The industrial metaverse integrates real-world manufacturing systems with advanced digital twins, enabling immersive simulations and real-time collaboration across global facilities. Virtual reality offers immersive training and design visualization but typically operates in isolated, non-connected environments. Explore how these technologies transform manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Industrial Metaverse and Virtual Reality is crucial for manufacturing because the Industrial Metaverse integrates real-time digital twins, IoT, and AI to optimize production processes, while Virtual Reality primarily offers immersive simulations for training and design. The Industrial Metaverse enables enhanced predictive maintenance, supply chain visualization, and collaborative remote operations, directly impacting efficiency and cost savings. Manufacturers leveraging these technologies can significantly improve product lifecycle management and operational agility. Clear differentiation ensures targeted investment and application of advanced industry 4.0 solutions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Industrial Metaverse | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
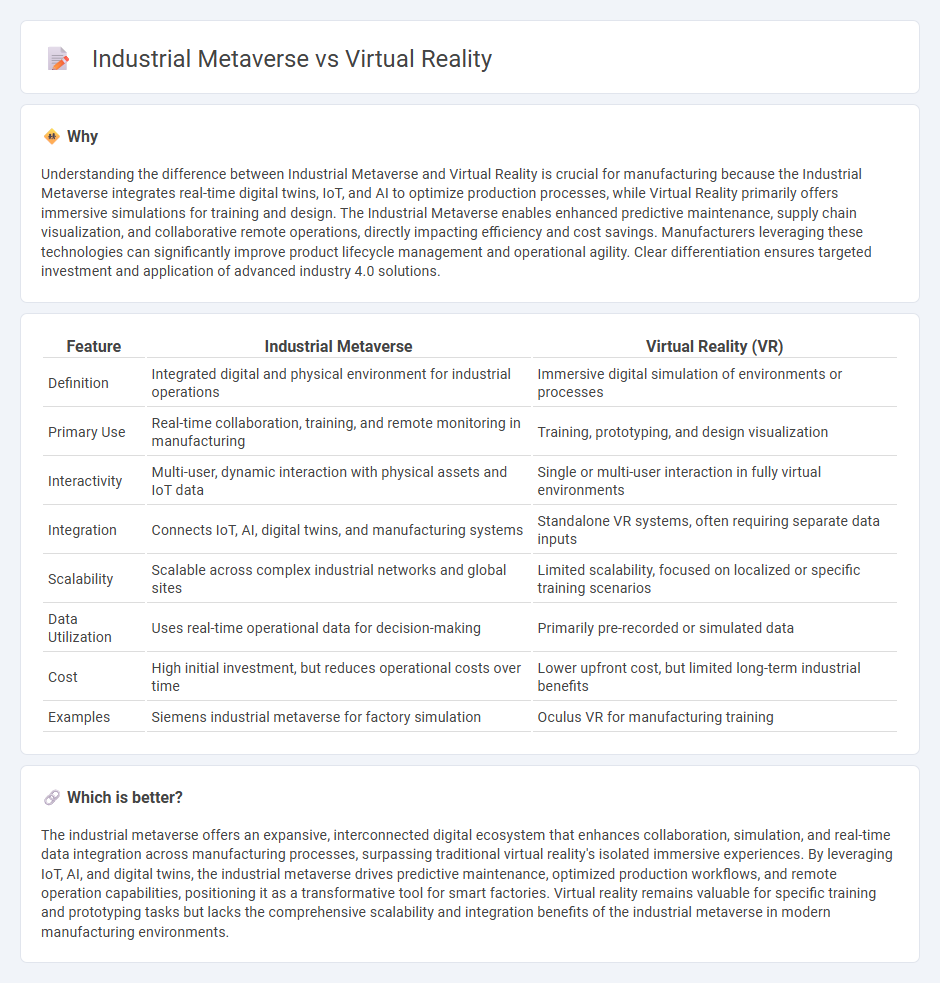
| Definition | Integrated digital and physical environment for industrial operations | Immersive digital simulation of environments or processes |
| Primary Use | Real-time collaboration, training, and remote monitoring in manufacturing | Training, prototyping, and design visualization |
| Interactivity | Multi-user, dynamic interaction with physical assets and IoT data | Single or multi-user interaction in fully virtual environments |
| Integration | Connects IoT, AI, digital twins, and manufacturing systems | Standalone VR systems, often requiring separate data inputs |
| Scalability | Scalable across complex industrial networks and global sites | Limited scalability, focused on localized or specific training scenarios |
| Data Utilization | Uses real-time operational data for decision-making | Primarily pre-recorded or simulated data |
| Cost | High initial investment, but reduces operational costs over time | Lower upfront cost, but limited long-term industrial benefits |
| Examples | Siemens industrial metaverse for factory simulation | Oculus VR for manufacturing training |
Which is better?
The industrial metaverse offers an expansive, interconnected digital ecosystem that enhances collaboration, simulation, and real-time data integration across manufacturing processes, surpassing traditional virtual reality's isolated immersive experiences. By leveraging IoT, AI, and digital twins, the industrial metaverse drives predictive maintenance, optimized production workflows, and remote operation capabilities, positioning it as a transformative tool for smart factories. Virtual reality remains valuable for specific training and prototyping tasks but lacks the comprehensive scalability and integration benefits of the industrial metaverse in modern manufacturing environments.
Connection
The industrial metaverse integrates virtual reality (VR) technology to create immersive simulations for manufacturing processes, enabling real-time collaboration and training. VR enhances digital twins within the metaverse, allowing manufacturers to visualize production lines, detect flaws, and optimize operations before physical implementation. This synergy reduces costs, improves efficiency, and accelerates innovation in smart factories.
Key Terms
Digital Twin
Virtual Reality (VR) creates immersive, simulated environments, whereas the Industrial Metaverse integrates VR with digital twins to enhance real-time data visualization and operational efficiency in manufacturing and infrastructure maintenance. Digital twins act as precise virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling predictive analytics, remote monitoring, and seamless interaction within the Industrial Metaverse. Explore more about how digital twins revolutionize industrial processes and drive the future of smart manufacturing.
Immersive Simulation
Virtual Reality (VR) offers fully immersive simulations primarily for individual users, enhancing training, design, and entertainment with high-fidelity 3D environments. The Industrial Metaverse extends VR by integrating real-time data, digital twins, and collaborative platforms, enabling complex, interconnected industrial simulations for optimized workflows and predictive maintenance. Explore more about how immersive simulation shapes the future of industrial innovation and efficiency.
Real-time Collaboration
Virtual Reality (VR) offers immersive environments primarily for individual or small group experiences, while the Industrial Metaverse integrates VR with IoT, AI, and digital twins to facilitate real-time collaboration among large teams across diverse industrial sectors. Industrial Metaverse platforms enable synchronized workflows, remote monitoring, and decision-making with high fidelity, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity in manufacturing, construction, and maintenance operations. Explore more about how these cutting-edge technologies revolutionize teamwork and operational efficiency in industrial settings.
Source and External Links
What is virtual reality (VR) and how does it work? - Virtual reality (VR) is a technology that immerses users in an artificial 3D environment, combining hardware like headsets and motion sensors with AI-driven software to simulate a realistic, interactive virtual world.
Immerse Yourself in Virtual Reality - The Future Now - VR simulates a three-dimensional environment that users explore and interact with via specialized devices such as headsets and controllers, offering immersive experiences across gaming, education, training, and healthcare.
Virtual reality (VR) | Definition, Development, Technology ... - Virtual reality uses computer modeling and simulation to enable interaction with artificial 3-D environments through devices like headsets and gloves, providing telepresence and real-time response to user movements for immersive experiences.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com