Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data analytics and IoT sensors to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive and preventive maintenance involving all employees to maximize equipment effectiveness and minimize breakdowns. Explore how integrating predictive maintenance with TPM strategies can revolutionize your manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
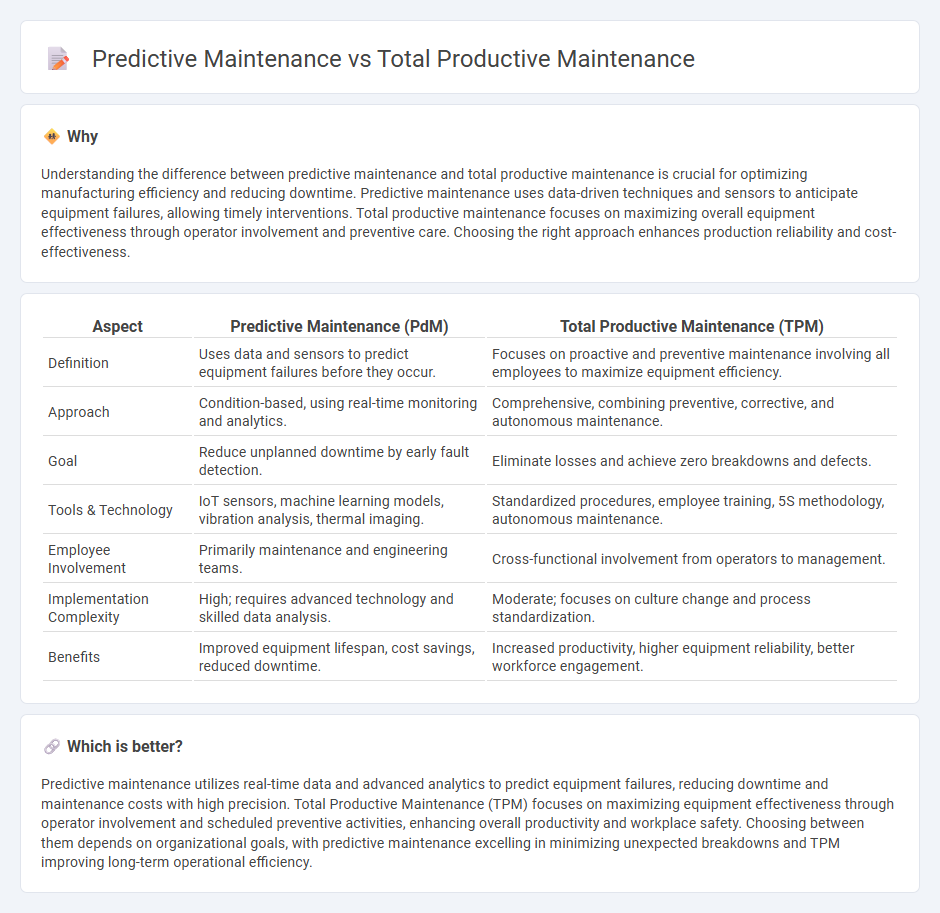
Understanding the difference between predictive maintenance and total productive maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing downtime. Predictive maintenance uses data-driven techniques and sensors to anticipate equipment failures, allowing timely interventions. Total productive maintenance focuses on maximizing overall equipment effectiveness through operator involvement and preventive care. Choosing the right approach enhances production reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance (PdM) | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses data and sensors to predict equipment failures before they occur. | Focuses on proactive and preventive maintenance involving all employees to maximize equipment efficiency. |
| Approach | Condition-based, using real-time monitoring and analytics. | Comprehensive, combining preventive, corrective, and autonomous maintenance. |
| Goal | Reduce unplanned downtime by early fault detection. | Eliminate losses and achieve zero breakdowns and defects. |
| Tools & Technology | IoT sensors, machine learning models, vibration analysis, thermal imaging. | Standardized procedures, employee training, 5S methodology, autonomous maintenance. |
| Employee Involvement | Primarily maintenance and engineering teams. | Cross-functional involvement from operators to management. |
| Implementation Complexity | High; requires advanced technology and skilled data analysis. | Moderate; focuses on culture change and process standardization. |
| Benefits | Improved equipment lifespan, cost savings, reduced downtime. | Increased productivity, higher equipment reliability, better workforce engagement. |
Which is better?
Predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data and advanced analytics to predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs with high precision. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) focuses on maximizing equipment effectiveness through operator involvement and scheduled preventive activities, enhancing overall productivity and workplace safety. Choosing between them depends on organizational goals, with predictive maintenance excelling in minimizing unexpected breakdowns and TPM improving long-term operational efficiency.
Connection
Predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data analytics and sensor technology to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely interventions that reduce downtime. Total productive maintenance (TPM) focuses on proactive and preventive maintenance activities to maximize equipment efficiency and involve all employees in maintaining optimal machine performance. Integrating predictive maintenance within TPM frameworks enhances machinery reliability and productivity by combining data-driven insights with comprehensive, organization-wide maintenance strategies.
Key Terms
**Total Productive Maintenance:**
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive equipment care through operator involvement, aiming to maximize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by reducing downtime, defects, and accidents. TPM integrates preventive maintenance, autonomous maintenance, and continuous improvement to foster a culture of shared responsibility and operational excellence. Explore how TPM strategies can transform your maintenance approach and boost productivity.
Autonomous Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes Autonomous Maintenance, where operators take responsibility for routine upkeep tasks to prevent equipment failure, enhancing overall productivity and equipment lifespan. Predictive Maintenance uses data-driven techniques like vibration analysis and IoT sensors to forecast machine failures before they occur, focusing on minimizing downtime through timely interventions. Explore how integrating Autonomous Maintenance within a predictive framework can optimize maintenance strategies and boost operational efficiency.
Focused Improvement
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes Focused Improvement by involving all employees in proactive equipment upkeep to eliminate losses and enhance productivity, while Predictive Maintenance relies on data-driven techniques such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging to forecast equipment failures before they occur. TPM's Focused Improvement targets specific bottlenecks and minor stops to drive continuous, incremental gains, whereas Predictive Maintenance aims to optimize maintenance schedules and reduce unplanned downtime through condition monitoring. Explore detailed methodologies and best practices to leverage Focused Improvement for superior maintenance strategy outcomes.
Source and External Links
TPM Meaning: Components, Benefits, & More - UpKeep - Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a process aimed at maximizing equipment effectiveness by involving all departments actively to eliminate losses such as downtime, waste, and equipment failure, thereby driving closer to "perfect production" through preventive, autonomous, and corrective maintenance.
TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) - Lean Manufacturing - TPM is a holistic equipment maintenance approach that empowers operators and integrates production and maintenance roles to enhance equipment reliability and productivity, founded on 5S principles and eight supporting activities focused on proactive and preventative maintenance.
Lean Thinking and Methods - TPM | US EPA - Total Productive Maintenance engages all organizational levels to maximize production equipment effectiveness, aiming to eliminate all types of losses--from breakdowns to defects--through autonomous maintenance, mistake-proofing, and equipment design that reduces maintenance needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com