Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and optimizing resource allocation. Planned maintenance, by contrast, follows a fixed schedule regardless of actual machine condition, often resulting in unnecessary inspections or unexpected breakdowns. Explore the benefits and applications of both strategies to enhance manufacturing efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between predictive maintenance and planned maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and analytics to forecast equipment failures before they occur, enabling timely interventions. Planned maintenance follows a fixed schedule regardless of equipment condition, which can lead to unnecessary downtime or unexpected breakdowns. Distinguishing these methods allows manufacturers to implement the most effective maintenance strategy, improving asset longevity and minimizing disruption.
Comparison Table
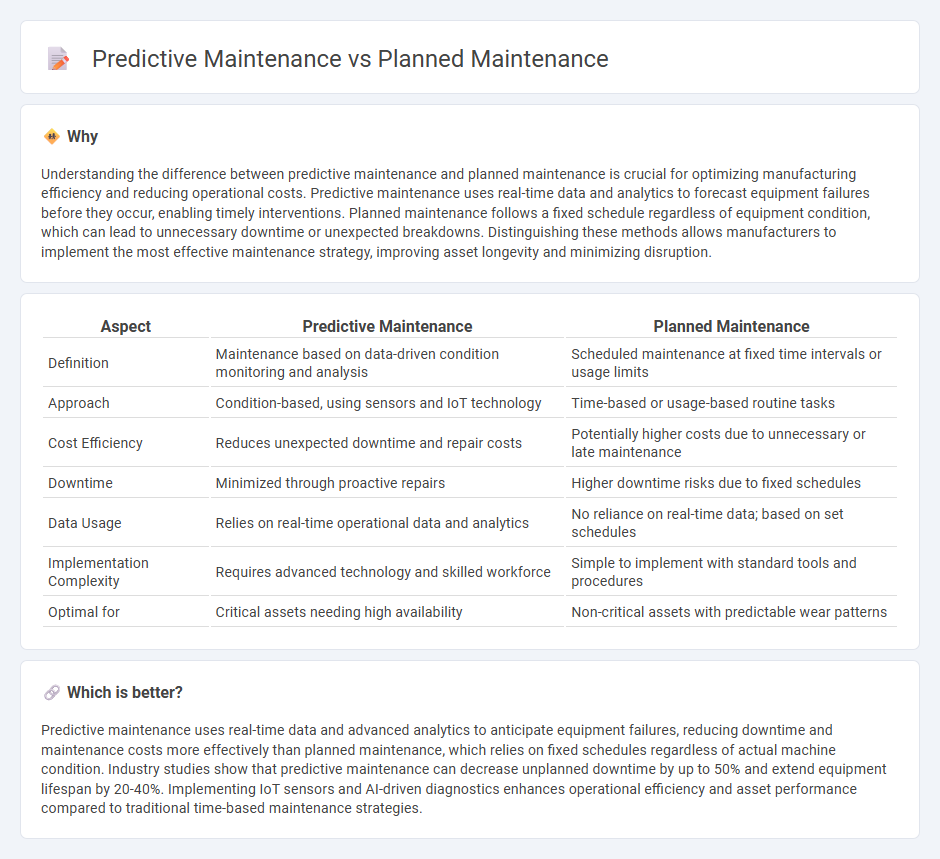
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Planned Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance based on data-driven condition monitoring and analysis | Scheduled maintenance at fixed time intervals or usage limits |
| Approach | Condition-based, using sensors and IoT technology | Time-based or usage-based routine tasks |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces unexpected downtime and repair costs | Potentially higher costs due to unnecessary or late maintenance |
| Downtime | Minimized through proactive repairs | Higher downtime risks due to fixed schedules |
| Data Usage | Relies on real-time operational data and analytics | No reliance on real-time data; based on set schedules |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires advanced technology and skilled workforce | Simple to implement with standard tools and procedures |
| Optimal for | Critical assets needing high availability | Non-critical assets with predictable wear patterns |
Which is better?
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and advanced analytics to anticipate equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs more effectively than planned maintenance, which relies on fixed schedules regardless of actual machine condition. Industry studies show that predictive maintenance can decrease unplanned downtime by up to 50% and extend equipment lifespan by 20-40%. Implementing IoT sensors and AI-driven diagnostics enhances operational efficiency and asset performance compared to traditional time-based maintenance strategies.
Connection
Predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely interventions that align with planned maintenance schedules. This integration reduces unexpected downtime and extends machinery lifespan by ensuring maintenance activities are performed efficiently and only when necessary. Coordinating predictive insights with planned maintenance optimizes resource allocation and improves overall manufacturing productivity.
Key Terms
Planned Maintenance:
Planned maintenance involves scheduled inspections and servicing based on time intervals or usage cycles to prevent equipment failure and extend asset lifespan. This proactive approach relies on historical data and manufacturer recommendations rather than real-time condition monitoring, ensuring routine tasks such as lubrication, adjustments, and part replacements are systematically conducted. Discover how integrating planned maintenance can optimize operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Scheduled Intervals
Planned maintenance involves performing equipment servicing at fixed, scheduled intervals regardless of current machine condition, ensuring routine upkeep and minimizing unexpected breakdowns. Predictive maintenance uses advanced sensor data and real-time analytics to forecast equipment failures, enabling maintenance activities to be scheduled precisely when needed, reducing downtime and extending asset lifespan. Explore the differences and benefits of these maintenance strategies to optimize your operational efficiency.
Preventive Tasks
Planned maintenance involves scheduling preventive tasks at fixed intervals based on time or usage, ensuring equipment reliability and minimizing unexpected failures. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and condition monitoring to anticipate equipment issues, allowing targeted preventive tasks only when indicators show potential problems. Explore more to understand how these approaches optimize asset management and maintenance efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Planned Maintenance? | IBM - Planned maintenance is the proactive identification and organization of maintenance tasks and resources, including preventive, predictive, reliability-centered, and run-to-failure strategies to maximize equipment uptime and manage asset life cycles effectively.
Planned Maintenance: From Reactive to Organized and Scheduled - Planned maintenance is a proactive strategy involving documentation, inspection, spare parts management, and scheduled tasks aiming to reduce equipment downtime and costs, commonly including planned preventive and unscheduled maintenance.
Planned Maintenance: Definition, Examples, & How to Implement - Planned maintenance refers to scheduled, proactive activities designed to minimize downtime and failure costs by preparing tools, parts, and tasks in advance and executing routine maintenance systematically, often supported by computerized management systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com