Lights out factory technology enables fully automated production with minimal human intervention, maximizing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Process manufacturing focuses on producing goods by combining supplies, ingredients, or raw materials through chemical, biological, or physical processes, commonly used in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Explore more about how these manufacturing approaches transform industrial productivity and innovation.
Why it is important
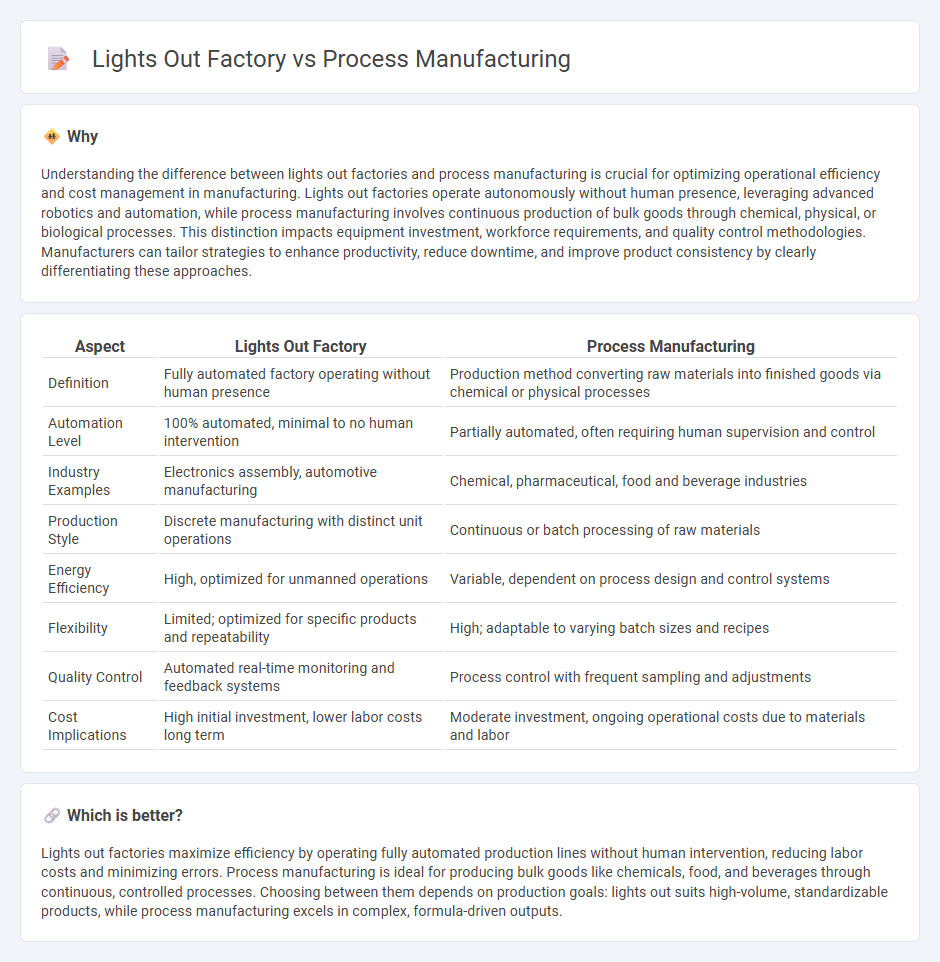
Understanding the difference between lights out factories and process manufacturing is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and cost management in manufacturing. Lights out factories operate autonomously without human presence, leveraging advanced robotics and automation, while process manufacturing involves continuous production of bulk goods through chemical, physical, or biological processes. This distinction impacts equipment investment, workforce requirements, and quality control methodologies. Manufacturers can tailor strategies to enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and improve product consistency by clearly differentiating these approaches.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights Out Factory | Process Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory operating without human presence | Production method converting raw materials into finished goods via chemical or physical processes |
| Automation Level | 100% automated, minimal to no human intervention | Partially automated, often requiring human supervision and control |
| Industry Examples | Electronics assembly, automotive manufacturing | Chemical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage industries |
| Production Style | Discrete manufacturing with distinct unit operations | Continuous or batch processing of raw materials |
| Energy Efficiency | High, optimized for unmanned operations | Variable, dependent on process design and control systems |
| Flexibility | Limited; optimized for specific products and repeatability | High; adaptable to varying batch sizes and recipes |
| Quality Control | Automated real-time monitoring and feedback systems | Process control with frequent sampling and adjustments |
| Cost Implications | High initial investment, lower labor costs long term | Moderate investment, ongoing operational costs due to materials and labor |
Which is better?
Lights out factories maximize efficiency by operating fully automated production lines without human intervention, reducing labor costs and minimizing errors. Process manufacturing is ideal for producing bulk goods like chemicals, food, and beverages through continuous, controlled processes. Choosing between them depends on production goals: lights out suits high-volume, standardizable products, while process manufacturing excels in complex, formula-driven outputs.
Connection
Lights out factories leverage automated process manufacturing systems to operate continuously without human intervention, maximizing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Integration of advanced robotics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven control in process manufacturing enables real-time monitoring and precise management of production workflows in a lights out environment. This synergy enhances product consistency, minimizes downtime, and accelerates throughput in complex industrial manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
Continuous Production
Continuous production in process manufacturing involves the nonstop transformation of raw materials into finished goods, emphasizing consistent quality and minimal downtime. A lights-out factory automates this process extensively, enabling 24/7 operation without human intervention, which maximizes efficiency and reduces labor costs. Explore how integrating lights-out technology can revolutionize continuous production in process manufacturing.
Automation
Process manufacturing relies heavily on automation to ensure consistent quality and efficient production of bulk goods such as chemicals, food, and pharmaceuticals. Lights out factories represent the pinnacle of automation, operating entirely without human intervention through advanced robotics and AI-driven systems. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each approach transforms manufacturing efficiency and scalability.
Data Integration
Process manufacturing relies heavily on seamless data integration to ensure consistent product quality, optimize production workflows, and manage complex ingredient traceability. Lights out factories leverage advanced data integration across IoT devices, AI-driven sensors, and automated control systems to enable fully autonomous operations with minimal human intervention. Explore how cutting-edge data integration strategies bridge these manufacturing approaches and drive innovation.
Source and External Links
Process Manufacturing | Propel Glossary - Process manufacturing is the production of products through precise chemical or mechanical processes where raw materials are transformed into finished goods using formulas or batch production, common in industries like pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
Process Manufacturing: Definition, Benefits, and Industries - This manufacturing type involves producing finished goods by combining raw materials under specific conditions via recipes or formulas, creating homogeneous, irreversible products in bulk such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
What is Process Manufacturing? Definition and Examples - Process manufacturing creates goods through bulk production with sequential steps based on predetermined formulas, resulting in products that cannot be disassembled into original parts, distinguishing it from discrete manufacturing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com