Digital twinning transforms manufacturing by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Manual inspection relies on human expertise to detect defects and ensure quality, but it is time-consuming and prone to errors. Explore how digital twinning enhances efficiency and accuracy beyond traditional manual inspection methods.
Why it is important
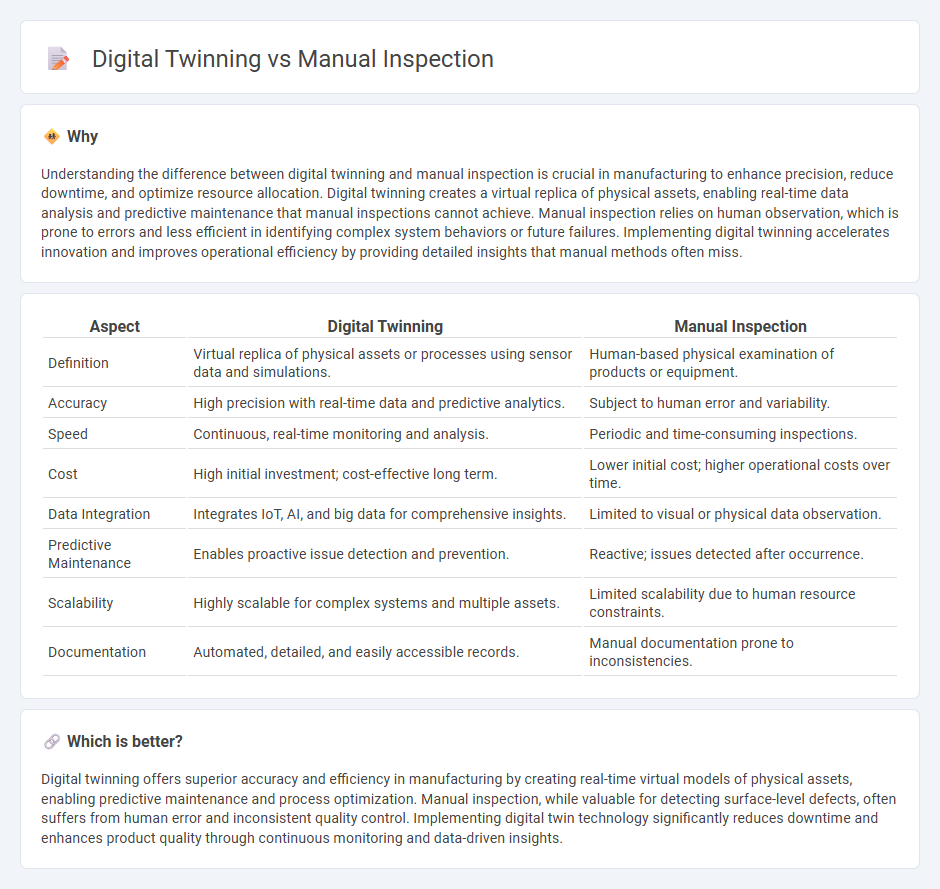
Understanding the difference between digital twinning and manual inspection is crucial in manufacturing to enhance precision, reduce downtime, and optimize resource allocation. Digital twinning creates a virtual replica of physical assets, enabling real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance that manual inspections cannot achieve. Manual inspection relies on human observation, which is prone to errors and less efficient in identifying complex system behaviors or future failures. Implementing digital twinning accelerates innovation and improves operational efficiency by providing detailed insights that manual methods often miss.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Twinning | Manual Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets or processes using sensor data and simulations. | Human-based physical examination of products or equipment. |
| Accuracy | High precision with real-time data and predictive analytics. | Subject to human error and variability. |
| Speed | Continuous, real-time monitoring and analysis. | Periodic and time-consuming inspections. |
| Cost | High initial investment; cost-effective long term. | Lower initial cost; higher operational costs over time. |
| Data Integration | Integrates IoT, AI, and big data for comprehensive insights. | Limited to visual or physical data observation. |
| Predictive Maintenance | Enables proactive issue detection and prevention. | Reactive; issues detected after occurrence. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for complex systems and multiple assets. | Limited scalability due to human resource constraints. |
| Documentation | Automated, detailed, and easily accessible records. | Manual documentation prone to inconsistencies. |
Which is better?
Digital twinning offers superior accuracy and efficiency in manufacturing by creating real-time virtual models of physical assets, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization. Manual inspection, while valuable for detecting surface-level defects, often suffers from human error and inconsistent quality control. Implementing digital twin technology significantly reduces downtime and enhances product quality through continuous monitoring and data-driven insights.
Connection
Digital twinning enhances manual inspection in manufacturing by creating accurate virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling inspectors to visualize and analyze complex components in real-time. This integration improves defect detection, reduces inspection time, and supports predictive maintenance by providing detailed data for decision-making. Combining digital twin simulations with manual expertise ensures higher-quality control and optimized production processes.
Key Terms
Human Visual Assessment
Human visual assessment remains critical in identifying subtle anomalies during manual inspection, leveraging expert experience to detect defects often missed by automated systems. Digital twinning enhances this process by creating accurate virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive analysis for improved maintenance strategies. Explore the advantages of integrating human expertise with digital twinning for optimized inspection outcomes.
Sensor Data Acquisition
Sensor data acquisition plays a pivotal role in both manual inspection and digital twinning, with each method offering unique advantages. Manual inspection relies on human expertise to gather sensor data, often resulting in limited real-time insights and potential for human error. Digital twinning leverages continuous, automated sensor data streams to create dynamic virtual models, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational efficiency; discover how this innovative approach transforms asset management.
Real-Time Simulation
Manual inspection relies on human observation to detect anomalies, often limited by subjective judgment and delayed feedback. Digital twinning leverages real-time simulation by creating a dynamic virtual model of physical assets, enabling continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance. Explore how real-time simulation in digital twinning transforms inspection efficiency and accuracy for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Automated Quality Control vs Manual Inspection - Averroes AI - Manual inspection involves human inspectors visually examining products to check for defects, relying on skill and judgment for adaptable and intuitive quality control but facing challenges like fatigue, subjectivity, and slower speed compared to automated systems.
Manual Inspection vs. AI Inspection with Instrumental - Manual inspection is commonly used for final visual checks, cosmetic inspections, and safety-critical regulated inspections because it is flexible and straightforward to ramp up or down, but it struggles with consistency and thoroughness compared to automated methods.
What is Manual Inspection? - Help Center - Manual inspection in WATS allows operators to manually add test and repair reports through a web-based interface, especially useful where automatic test equipment is unavailable or inefficient, with features designed to streamline reporting and test sequence management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com