Green steel production utilizes hydrogen or renewable energy sources to significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional steelmaking methods. Electric arc furnace (EAF) steel relies on scrap steel and electricity, offering lower environmental impact than blast furnace operations but still dependent on electricity sources. Explore the latest advancements and benefits of green steel and EAF steel technologies to understand their role in sustainable manufacturing.
Why it is important
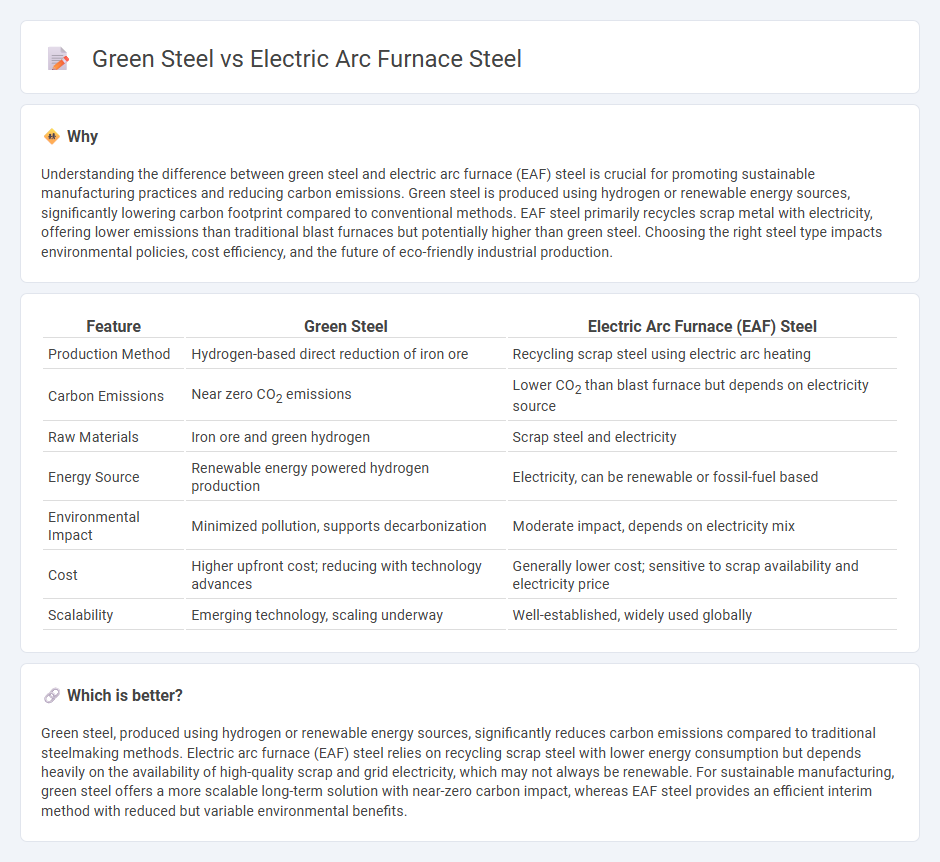
Understanding the difference between green steel and electric arc furnace (EAF) steel is crucial for promoting sustainable manufacturing practices and reducing carbon emissions. Green steel is produced using hydrogen or renewable energy sources, significantly lowering carbon footprint compared to conventional methods. EAF steel primarily recycles scrap metal with electricity, offering lower emissions than traditional blast furnaces but potentially higher than green steel. Choosing the right steel type impacts environmental policies, cost efficiency, and the future of eco-friendly industrial production.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Green Steel | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Hydrogen-based direct reduction of iron ore | Recycling scrap steel using electric arc heating |
| Carbon Emissions | Near zero CO2 emissions | Lower CO2 than blast furnace but depends on electricity source |
| Raw Materials | Iron ore and green hydrogen | Scrap steel and electricity |
| Energy Source | Renewable energy powered hydrogen production | Electricity, can be renewable or fossil-fuel based |
| Environmental Impact | Minimized pollution, supports decarbonization | Moderate impact, depends on electricity mix |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost; reducing with technology advances | Generally lower cost; sensitive to scrap availability and electricity price |
| Scalability | Emerging technology, scaling underway | Well-established, widely used globally |
Which is better?
Green steel, produced using hydrogen or renewable energy sources, significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional steelmaking methods. Electric arc furnace (EAF) steel relies on recycling scrap steel with lower energy consumption but depends heavily on the availability of high-quality scrap and grid electricity, which may not always be renewable. For sustainable manufacturing, green steel offers a more scalable long-term solution with near-zero carbon impact, whereas EAF steel provides an efficient interim method with reduced but variable environmental benefits.
Connection
Green steel production relies heavily on electric arc furnace (EAF) technology, which uses electric arcs to melt scrap steel, significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnaces. EAFs powered by renewable energy sources enable greener steel manufacturing by minimizing reliance on coal and lowering the steel industry's carbon footprint. This synergy between green steel initiatives and electric arc furnace steel production is pivotal in achieving sustainable and eco-friendly steelmaking processes.
Key Terms
Carbon Emissions
Electric arc furnace steel significantly reduces carbon emissions by recycling scrap steel using electricity, often sourced from renewable energy, resulting in up to 70% lower CO2 emissions compared to traditional blast furnace methods. Green steel aims to further cut carbon footprints by producing steel through hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI) or other zero-carbon technologies, targeting near-zero emissions in steel manufacturing. Explore the latest innovations and carbon reduction strategies in steel production to understand their environmental benefits better.
Energy Source
Electric arc furnace steel production primarily relies on electricity derived from various sources, offering flexibility in energy inputs and the potential for incorporating renewable energy to reduce carbon emissions. Green steel emphasizes the exclusive use of renewable energy sources like wind, solar, or hydro, drastically lowering the carbon footprint compared to conventional electric arc furnace methods. Discover how adopting green steel technologies can transform the steel industry's environmental impact.
Scrap Recycling
Electric arc furnace (EAF) steel production relies heavily on scrap metal recycling, significantly reducing raw material consumption and energy use compared to traditional blast furnace methods. Green steel emphasizes further decarbonization by integrating renewable energy sources and innovative technologies to minimize carbon emissions throughout the steelmaking process. Discover more about how scrap recycling drives sustainability in steel production and the evolving role of green steel in the industry.
Source and External Links
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) - Tenova - Electric arc furnaces (EAF) melt steel by an electric arc combined with chemical power from oxygen and fuel, capable of melting various charge mixes from scrap to direct reduced iron and hot metal, representing state-of-the-art steelmaking technology worldwide.
Electric arc furnace - Wikipedia - An electric arc furnace for steelmaking consists of a refractory-lined vessel with graphite electrodes introducing electric arcs to melt the charged metal, featuring a shell, hearth, and roof, often water-cooled for larger units.
Steel Industry Pivoting to Electric Furnaces, Analysis Shows - Electric arc furnaces offer a low-carbon alternative to coal-based blast furnaces in steel production, with growing global adoption though the transition to clean steel is proceeding slower than needed to meet climate goals by 2050.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com