Additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer using digital models, enabling complex geometries and reducing material waste compared to traditional sheet metal fabrication, which involves cutting and shaping flat metal sheets through processes like bending, stamping, and welding. Additive methods excel in producing customized, lightweight components with intricate internal structures, while sheet metal fabrication is favored for large-scale, high-strength parts with consistent mechanical properties. Explore the advantages and applications of both manufacturing techniques to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
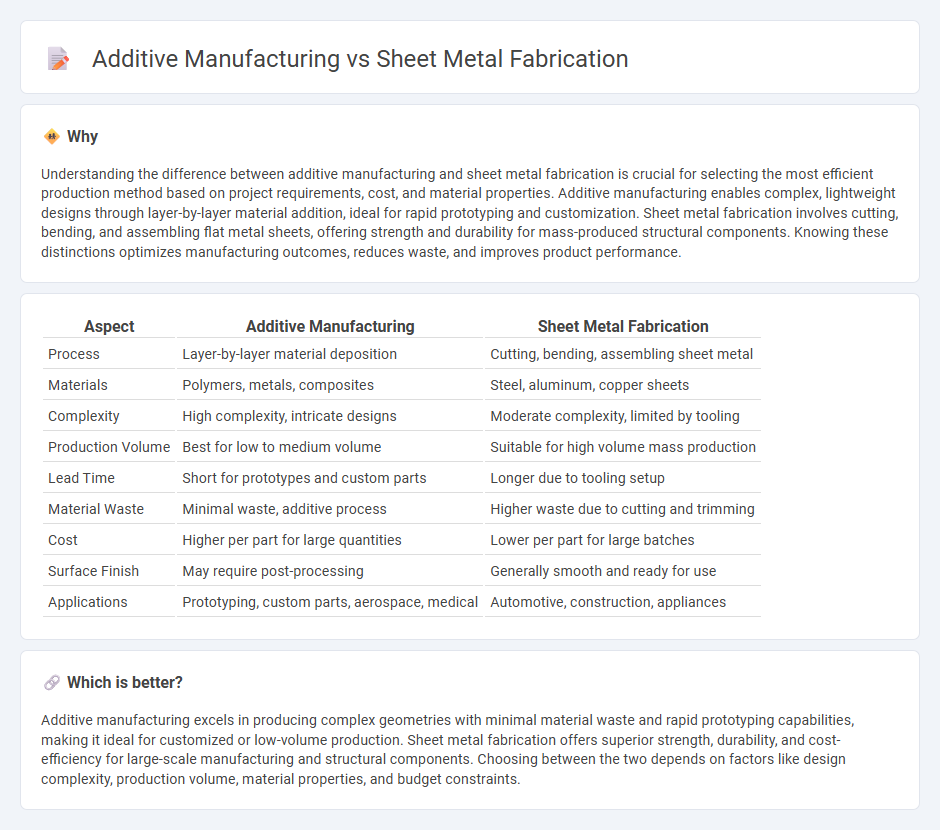
Understanding the difference between additive manufacturing and sheet metal fabrication is crucial for selecting the most efficient production method based on project requirements, cost, and material properties. Additive manufacturing enables complex, lightweight designs through layer-by-layer material addition, ideal for rapid prototyping and customization. Sheet metal fabrication involves cutting, bending, and assembling flat metal sheets, offering strength and durability for mass-produced structural components. Knowing these distinctions optimizes manufacturing outcomes, reduces waste, and improves product performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Additive Manufacturing | Sheet Metal Fabrication |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Layer-by-layer material deposition | Cutting, bending, assembling sheet metal |
| Materials | Polymers, metals, composites | Steel, aluminum, copper sheets |
| Complexity | High complexity, intricate designs | Moderate complexity, limited by tooling |
| Production Volume | Best for low to medium volume | Suitable for high volume mass production |
| Lead Time | Short for prototypes and custom parts | Longer due to tooling setup |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste, additive process | Higher waste due to cutting and trimming |
| Cost | Higher per part for large quantities | Lower per part for large batches |
| Surface Finish | May require post-processing | Generally smooth and ready for use |
| Applications | Prototyping, custom parts, aerospace, medical | Automotive, construction, appliances |
Which is better?
Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex geometries with minimal material waste and rapid prototyping capabilities, making it ideal for customized or low-volume production. Sheet metal fabrication offers superior strength, durability, and cost-efficiency for large-scale manufacturing and structural components. Choosing between the two depends on factors like design complexity, production volume, material properties, and budget constraints.
Connection
Additive manufacturing and sheet metal fabrication are connected through their complementary roles in modern production processes, where additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping and complex geometries while sheet metal fabrication provides strength and precision for functional components. Advanced hybrid manufacturing systems integrate additive layering with traditional sheet metal shaping methods to enhance design flexibility and reduce material waste. This synergy supports industries such as automotive and aerospace by optimizing production efficiency and enabling customized, lightweight structures.
Key Terms
Subtractive Process (sheet metal fabrication)
Sheet metal fabrication relies on subtractive processes such as cutting, bending, and punching to shape metal sheets by removing material, offering high precision and strength suitable for industrial applications. This method excels in producing durable components with consistent mechanical properties from a wide range of metals including steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. Explore further to understand the advantages and limitations of subtractive manufacturing compared to additive techniques.
Layer-by-Layer Deposition (additive manufacturing)
Layer-by-layer deposition in additive manufacturing builds complex geometries by successively adding material, allowing for intricate designs and reduced waste compared to traditional sheet metal fabrication, which involves cutting, bending, and assembling flat metal sheets. Additive manufacturing enhances customization and material efficiency due to precise control over each deposited layer, while sheet metal fabrication remains faster and more cost-effective for high-volume, simpler parts. Explore deeper into how layer-by-layer deposition revolutionizes production flexibility and design possibilities.
Material Utilization
Sheet metal fabrication primarily uses subtractive methods involving cutting and bending, which can result in substantial material waste due to offcuts and scrap. Additive manufacturing builds parts layer-by-layer, significantly improving material utilization by depositing material only where needed, reducing excess waste. Explore more to understand how these processes impact cost-efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Protolabs: Online Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication Service - This service provides fast and custom sheet metal fabrication with a focus on rapid production and multiple finishing options.
Sheet Metal Fabrication: A Comprehensive Guide - Geomiq - This guide offers a detailed overview of the sheet metal fabrication process, covering its versatility and applications across various industries.
Metal Fabrication - Wikipedia - This article provides general information on metal fabrication, including sheet metal, structural steel, and various cutting and forming techniques used in the process.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com