Industrial Internet enhances manufacturing efficiency through real-time data analytics and interconnected machinery, enabling predictive maintenance and optimized production workflows. Additive Manufacturing revolutionizes production by enabling the creation of complex, customized parts through layer-by-layer material deposition, reducing waste and lead times. Explore the transformative impact of these technologies on modern manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
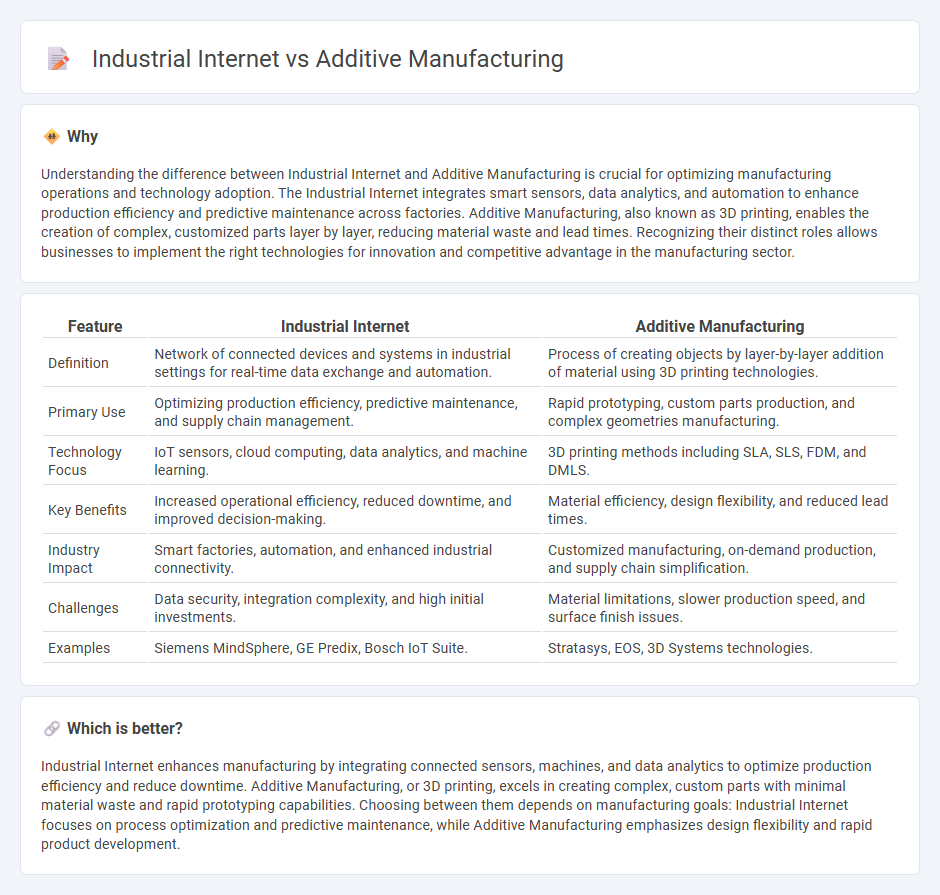
Understanding the difference between Industrial Internet and Additive Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing manufacturing operations and technology adoption. The Industrial Internet integrates smart sensors, data analytics, and automation to enhance production efficiency and predictive maintenance across factories. Additive Manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, enables the creation of complex, customized parts layer by layer, reducing material waste and lead times. Recognizing their distinct roles allows businesses to implement the right technologies for innovation and competitive advantage in the manufacturing sector.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Industrial Internet | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of connected devices and systems in industrial settings for real-time data exchange and automation. | Process of creating objects by layer-by-layer addition of material using 3D printing technologies. |
| Primary Use | Optimizing production efficiency, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management. | Rapid prototyping, custom parts production, and complex geometries manufacturing. |
| Technology Focus | IoT sensors, cloud computing, data analytics, and machine learning. | 3D printing methods including SLA, SLS, FDM, and DMLS. |
| Key Benefits | Increased operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved decision-making. | Material efficiency, design flexibility, and reduced lead times. |
| Industry Impact | Smart factories, automation, and enhanced industrial connectivity. | Customized manufacturing, on-demand production, and supply chain simplification. |
| Challenges | Data security, integration complexity, and high initial investments. | Material limitations, slower production speed, and surface finish issues. |
| Examples | Siemens MindSphere, GE Predix, Bosch IoT Suite. | Stratasys, EOS, 3D Systems technologies. |
Which is better?
Industrial Internet enhances manufacturing by integrating connected sensors, machines, and data analytics to optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime. Additive Manufacturing, or 3D printing, excels in creating complex, custom parts with minimal material waste and rapid prototyping capabilities. Choosing between them depends on manufacturing goals: Industrial Internet focuses on process optimization and predictive maintenance, while Additive Manufacturing emphasizes design flexibility and rapid product development.
Connection
The Industrial Internet integrates smart sensors and connectivity to monitor and optimize Additive Manufacturing processes, enhancing precision and reducing production time. Data analytics from the Industrial Internet enable real-time quality control and predictive maintenance in 3D printing operations. This synergy drives increased efficiency, lower costs, and improved customization in manufacturing workflows.
Key Terms
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, involves creating objects layer by layer from digital models, enabling rapid prototyping and customized production across industries like aerospace, healthcare, and automotive. The industrial internet integrates advanced sensors, data analytics, and connected devices to optimize manufacturing processes, improve equipment efficiency, and enable predictive maintenance. Explore how the convergence of 3D printing and the industrial internet is transforming modern manufacturing for more innovation and productivity.
IoT Sensors
IoT sensors play a crucial role in additive manufacturing by enabling real-time monitoring of 3D printing processes, enhancing precision, and reducing material waste. Industrial Internet integrates these sensors into a broader network, facilitating data analytics, predictive maintenance, and improved operational efficiency across manufacturing systems. Explore how IoT sensors bridge additive manufacturing and the industrial internet to revolutionize smart factories.
Digital Twin
Additive Manufacturing revolutionizes production by enabling layer-by-layer fabrication of complex parts, while the Industrial Internet integrates interconnected sensors and devices for real-time data analytics and automation. The Digital Twin bridges these technologies by creating accurate virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing predictive maintenance and process optimization in manufacturing environments. Explore how Digital Twin technology enhances both Additive Manufacturing and Industrial Internet applications for smarter industrial operations.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing creates objects layer by layer directly from digital designs, originally used for prototyping in the 1980s and now producing functional products using a wide range of materials like polymers, metals, and biomaterials.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Also known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing fabricates 3D products by building them layer-by-layer from digital designs, allowing complex geometries, material efficiency, and applications like aerospace parts and customized biomedical implants.
The 7 categories of Additive Manufacturing - Loughborough University - Additive manufacturing encompasses 7 standardized process categories including vat photopolymerisation, material jetting, and binder jetting, which differ by material and machine technology for layer construction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com