Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing efficiency by enabling collaboration between different industries to utilize each other's by-products, reducing waste and costs. Just-in-time manufacturing focuses on minimizing inventory by producing goods only as needed, which lowers storage expenses and increases responsiveness to market demand. Explore how integrating these strategies can revolutionize production processes and sustainability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between industrial symbiosis and just-in-time manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact in production processes. Industrial symbiosis focuses on the exchange of materials, energy, and by-products among industries to minimize waste, while just-in-time manufacturing emphasizes minimizing inventory and reducing lead times by producing goods only as needed. Knowing these distinctions allows companies to implement the appropriate strategy for sustainability or operational efficiency. This knowledge drives informed decision-making to enhance competitiveness and promote circular economy principles in manufacturing.
Comparison Table
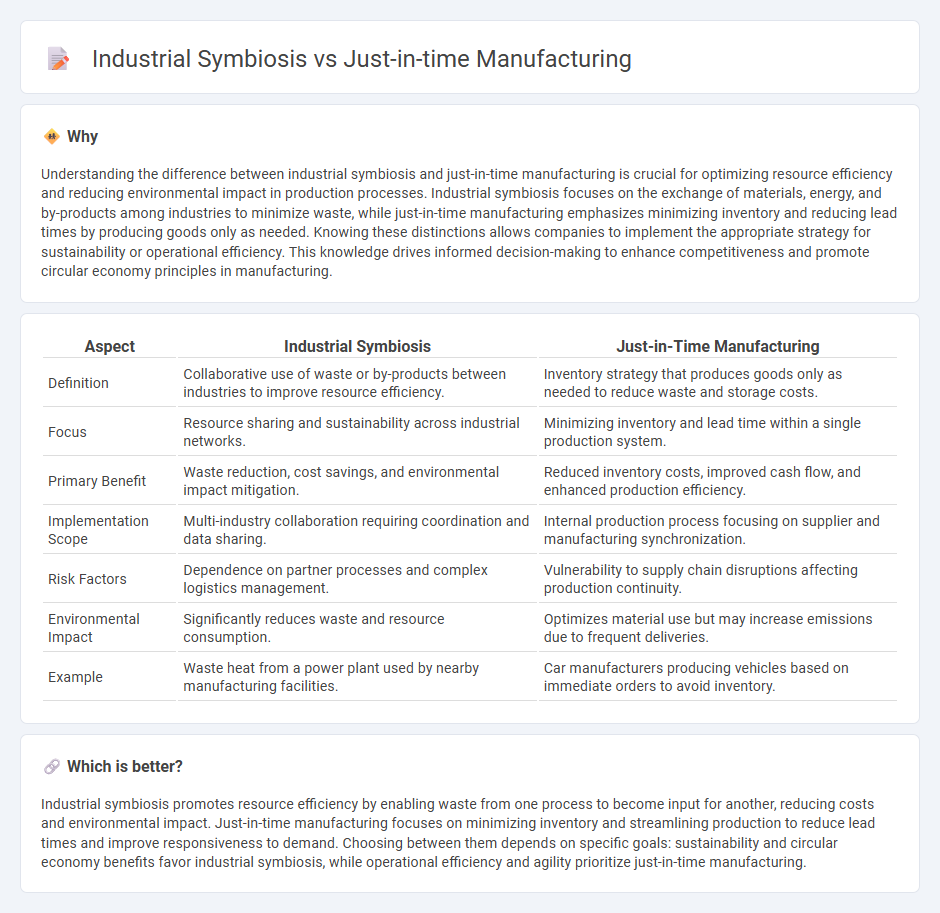
| Aspect | Industrial Symbiosis | Just-in-Time Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative use of waste or by-products between industries to improve resource efficiency. | Inventory strategy that produces goods only as needed to reduce waste and storage costs. |
| Focus | Resource sharing and sustainability across industrial networks. | Minimizing inventory and lead time within a single production system. |
| Primary Benefit | Waste reduction, cost savings, and environmental impact mitigation. | Reduced inventory costs, improved cash flow, and enhanced production efficiency. |
| Implementation Scope | Multi-industry collaboration requiring coordination and data sharing. | Internal production process focusing on supplier and manufacturing synchronization. |
| Risk Factors | Dependence on partner processes and complex logistics management. | Vulnerability to supply chain disruptions affecting production continuity. |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly reduces waste and resource consumption. | Optimizes material use but may increase emissions due to frequent deliveries. |
| Example | Waste heat from a power plant used by nearby manufacturing facilities. | Car manufacturers producing vehicles based on immediate orders to avoid inventory. |
Which is better?
Industrial symbiosis promotes resource efficiency by enabling waste from one process to become input for another, reducing costs and environmental impact. Just-in-time manufacturing focuses on minimizing inventory and streamlining production to reduce lead times and improve responsiveness to demand. Choosing between them depends on specific goals: sustainability and circular economy benefits favor industrial symbiosis, while operational efficiency and agility prioritize just-in-time manufacturing.
Connection
Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing efficiency by facilitating resource sharing among companies, reducing waste and lowering costs. Just-in-time manufacturing relies on this streamlined resource flow to minimize inventory and optimize production schedules. The integration of these systems leads to sustainable manufacturing practices with improved supply chain coordination.
Key Terms
Inventory Reduction
Just-in-time manufacturing minimizes inventory by aligning production schedules closely with demand, significantly reducing storage costs and waste. Industrial symbiosis further innovates by sharing resources, materials, and by-products among interconnected industries to optimize overall inventory levels and foster sustainability. Explore how integrating these strategies can transform inventory management for maximum efficiency and environmental benefit.
Resource Exchange
Just-in-time manufacturing minimizes inventory by synchronizing production schedules with demand, reducing waste and storage costs. Industrial symbiosis enhances resource exchange by connecting multiple industries to share materials, energy, and by-products, promoting circular economy principles. Explore how these strategies optimize resource efficiency and sustainability in modern industrial practices.
Lean Production
Just-in-time manufacturing emphasizes reducing inventory and waste by producing goods only as needed, tightly aligning production schedules with customer demand to enhance Lean Production efficiency. Industrial symbiosis involves collaboration between different industries to reuse resources, energy, and by-products, thereby minimizing waste and promoting sustainability within Lean Production frameworks. Explore how integrating these strategies can optimize operational efficiency and environmental impact in modern manufacturing systems.
Source and External Links
Just In Time Manufacturing: Definition, Benefits, and Origin - Just In Time manufacturing is a strategy that increases efficiency and reduces waste by producing goods only as needed, offering benefits like lower inventory costs, improved quality, faster lead times, and better supplier relationships.
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Just-in-time manufacturing matches production to demand by producing at the rate of takt time and includes methods such as defect elimination, small lot sizes, balanced flow, and pull systems to streamline manufacturing processes.
What is just-in-time manufacturing (JIT manufacturing)? - TechTarget - JIT manufacturing is a production model focused on creating items to meet demand exactly, reducing waste such as overproduction and inventory, thereby increasing efficiency, lowering costs, and speeding delivery.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com