Smart factories leverage advanced automation, IoT sensors, and AI-driven analytics to optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime, transforming traditional manufacturing processes into highly adaptive systems. Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement, employee involvement, and customer-focused strategies to ensure product quality and organizational excellence. Explore how integrating smart factory technologies with TQM principles can revolutionize manufacturing outcomes.
Why it is important
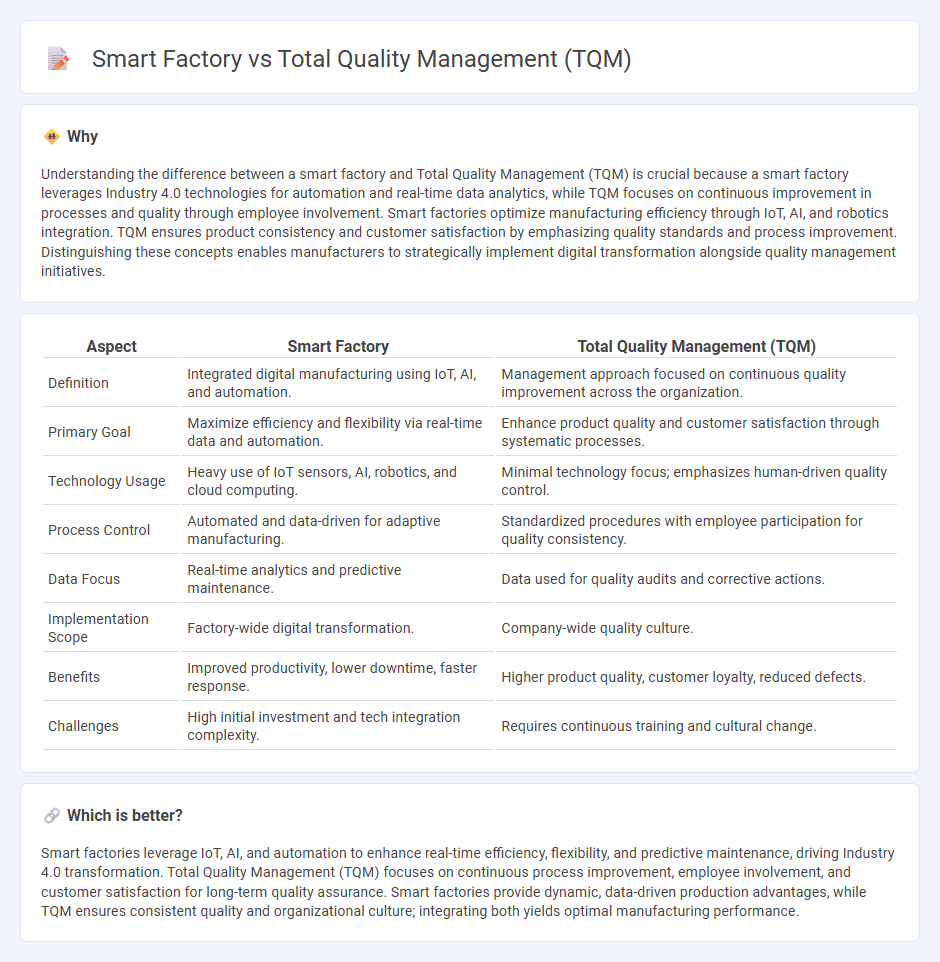
Understanding the difference between a smart factory and Total Quality Management (TQM) is crucial because a smart factory leverages Industry 4.0 technologies for automation and real-time data analytics, while TQM focuses on continuous improvement in processes and quality through employee involvement. Smart factories optimize manufacturing efficiency through IoT, AI, and robotics integration. TQM ensures product consistency and customer satisfaction by emphasizing quality standards and process improvement. Distinguishing these concepts enables manufacturers to strategically implement digital transformation alongside quality management initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Factory | Total Quality Management (TQM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated digital manufacturing using IoT, AI, and automation. | Management approach focused on continuous quality improvement across the organization. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize efficiency and flexibility via real-time data and automation. | Enhance product quality and customer satisfaction through systematic processes. |
| Technology Usage | Heavy use of IoT sensors, AI, robotics, and cloud computing. | Minimal technology focus; emphasizes human-driven quality control. |
| Process Control | Automated and data-driven for adaptive manufacturing. | Standardized procedures with employee participation for quality consistency. |
| Data Focus | Real-time analytics and predictive maintenance. | Data used for quality audits and corrective actions. |
| Implementation Scope | Factory-wide digital transformation. | Company-wide quality culture. |
| Benefits | Improved productivity, lower downtime, faster response. | Higher product quality, customer loyalty, reduced defects. |
| Challenges | High initial investment and tech integration complexity. | Requires continuous training and cultural change. |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage IoT, AI, and automation to enhance real-time efficiency, flexibility, and predictive maintenance, driving Industry 4.0 transformation. Total Quality Management (TQM) focuses on continuous process improvement, employee involvement, and customer satisfaction for long-term quality assurance. Smart factories provide dynamic, data-driven production advantages, while TQM ensures consistent quality and organizational culture; integrating both yields optimal manufacturing performance.
Connection
Smart factories leverage IoT, AI, and automation to enhance manufacturing processes, which aligns closely with Total Quality Management's emphasis on continuous improvement and defect reduction. Integration of real-time data analytics in smart factories enables TQM practices by facilitating immediate quality control and proactive maintenance. This synergy drives higher product consistency, reduced waste, and increased operational efficiency across the manufacturing value chain.
Key Terms
Continuous Improvement (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through systematic processes, employee involvement, and customer-focused strategies to enhance product quality and operational efficiency. In contrast, smart factories leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production in real-time, supporting continuous improvement with data-driven insights. Discover how integrating TQM principles with smart factory innovations can revolutionize manufacturing quality and performance.
Data Analytics (Smart Factory)
Data Analytics in a smart factory leverages real-time sensor data and AI algorithms to optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and predict maintenance needs, enhancing operational efficiency beyond traditional Total Quality Management (TQM) methods. While TQM emphasizes continuous improvement through employee involvement and standardized procedures, smart factories integrate advanced IoT devices and machine learning for proactive decision-making and adaptive quality control. Discover how data-driven smart factory solutions can transform manufacturing performance by exploring the latest industry innovations.
Real-Time Monitoring (Smart Factory)
Real-Time Monitoring in smart factories leverages IoT sensors and advanced analytics to provide continuous, data-driven insights, enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance beyond the periodic checks typical of Total Quality Management (TQM). This technology enables instantaneous detection of anomalies and adaptive process control, which significantly reduces downtime and improves product quality in manufacturing environments. Explore how integrating Real-Time Monitoring can revolutionize your quality management system and production workflow.
Source and External Links
Total Quality Management (TQM) - Total Quality Management is a management framework that focuses on continuous improvement and quality, involving all members of an organization to enhance customer satisfaction and long-term success.
Total Quality Management (TQM) - Definition & Importance - TQM is a comprehensive approach to organizational management emphasizing quality excellence and continuous improvement in all processes to achieve operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Total Quality Management [Principles + Benefits] - TQM is a company-wide approach to improving and maintaining quality across all business operations, engaging everyone from the CEO to frontline workers in quality management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com