Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and dolly systems enhance material handling efficiency in manufacturing environments by streamlining internal logistics and reducing manual labor. AGVs utilize advanced navigation technologies for autonomous transport, while dolly systems rely on manual or semi-automated movement of carts carrying materials. Explore the detailed comparison to determine which system aligns best with your manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
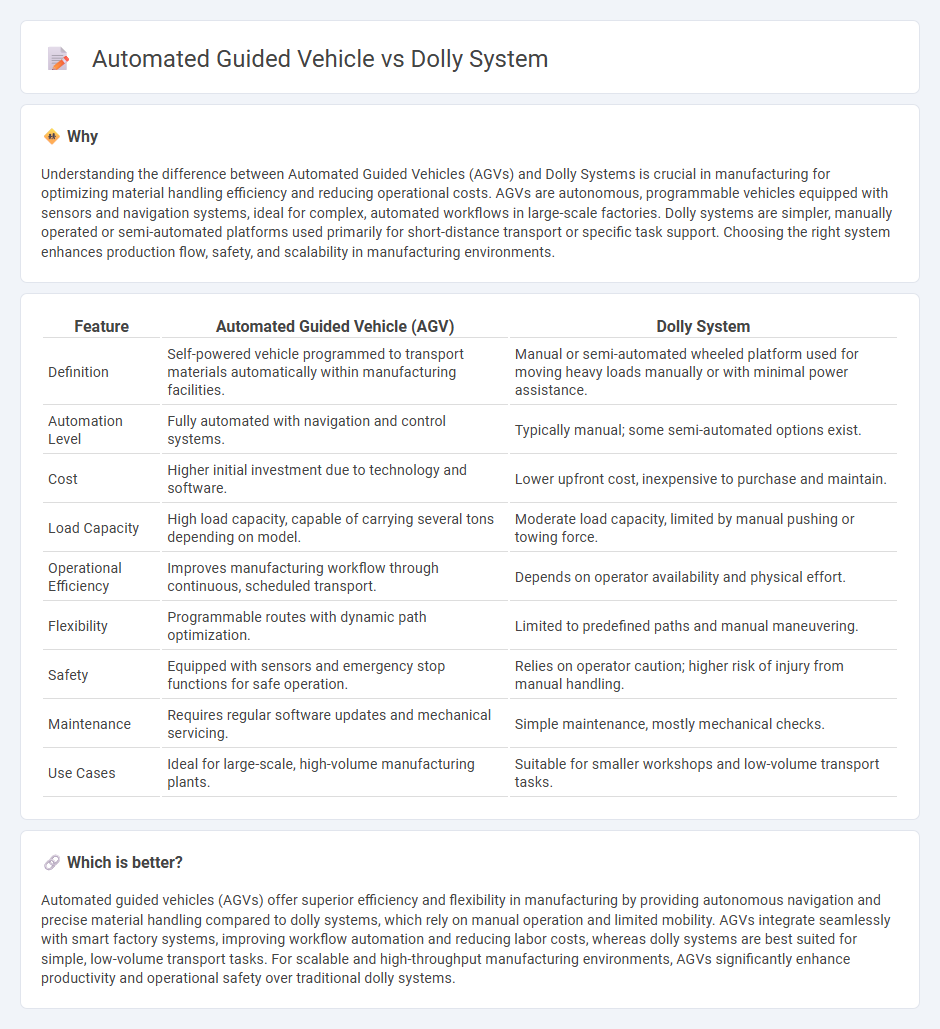
Understanding the difference between Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Dolly Systems is crucial in manufacturing for optimizing material handling efficiency and reducing operational costs. AGVs are autonomous, programmable vehicles equipped with sensors and navigation systems, ideal for complex, automated workflows in large-scale factories. Dolly systems are simpler, manually operated or semi-automated platforms used primarily for short-distance transport or specific task support. Choosing the right system enhances production flow, safety, and scalability in manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) | Dolly System |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-powered vehicle programmed to transport materials automatically within manufacturing facilities. | Manual or semi-automated wheeled platform used for moving heavy loads manually or with minimal power assistance. |
| Automation Level | Fully automated with navigation and control systems. | Typically manual; some semi-automated options exist. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to technology and software. | Lower upfront cost, inexpensive to purchase and maintain. |
| Load Capacity | High load capacity, capable of carrying several tons depending on model. | Moderate load capacity, limited by manual pushing or towing force. |
| Operational Efficiency | Improves manufacturing workflow through continuous, scheduled transport. | Depends on operator availability and physical effort. |
| Flexibility | Programmable routes with dynamic path optimization. | Limited to predefined paths and manual maneuvering. |
| Safety | Equipped with sensors and emergency stop functions for safe operation. | Relies on operator caution; higher risk of injury from manual handling. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular software updates and mechanical servicing. | Simple maintenance, mostly mechanical checks. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for large-scale, high-volume manufacturing plants. | Suitable for smaller workshops and low-volume transport tasks. |
Which is better?
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) offer superior efficiency and flexibility in manufacturing by providing autonomous navigation and precise material handling compared to dolly systems, which rely on manual operation and limited mobility. AGVs integrate seamlessly with smart factory systems, improving workflow automation and reducing labor costs, whereas dolly systems are best suited for simple, low-volume transport tasks. For scalable and high-throughput manufacturing environments, AGVs significantly enhance productivity and operational safety over traditional dolly systems.
Connection
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are often integrated with Dolly systems to enhance material handling efficiency in manufacturing environments. The Dolly serves as a mobile platform that can carry heavy loads or containers, while AGVs provide autonomous navigation and control, enabling precise transportation of goods throughout the facility. This synergy reduces manual labor, minimizes downtime, and optimizes production workflows by streamlining inventory movement.
Key Terms
Material Handling
Dolly systems facilitate material handling by providing simple, manual transport solutions ideal for short distances and lightweight loads, reducing physical strain and improving workflow efficiency. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) enhance material handling through autonomous navigation and programmable routes, enabling precise, continuous movement of heavy or bulky items with minimal human intervention. Explore the key differences and applications to optimize your material handling strategy effectively.
Flexibility
The Dolly system offers limited flexibility, primarily designed for fixed routes and static load positions, making it less adaptable to dynamic industrial environments. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) boast advanced navigation and obstacle avoidance technologies, enabling seamless route adjustments and varied load handling in real-time. Discover how AGVs enhance operational flexibility and efficiency across diverse industries.
Automation
The Dolly system employs semi-automated towing with manual control support, enabling flexible load transportation in warehouses and manufacturing plants. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) utilize fully automated navigation and obstacle detection systems to transport materials autonomously along predefined paths, increasing efficiency and reducing labor dependence. Explore how integrating Dolly systems and AGVs can optimize automation tailored to your operational needs.
Source and External Links
Camera dolly - Wikipedia - A camera dolly is a wheeled cart used in filmmaking to create smooth horizontal camera movements, often mounted on tracks for precise tracking shots.
Dana Dolly: Professional Camera Dolly Systems - The Dana Dolly features a sixteen-wheel, floating truck design for smooth gliding, works with various pipe tracks, and is portable for fast setup on location.
Best Professional Camera Skater Dolly System - MYT Works - The MYT Works Skater System offers detachable wheel modules, aluminum trusses, and a versatile mounting plate, supporting cameras from DSLRs to broadcast rigs on standard speed rail.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com