Biofabrication utilizes advanced techniques such as 3D bioprinting and tissue engineering to create complex biological structures with high precision and customization. Die stamping focuses on high-volume metal shaping using molds to produce consistent, cost-effective parts with rapid turnaround. Explore the unique advantages and applications of biofabrication and die stamping in modern manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
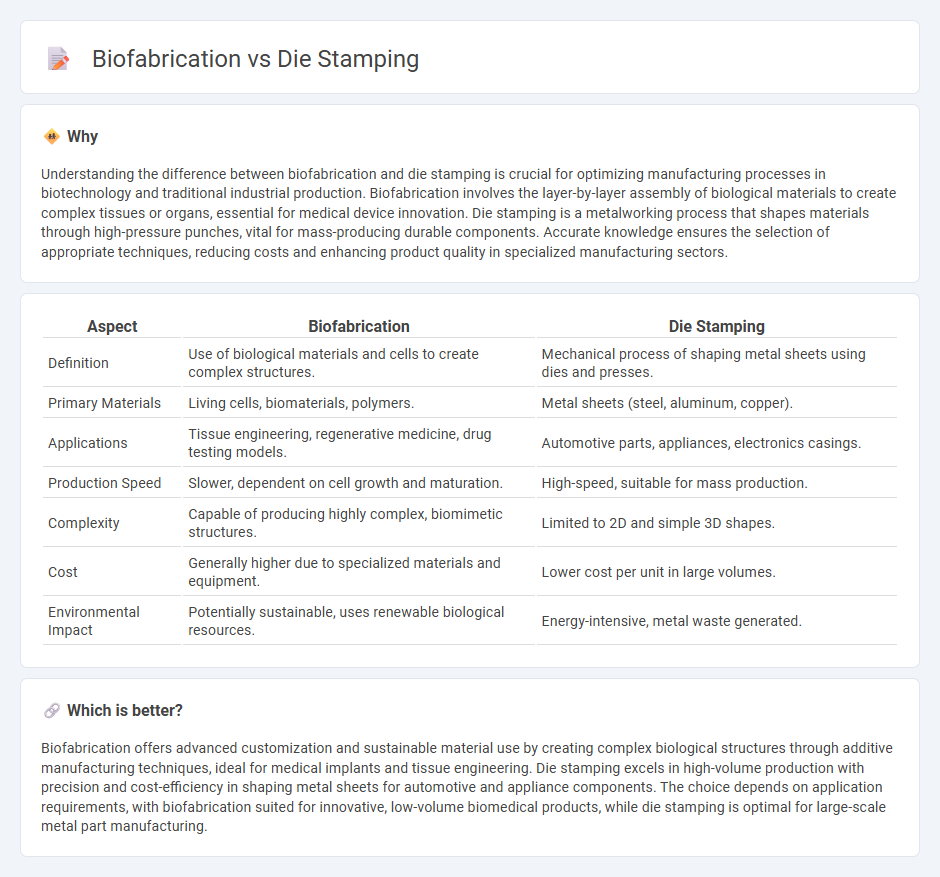
Understanding the difference between biofabrication and die stamping is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes in biotechnology and traditional industrial production. Biofabrication involves the layer-by-layer assembly of biological materials to create complex tissues or organs, essential for medical device innovation. Die stamping is a metalworking process that shapes materials through high-pressure punches, vital for mass-producing durable components. Accurate knowledge ensures the selection of appropriate techniques, reducing costs and enhancing product quality in specialized manufacturing sectors.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biofabrication | Die Stamping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of biological materials and cells to create complex structures. | Mechanical process of shaping metal sheets using dies and presses. |
| Primary Materials | Living cells, biomaterials, polymers. | Metal sheets (steel, aluminum, copper). |
| Applications | Tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, drug testing models. | Automotive parts, appliances, electronics casings. |
| Production Speed | Slower, dependent on cell growth and maturation. | High-speed, suitable for mass production. |
| Complexity | Capable of producing highly complex, biomimetic structures. | Limited to 2D and simple 3D shapes. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized materials and equipment. | Lower cost per unit in large volumes. |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially sustainable, uses renewable biological resources. | Energy-intensive, metal waste generated. |
Which is better?
Biofabrication offers advanced customization and sustainable material use by creating complex biological structures through additive manufacturing techniques, ideal for medical implants and tissue engineering. Die stamping excels in high-volume production with precision and cost-efficiency in shaping metal sheets for automotive and appliance components. The choice depends on application requirements, with biofabrication suited for innovative, low-volume biomedical products, while die stamping is optimal for large-scale metal part manufacturing.
Connection
Biofabrication integrates biological materials with manufacturing processes to produce complex structures, while die stamping shapes materials through precise mechanical force to create detailed components. These technologies intersect when biofabricated materials require accurate shaping or structural reinforcement, leveraging die stamping to form bio-based parts with high precision. Combining biofabrication and die stamping enhances scalability and functionality in producing bioengineered products for medical and industrial applications.
Key Terms
Tooling
Die stamping involves precise metal tooling designed for high-volume manufacturing with consistent repeatability and durability, often utilizing hardened steel dies for shaping or cutting materials. Biofabrication relies on specialized custom tooling such as bioprinters and microfluidic devices to create complex biological structures with spatial accuracy and minimal damage to cells. Explore further to understand the advancements and tooling innovations driving these contrasting fabrication technologies.
Biomaterials
Die stamping offers precise micro-patterning on biomaterial surfaces, enhancing cellular interactions by controlling topography and chemical functionality. In contrast, biofabrication integrates living cells and biomaterials to create complex, tissue-like structures with enhanced biological functionality and regenerative potential. Explore the latest advances in biomaterials to understand how these technologies revolutionize tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Additive Manufacturing
Die stamping involves shaping metal sheets through mechanical pressing, while biofabrication leverages additive manufacturing techniques like 3D bioprinting to create complex biological structures layer by layer. Additive manufacturing in biofabrication enables precise control over cell placement and scaffold architecture, enhancing tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Explore the latest advancements in additive manufacturing to understand its transformative impact on die stamping and biofabrication technologies.
Source and External Links
What is a Stamping Die? - Die Co., Inc. - Stamping dies are precision tools made typically of tool steel, used in cold-forming processes to cut and form metal sheets into specific shapes through operations like cutting, lancing, and shearing.
Die Stamping: Steps, Operations and Processes - IQS Directory - Die stamping is a cold forming process using dies that perform cutting and forming in single or combined operations to shape metal strips for use in industries such as automotive and electronics.
Die (manufacturing) - Wikipedia - Stamping dies are specialized machine tools used with presses to cut or form materials like sheet metal in operations including blanking, piercing, and bending, involving parts such as punches and die blocks to achieve the final shape.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com