery | Personal use by workers |
| Real-time Monitoring | Yes, through networked sensors | Yes, via direct user interface |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower per-unit cost at scale | Moderate to high, device maintenance required |
| Privacy Concerns | Minimal, focused on environment and equipment | High, involves personal biometric data |
Which is better?
Smart dust offers unparalleled advantages in manufacturing through its ability to monitor environments at a microscopic level, enabling real-time data collection on temperature, humidity, and machine conditions for predictive maintenance. Wearable devices enhance worker productivity and safety by providing hands-free access to information, tracking health metrics, and facilitating communication on the factory floor. The choice depends on specific manufacturing needs--smart dust excels in detailed environmental monitoring, while wearable devices optimize human-machine interaction and workforce management.
Connection
Smart dust and wearable devices are interconnected through their shared use of micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) and sensors for real-time data collection in manufacturing environments. Smart dust consists of tiny wireless sensors that can monitor machinery conditions, while wearable devices provide operators with immediate feedback and environmental insights, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. Integrating these technologies enables seamless communication and data analysis, driving advancements in Industry 4.0 manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
**Sensors Integration**
Wearable devices integrate multiple sensors such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, heart rate monitors, and GPS modules to track physical activity, health metrics, and environmental data in real-time. Smart dust consists of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) sensors embedded in tiny particles capable of detecting vibrations, light, temperature, and chemical changes in distributed networks. Explore the cutting-edge differences in sensor integration and applications between wearable devices and smart dust to understand their impact on IoT advancements.
**Data Transmission**
Wearable devices typically use Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies for data transmission, providing real-time connectivity and moderate to high data rates suited for health monitoring and fitness tracking. Smart dust relies on ultra-low-power wireless communication protocols such as RFID and backscatter for data transmission, enabling dense deployment in environments but with limited range and bandwidth. Explore the latest advancements in wireless communication techniques to understand the evolving landscape of data transmission in wearable technology and smart dust.
**Miniaturization**
Wearable devices have advanced miniaturization through compact sensors and efficient power management, enabling convenient health monitoring and seamless integration into daily life. Smart dust pushes miniaturization further by utilizing microscopic wireless sensors capable of pervasive environmental data collection with minimal physical footprint. Explore the breakthroughs in nanoscale technology driving the future of miniaturized sensing systems.
Source and External Links
What is Wearable Technology? Definition, Uses and ... - Wearable technology encompasses electronic devices designed to be worn on the body, including smartwatches, fitness trackers, and more, which can monitor health and fitness.
Wearable technology - Wearable technology refers to devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers that are worn on the body to collect data on health and fitness.
7 ways wearable technology can help you reach your health - Wearable devices can improve health by tracking physical activity, monitoring heart health, and providing insights into sleep and diet.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com