Generative design leverages artificial intelligence algorithms to explore numerous design possibilities, optimizing for parameters like weight, strength, and material usage, whereas traditional CAD design relies on manual input and predefined constraints to create models. This AI-driven approach accelerates innovation by producing complex, efficient structures that often surpass human-designed solutions in performance and sustainability. Discover how integrating generative design can revolutionize your manufacturing processes and product development.
Why it is important
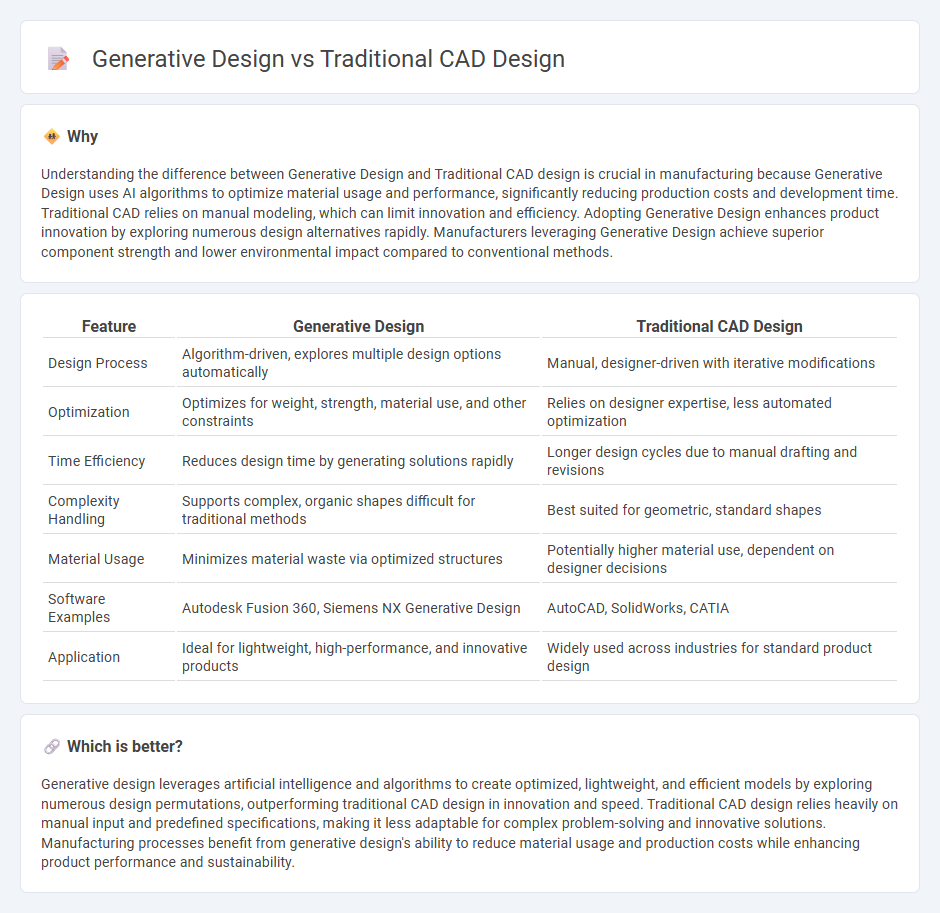
Understanding the difference between Generative Design and Traditional CAD design is crucial in manufacturing because Generative Design uses AI algorithms to optimize material usage and performance, significantly reducing production costs and development time. Traditional CAD relies on manual modeling, which can limit innovation and efficiency. Adopting Generative Design enhances product innovation by exploring numerous design alternatives rapidly. Manufacturers leveraging Generative Design achieve superior component strength and lower environmental impact compared to conventional methods.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Generative Design | Traditional CAD Design |
|---|---|---|
| Design Process | Algorithm-driven, explores multiple design options automatically | Manual, designer-driven with iterative modifications |
| Optimization | Optimizes for weight, strength, material use, and other constraints | Relies on designer expertise, less automated optimization |
| Time Efficiency | Reduces design time by generating solutions rapidly | Longer design cycles due to manual drafting and revisions |
| Complexity Handling | Supports complex, organic shapes difficult for traditional methods | Best suited for geometric, standard shapes |
| Material Usage | Minimizes material waste via optimized structures | Potentially higher material use, dependent on designer decisions |
| Software Examples | Autodesk Fusion 360, Siemens NX Generative Design | AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA |
| Application | Ideal for lightweight, high-performance, and innovative products | Widely used across industries for standard product design |
Which is better?
Generative design leverages artificial intelligence and algorithms to create optimized, lightweight, and efficient models by exploring numerous design permutations, outperforming traditional CAD design in innovation and speed. Traditional CAD design relies heavily on manual input and predefined specifications, making it less adaptable for complex problem-solving and innovative solutions. Manufacturing processes benefit from generative design's ability to reduce material usage and production costs while enhancing product performance and sustainability.
Connection
Generative design and traditional CAD design are interconnected through their complementary roles in the manufacturing process, where generative design uses AI algorithms to create optimized design alternatives based on specific constraints, and traditional CAD allows engineers to refine and finalize those designs with precise control and detailed specifications. This synergy accelerates product development by combining the innovative, data-driven approach of generative design with the proven accuracy and functionality of CAD modeling. Manufacturers benefit from reduced material usage, improved performance, and streamlined workflows by integrating these technologies.
Key Terms
Parametric Modeling
Traditional CAD design relies heavily on manual parametric modeling, allowing designers to control dimensions and constraints to modify geometry precisely. Generative design uses algorithms and AI to explore numerous parametric variations, optimizing structures based on performance criteria such as weight, strength, or material usage. Discover how integrating generative design with parametric modeling can revolutionize your product development process.
Algorithmic Optimization
Traditional CAD design relies on manual input and geometric constraints, offering explicit control over dimensions and shapes but limited exploration of complex solutions. Generative design uses algorithmic optimization techniques like genetic algorithms and topology optimization to automatically generate multiple design alternatives based on specified performance criteria and constraints. Discover how algorithm-driven generative design transforms innovation and efficiency in product development.
Design Iteration
Traditional CAD design relies on manual adjustments and designer expertise, often resulting in longer iteration cycles and limited exploration of design alternatives. Generative design leverages algorithms and AI to rapidly produce multiple optimized iterations based on predefined constraints, significantly accelerating the design process and expanding creative possibilities. Discover how generative design can transform your workflow and increase innovation efficiency.
Source and External Links
3D CAD vs. Traditional Design Methods: A Revolution in Design - Traditional CAD design refers to manual drafting techniques using tools like rulers and compasses, which are time-consuming, error-prone, and limited to 2D drawings that require significant imagination to visualize the final product.
A Brief Overview of the History of CAD - Traditional CAD design involved skilled craftsmanship with pencil, T-square, triangles, and protractors, often requiring precise hand-drafting skills and additional tools like the Universal Drafting Machine to create accurate technical drawings.
How CAD Has Evolved Since 1982 - Scan2CAD - Traditional CAD started with 2D drafting emulating manual methods before evolving into wireframe and surface modeling, marked by pivotal developments like Bezier curves in the 1960s that advanced the precise representation of curved surfaces digitally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com