Smart factories leverage Internet of Things (IoT) technology, real-time data analytics, and automation to optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) allow rapid adaptation to changing product requirements through modular machinery and computer-controlled processes. Explore how integrating smart factory principles and FMS can revolutionize modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a smart factory and a flexible manufacturing system is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and technology integration. A smart factory uses advanced sensors, IoT, and AI to enable real-time data analysis and autonomous decision-making, while a flexible manufacturing system focuses on adaptable machinery that can quickly switch between product types. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses implement the right solutions to enhance automation, reduce downtime, and improve scalability. This knowledge drives more informed investment decisions and operational strategies in modern manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
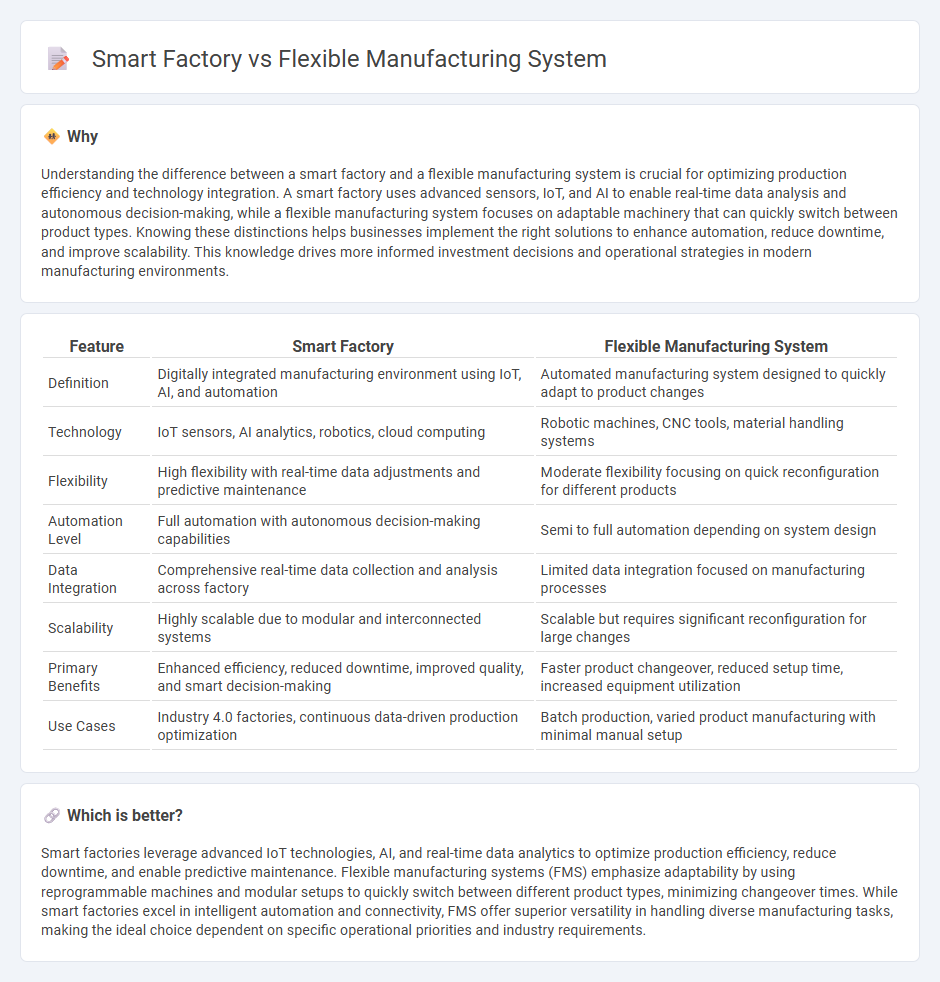
| Feature | Smart Factory | Flexible Manufacturing System |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitally integrated manufacturing environment using IoT, AI, and automation | Automated manufacturing system designed to quickly adapt to product changes |
| Technology | IoT sensors, AI analytics, robotics, cloud computing | Robotic machines, CNC tools, material handling systems |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with real-time data adjustments and predictive maintenance | Moderate flexibility focusing on quick reconfiguration for different products |
| Automation Level | Full automation with autonomous decision-making capabilities | Semi to full automation depending on system design |
| Data Integration | Comprehensive real-time data collection and analysis across factory | Limited data integration focused on manufacturing processes |
| Scalability | Highly scalable due to modular and interconnected systems | Scalable but requires significant reconfiguration for large changes |
| Primary Benefits | Enhanced efficiency, reduced downtime, improved quality, and smart decision-making | Faster product changeover, reduced setup time, increased equipment utilization |
| Use Cases | Industry 4.0 factories, continuous data-driven production optimization | Batch production, varied product manufacturing with minimal manual setup |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage advanced IoT technologies, AI, and real-time data analytics to optimize production efficiency, reduce downtime, and enable predictive maintenance. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) emphasize adaptability by using reprogrammable machines and modular setups to quickly switch between different product types, minimizing changeover times. While smart factories excel in intelligent automation and connectivity, FMS offer superior versatility in handling diverse manufacturing tasks, making the ideal choice dependent on specific operational priorities and industry requirements.
Connection
Smart factories leverage advanced IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and automation to enhance production efficiency, which aligns closely with the principles of flexible manufacturing systems designed for rapid adaptation to changing product demands. Integration of smart factory technologies enables flexible manufacturing systems to optimize machine utilization, reduce downtime, and facilitate seamless reconfiguration of production lines. This synergy drives increased operational agility, cost savings, and improved quality control within modern industrial environments.
Key Terms
Flexible Manufacturing System:
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) integrate computer-controlled machines and automation to efficiently produce a variety of products with minimal manual intervention, enhancing adaptability and reducing downtime. Unlike traditional smart factories that emphasize interconnected IoT devices for real-time data exchange, FMS prioritizes rapid changeover and customization in manufacturing processes. Explore more to understand how FMS drives agility and cost-efficiency in modern production environments.
Automation
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) utilize programmable machines and robotics to automate production processes, allowing for quick adaptations to varying product types and volumes. Smart factories integrate Internet of Things (IoT) devices, AI, and advanced data analytics to enable real-time automation, predictive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making across the entire production line. Explore the key differences and advancements in automation between FMS and smart factory technologies to optimize manufacturing efficiency.
CNC Machines
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) utilize CNC machines to enable adaptable production workflows, allowing rapid changes in tooling and process parameters for varied product types. Smart factories integrate CNC machines with IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and real-time monitoring systems to optimize machine performance, predictive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making. Explore how CNC advancements propel the evolution from FMS to fully connected smart factories by discovering the latest industry innovations.
Source and External Links
Flexible manufacturing system - Wikipedia - A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a manufacturing setup that provides flexibility in managing production through routing and machine flexibility, using automated CNC machines, material handling, and a central control computer to adapt to changes in product type or volume efficiently.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) - Autodesk - FMS is a computer-controlled production setup designed to adapt quickly to changes in product design, batch sizes, machine maintenance, or production sequence, with types including dedicated, sequential, engineered, random, and modular systems tailored for various industries.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems: Types, Examples, & Advantages - Flexible manufacturing systems automate processes like machining, assembly, and inspection to reduce production time and resources while enabling adaptation to product changes or varying production volumes with less human labor involved.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com