Cloud manufacturing leverages digital networks and cloud computing to enable real-time data sharing, resource optimization, and scalability across multiple production sites, contrasting with traditional manufacturing's reliance on localized, manual processes and fixed infrastructure. This transformation enhances flexibility, reduces costs, and accelerates innovation cycles by integrating IoT devices, AI analytics, and virtual simulations. Explore further to understand the strategic benefits and implementation challenges of cloud manufacturing compared to traditional models.
Why it is important
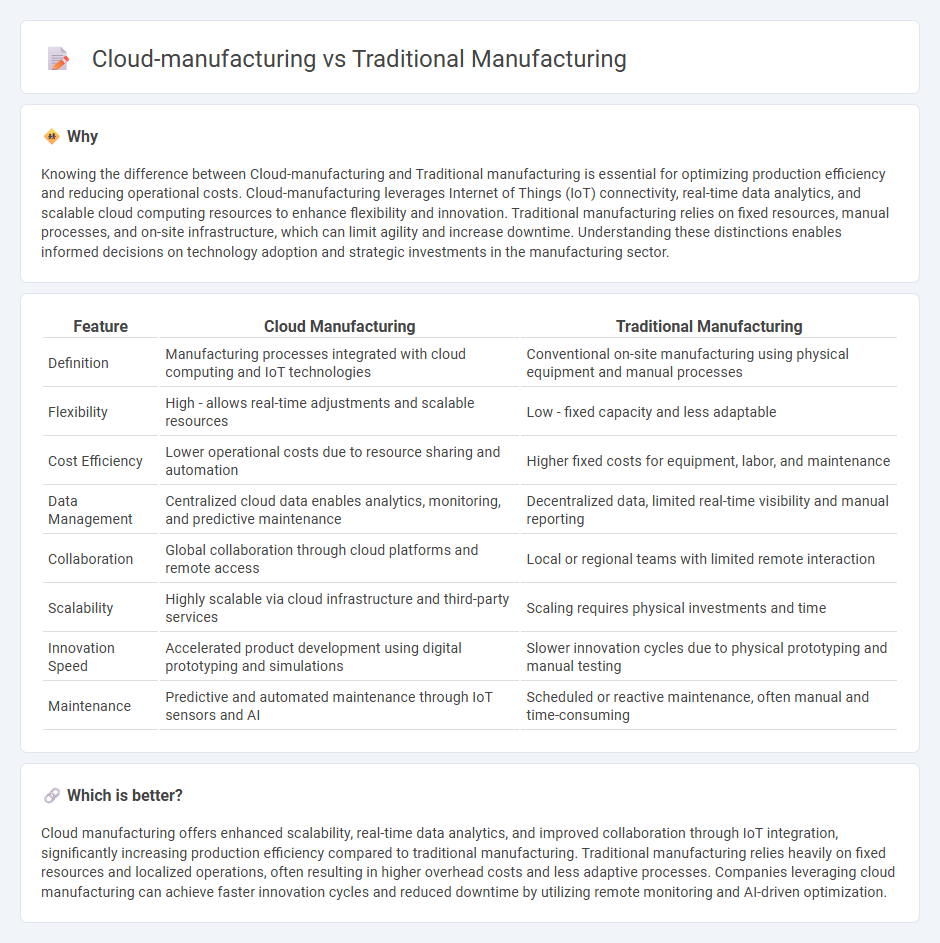
Knowing the difference between Cloud-manufacturing and Traditional manufacturing is essential for optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs. Cloud-manufacturing leverages Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, real-time data analytics, and scalable cloud computing resources to enhance flexibility and innovation. Traditional manufacturing relies on fixed resources, manual processes, and on-site infrastructure, which can limit agility and increase downtime. Understanding these distinctions enables informed decisions on technology adoption and strategic investments in the manufacturing sector.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cloud Manufacturing | Traditional Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturing processes integrated with cloud computing and IoT technologies | Conventional on-site manufacturing using physical equipment and manual processes |
| Flexibility | High - allows real-time adjustments and scalable resources | Low - fixed capacity and less adaptable |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs due to resource sharing and automation | Higher fixed costs for equipment, labor, and maintenance |
| Data Management | Centralized cloud data enables analytics, monitoring, and predictive maintenance | Decentralized data, limited real-time visibility and manual reporting |
| Collaboration | Global collaboration through cloud platforms and remote access | Local or regional teams with limited remote interaction |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via cloud infrastructure and third-party services | Scaling requires physical investments and time |
| Innovation Speed | Accelerated product development using digital prototyping and simulations | Slower innovation cycles due to physical prototyping and manual testing |
| Maintenance | Predictive and automated maintenance through IoT sensors and AI | Scheduled or reactive maintenance, often manual and time-consuming |
Which is better?
Cloud manufacturing offers enhanced scalability, real-time data analytics, and improved collaboration through IoT integration, significantly increasing production efficiency compared to traditional manufacturing. Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on fixed resources and localized operations, often resulting in higher overhead costs and less adaptive processes. Companies leveraging cloud manufacturing can achieve faster innovation cycles and reduced downtime by utilizing remote monitoring and AI-driven optimization.
Connection
Cloud manufacturing integrates traditional manufacturing systems by utilizing internet-based platforms to enable real-time data sharing, remote monitoring, and resource optimization. It enhances traditional manufacturing processes through virtualization, allowing factories to scale production efficiently and reduce operational costs. The synergy between cloud technologies and conventional manufacturing drives innovation, improves supply chain management, and increases overall production flexibility.
Key Terms
Physical Production Line
Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on physical production lines with fixed machinery and manual labor, limiting flexibility and scalability. Cloud-manufacturing integrates IoT devices, real-time data analytics, and virtualized resources, enabling dynamic reconfiguration of production assets for increased efficiency and reduced downtime. Explore how cloud-manufacturing transforms physical production lines to drive innovation and operational excellence.
Digital Platform Integration
Traditional manufacturing relies on physical assets and localized processes, limiting scalability and real-time data access. Cloud-manufacturing leverages digital platform integration to enable decentralized production, enhanced collaboration, and dynamic resource allocation across locations. Explore how cloud manufacturing's digital platforms revolutionize production efficiency and agility.
Resource Virtualization
Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on physical resource allocation with fixed capacities, leading to limitations in scalability and flexibility. Cloud-manufacturing leverages resource virtualization to pool and dynamically allocate manufacturing assets over the internet, enabling real-time collaboration and efficient usage of distributed resources. Explore how resource virtualization transforms production processes by enhancing adaptability and reducing operational costs.
Source and External Links
Lean Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing - eVSM - Traditional manufacturing is a mass production method focusing on economies of scale and high output volumes with a push-based system relying on demand forecasts rather than real-time demand, often resulting in less flexibility and more inventory compared to lean methods.
Which is Better? Traditional vs. On-Demand Manufacturing | News - Traditional manufacturing uses established processes like casting and machining, offering reliability and efficiency for high-volume production with a variety of materials.
Advanced Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing - SixDe - Traditional manufacturing is hierarchical, focused on mass production using labor-intensive methods such as welding and molding, contrasting with advanced manufacturing, which incorporates customization and technology-driven processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com