Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and mobile robots are transforming manufacturing by enhancing material handling and operational efficiency. AGVs follow predetermined paths using markers or wires, while mobile robots utilize advanced sensors and AI for autonomous navigation and complex tasks. Explore how these technologies differ and their impact on factory automation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Mobile Robots is crucial for optimizing manufacturing logistics and workflow efficiency. AGVs follow fixed paths using predefined guides, while Mobile Robots have autonomous navigation capabilities with advanced sensors and AI for dynamic environments. Selecting the appropriate technology impacts operational flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and integration with production systems. This knowledge enables manufacturers to enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and adapt to evolving industrial demands.
Comparison Table
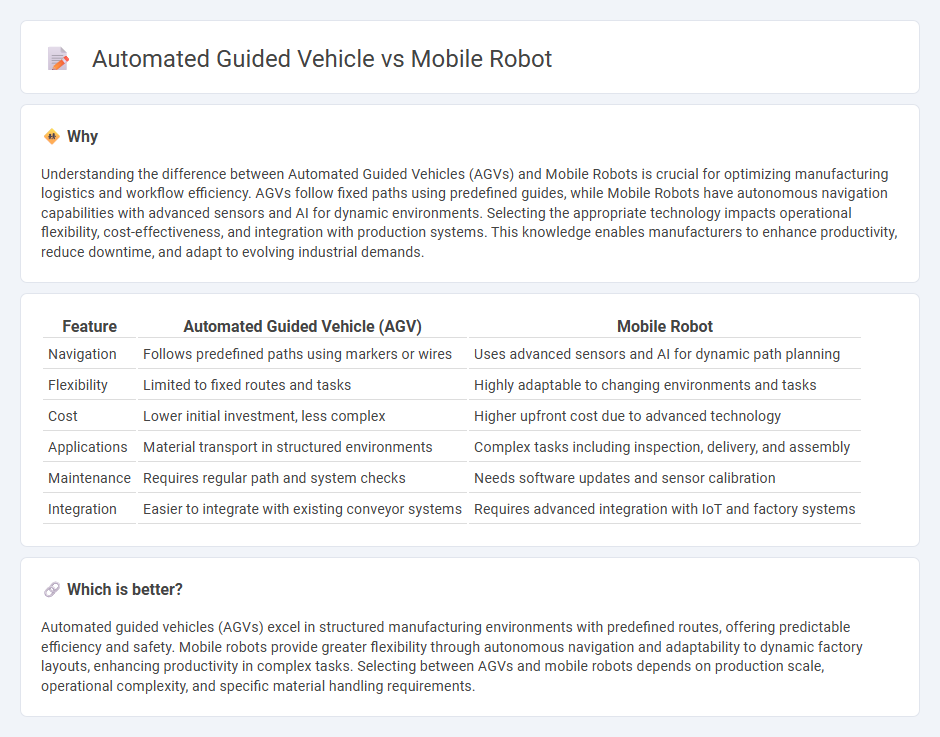
| Feature | Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) | Mobile Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Navigation | Follows predefined paths using markers or wires | Uses advanced sensors and AI for dynamic path planning |
| Flexibility | Limited to fixed routes and tasks | Highly adaptable to changing environments and tasks |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, less complex | Higher upfront cost due to advanced technology |
| Applications | Material transport in structured environments | Complex tasks including inspection, delivery, and assembly |
| Maintenance | Requires regular path and system checks | Needs software updates and sensor calibration |
| Integration | Easier to integrate with existing conveyor systems | Requires advanced integration with IoT and factory systems |
Which is better?
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) excel in structured manufacturing environments with predefined routes, offering predictable efficiency and safety. Mobile robots provide greater flexibility through autonomous navigation and adaptability to dynamic factory layouts, enhancing productivity in complex tasks. Selecting between AGVs and mobile robots depends on production scale, operational complexity, and specific material handling requirements.
Connection
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and mobile robots are interconnected through advanced navigation and control systems that enable efficient material handling in manufacturing environments. Both technologies utilize sensors, laser guidance, and AI-driven algorithms to optimize logistics, enhance productivity, and reduce human labor in factory automation. Integration of AGVs and mobile robots facilitates seamless coordination in transport tasks, promoting smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
Key Terms
Navigation System
Mobile robots feature advanced navigation systems utilizing LiDAR, vision sensors, and SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) for dynamic and autonomous pathfinding in complex environments. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) typically rely on fixed navigation methods such as magnetic tape, QR codes, or reflective markers, restricting their flexibility to predefined routes. Discover the key differences in navigation technologies shaping the future of industrial automation.
Flexibility
Mobile robots offer higher operational flexibility compared to Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) due to their ability to navigate dynamic environments and adapt to changing paths without physical guides. AGVs rely on fixed routes such as magnetic strips or wires, limiting their flexibility in complex or evolving industrial settings. Explore the distinct advantages of mobile robots to understand how they enhance adaptability in automated material handling.
Path Guidance
Mobile robots utilize advanced sensor fusion and AI algorithms to dynamically navigate complex environments without relying on fixed paths. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) follow predetermined routes using physical markers such as magnetic tapes, wires, or reflectors for precise path guidance within controlled industrial settings. Explore more about the technological distinctions and applications of mobile robots versus AGVs in modern logistics.
Source and External Links
What is a mobile robot? Definition with examples - Mobile robots are autonomous or semi-autonomous machines that can freely navigate and operate in various environments using sensors, locomotion systems, onboard computers, and wireless communication.
Products Autonomous mobile robotics (AMR) - Autonomous mobile robots use advanced sensor technology and AI-driven software to automate transport and logistics, enabling 24/7 operation and high efficiency in industries like warehousing, manufacturing, healthcare, and retail.
Mobile Industrial Robots - Automate your internal transportation - MiR robots are customizable autonomous mobile solutions that streamline internal transport, handle loads up to 1200 kg, and optimize logistics with flexible top modules for tasks like towing carts and moving pallets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com