Machine vision inspection utilizes high-resolution cameras and advanced image processing algorithms to detect defects and ensure product quality with precision and speed. Robotic inspection combines automated robotic arms with sensors to perform versatile and flexible quality checks in complex manufacturing environments. Explore the differences and advantages of each method to optimize your production line performance.
Why it is important
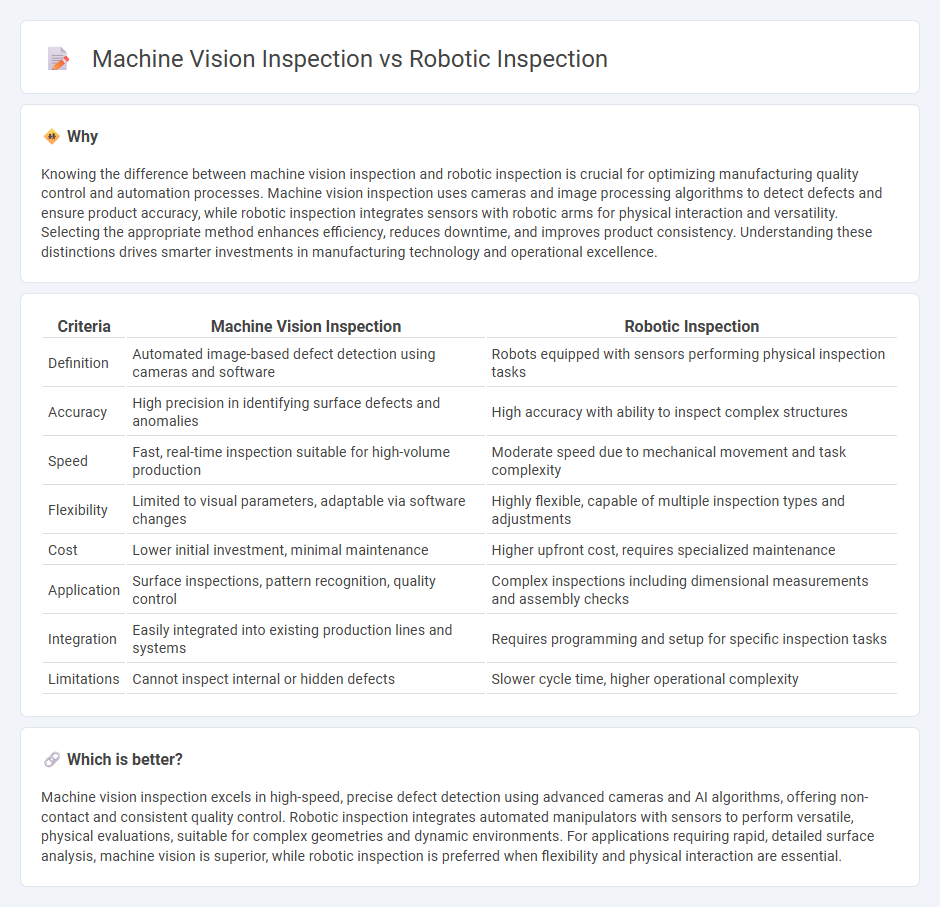
Knowing the difference between machine vision inspection and robotic inspection is crucial for optimizing manufacturing quality control and automation processes. Machine vision inspection uses cameras and image processing algorithms to detect defects and ensure product accuracy, while robotic inspection integrates sensors with robotic arms for physical interaction and versatility. Selecting the appropriate method enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves product consistency. Understanding these distinctions drives smarter investments in manufacturing technology and operational excellence.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Machine Vision Inspection | Robotic Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated image-based defect detection using cameras and software | Robots equipped with sensors performing physical inspection tasks |
| Accuracy | High precision in identifying surface defects and anomalies | High accuracy with ability to inspect complex structures |
| Speed | Fast, real-time inspection suitable for high-volume production | Moderate speed due to mechanical movement and task complexity |
| Flexibility | Limited to visual parameters, adaptable via software changes | Highly flexible, capable of multiple inspection types and adjustments |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, minimal maintenance | Higher upfront cost, requires specialized maintenance |
| Application | Surface inspections, pattern recognition, quality control | Complex inspections including dimensional measurements and assembly checks |
| Integration | Easily integrated into existing production lines and systems | Requires programming and setup for specific inspection tasks |
| Limitations | Cannot inspect internal or hidden defects | Slower cycle time, higher operational complexity |
Which is better?
Machine vision inspection excels in high-speed, precise defect detection using advanced cameras and AI algorithms, offering non-contact and consistent quality control. Robotic inspection integrates automated manipulators with sensors to perform versatile, physical evaluations, suitable for complex geometries and dynamic environments. For applications requiring rapid, detailed surface analysis, machine vision is superior, while robotic inspection is preferred when flexibility and physical interaction are essential.
Connection
Machine vision inspection and robotic inspection are interconnected technologies improving manufacturing quality control by integrating advanced imaging systems with automated robotic arms. Machine vision systems capture high-resolution images and analyze defects in real-time, providing precise data for robotic inspection processes to perform accurate and consistent quality assessments. This synergy enhances production efficiency, reduces human error, and supports predictive maintenance in smart manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
**Robotic Inspection:**
Robotic inspection integrates programmable robots equipped with advanced sensors to perform precise, repeatable evaluations in manufacturing and quality control. These systems enable real-time data collection, improving defect detection accuracy and operational efficiency across complex environments. Explore more to understand how robotic inspection transforms industrial quality assurance and maintenance processes.
Automated Manipulation
Robotic inspection harnesses automated manipulation to perform precise, repeatable movements for thorough quality control, surpassing machine vision inspection that primarily relies on image processing algorithms without physical interaction. Automated manipulation enables robots to handle complex tasks such as component alignment and defect detection in challenging environments, enhancing accuracy and reducing human error. Explore the advancements in robotic inspection to understand how automated manipulation transforms industrial quality assurance.
Sensor Integration
Robotic inspection leverages advanced sensor integration by combining multiple sensors such as LIDAR, ultrasonic, and infrared sensors to perform comprehensive, automated evaluations in complex environments. Machine vision inspection primarily relies on high-resolution cameras and image processing algorithms to detect surface defects and ensure quality control with precision. Explore further to understand how sensor integration enhances inspection accuracy and efficiency across these technologies.
Source and External Links
Robotic inspection: Leaner quality control - Robotic inspection leverages sensors, vision systems, and AI-driven machine learning to automatically detect defects, outperforming traditional manual inspection in speed, consistency, and precision.
Inspection robots: simplifying industrial inspections - Inspection robots autonomously or remotely navigate complex environments, collecting real-time data for immediate analysis and enabling safer, more thorough inspections of hazardous or hard-to-reach areas.
Robotic Inspection | Remote Visual inspection | Robotic NDT - Remote Visual Inspection (RVI) uses robotic crawlers, drones, and other camera-equipped systems to conduct non-destructive testing in confined, hazardous, or inaccessible spaces, reducing risk and improving efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com