Adaptive machining leverages real-time data and AI-driven adjustments to optimize cutting processes, reducing waste and increasing precision in manufacturing. Robotic machining employs automated robotic arms and CNC integration to enhance repeatability and efficiency on complex production lines. Discover how these advanced techniques revolutionize manufacturing performance and flexibility.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between adaptive machining and robotic machining is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and enhancing production efficiency. Adaptive machining utilizes real-time feedback to adjust tool paths and cutting conditions, ensuring precision and reducing material waste. Robotic machining leverages programmable robots to automate complex tasks and improve flexibility in production lines. Knowing these distinctions enables manufacturers to select the most suitable technology for their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Adaptive Machining | Robotic Machining |
|---|---|---|
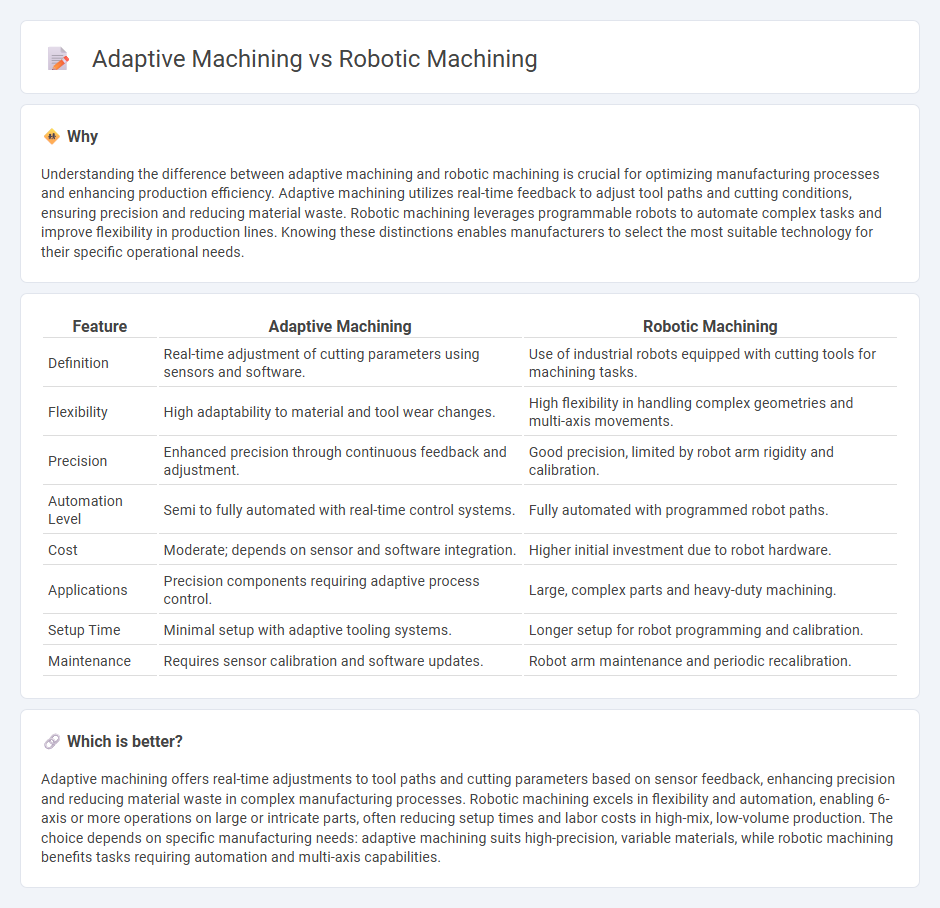
| Definition | Real-time adjustment of cutting parameters using sensors and software. | Use of industrial robots equipped with cutting tools for machining tasks. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to material and tool wear changes. | High flexibility in handling complex geometries and multi-axis movements. |
| Precision | Enhanced precision through continuous feedback and adjustment. | Good precision, limited by robot arm rigidity and calibration. |
| Automation Level | Semi to fully automated with real-time control systems. | Fully automated with programmed robot paths. |
| Cost | Moderate; depends on sensor and software integration. | Higher initial investment due to robot hardware. |
| Applications | Precision components requiring adaptive process control. | Large, complex parts and heavy-duty machining. |
| Setup Time | Minimal setup with adaptive tooling systems. | Longer setup for robot programming and calibration. |
| Maintenance | Requires sensor calibration and software updates. | Robot arm maintenance and periodic recalibration. |
Which is better?
Adaptive machining offers real-time adjustments to tool paths and cutting parameters based on sensor feedback, enhancing precision and reducing material waste in complex manufacturing processes. Robotic machining excels in flexibility and automation, enabling 6-axis or more operations on large or intricate parts, often reducing setup times and labor costs in high-mix, low-volume production. The choice depends on specific manufacturing needs: adaptive machining suits high-precision, variable materials, while robotic machining benefits tasks requiring automation and multi-axis capabilities.
Connection
Adaptive machining and robotic machining are interconnected through their use of real-time data and automation to enhance precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Adaptive machining uses sensors and feedback systems to adjust cutting parameters dynamically, while robotic machining integrates robotic arms to execute these adaptive adjustments with high accuracy. Together, they streamline production workflows, reduce human error, and optimize machining operations for complex and customized manufacturing tasks.
Key Terms
Precision Control
Robotic machining offers high flexibility and automation, but may face challenges in maintaining consistent precision due to robot arm dynamics and calibration requirements. Adaptive machining incorporates real-time feedback and sensor data to adjust cutting parameters dynamically, significantly enhancing precision control and surface quality. Explore further to understand how precision advantages impact your manufacturing processes.
Real-time Feedback
Robotic machining leverages pre-programmed paths with limited adaptability, while adaptive machining utilizes real-time feedback from sensors to dynamically adjust cutting parameters, improving precision and tool life. Real-time feedback in adaptive machining enables immediate responses to variations in material hardness or tool wear, leading to enhanced efficiency and reduced downtime. Explore more to understand how real-time feedback transforms machining processes for superior outcomes.
Tool Path Optimization
Robotic machining leverages pre-programmed, fixed tool paths that prioritize repeatability and speed, whereas adaptive machining dynamically adjusts tool paths in real-time based on sensor feedback to optimize cutting efficiency and surface quality. Adaptive machining's real-time data integration helps minimize tool wear and reduce cycle times by continuously modifying the tool trajectory to respond to material inconsistencies or environmental changes. Explore the latest advancements in tool path optimization to discover how adaptive machining enhances precision and productivity beyond traditional robotic methods.
Source and External Links
Robotic Machining - Robotic machining uses advanced programming solutions to automate milling and machining tasks, offering the ability to create complex parts of any size with reduced costs and versatile tool management.
Robotic Solutions - Advanced Robotic Machining Systems - Robotic machining systems provide high flexibility, lower costs, and scalable size options for milling, trimming, and other machining tasks, making them ideal for manufacturers needing agility and cost efficiency.
The Rise of Robot Machining - Robot machining integrates industrial robots with machining end effectors, offering enhanced flexibility, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional CNC machining, especially for complex or large-scale projects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com