Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of physical manufacturing assets, enabling real-time simulation and predictive analysis to optimize production processes. The Internet of Things (IoT) facilitates seamless connectivity between machines and systems, collecting and transmitting data for enhanced operational efficiency and monitoring. Explore how integrating digital twins with IoT can transform manufacturing performance and innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital twin and IoT in manufacturing enables precise simulation of physical assets versus real-time data collection through connected devices. Digital twins create virtual replicas of manufacturing processes for predictive analytics and optimization, while IoT focuses on sensor networks for monitoring and data acquisition. This distinction drives informed decisions, reduces downtime, and improves operational efficiency by leveraging the strengths of both technologies. Manufacturing leaders can maximize productivity and innovation by aligning strategies with their unique digital transformation goals.
Comparison Table
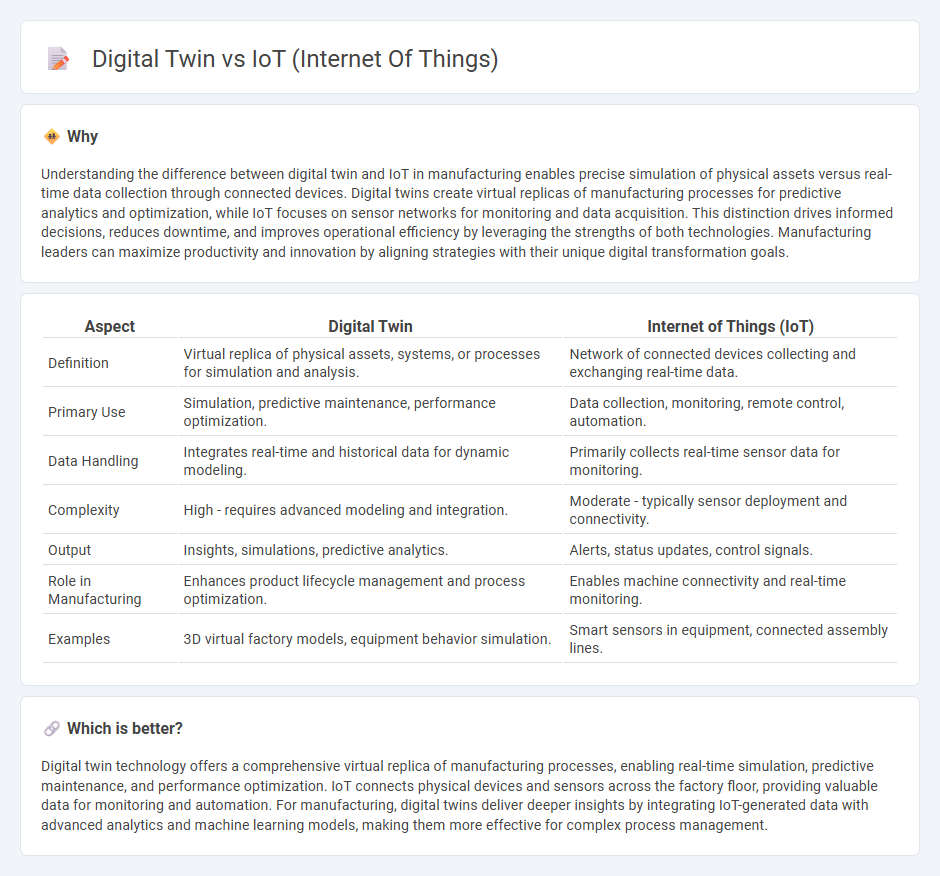
| Aspect | Digital Twin | Internet of Things (IoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets, systems, or processes for simulation and analysis. | Network of connected devices collecting and exchanging real-time data. |
| Primary Use | Simulation, predictive maintenance, performance optimization. | Data collection, monitoring, remote control, automation. |
| Data Handling | Integrates real-time and historical data for dynamic modeling. | Primarily collects real-time sensor data for monitoring. |
| Complexity | High - requires advanced modeling and integration. | Moderate - typically sensor deployment and connectivity. |
| Output | Insights, simulations, predictive analytics. | Alerts, status updates, control signals. |
| Role in Manufacturing | Enhances product lifecycle management and process optimization. | Enables machine connectivity and real-time monitoring. |
| Examples | 3D virtual factory models, equipment behavior simulation. | Smart sensors in equipment, connected assembly lines. |
Which is better?
Digital twin technology offers a comprehensive virtual replica of manufacturing processes, enabling real-time simulation, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization. IoT connects physical devices and sensors across the factory floor, providing valuable data for monitoring and automation. For manufacturing, digital twins deliver deeper insights by integrating IoT-generated data with advanced analytics and machine learning models, making them more effective for complex process management.
Connection
Digital twin technology leverages IoT sensors to collect real-time data from manufacturing equipment, enabling accurate virtual replicas for monitoring and optimization. This integration facilitates predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. IoT-driven data streams empower digital twins to simulate processes, enhancing decision-making and accelerating innovation in manufacturing.
Key Terms
Sensors
IoT sensors collect real-time data from physical objects, enabling seamless connectivity and automation across interconnected devices. Digital twins utilize this sensor data to create dynamic virtual replicas that simulate and analyze the performance, behavior, and conditions of their physical counterparts. Explore how integrating advanced sensors enhances the accuracy and functionality of digital twins in smart environments.
Real-time Data
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables real-time data collection from interconnected devices, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making accuracy. Digital twins use this live data to create dynamic virtual models that simulate, predict, and optimize physical asset performance in real time. Explore detailed insights on how integrating IoT with digital twin technology revolutionizes industries.
Simulation Model
IoT (Internet of Things) generates real-time data from interconnected devices, enabling continuous monitoring and operational insights. Digital twins utilize simulation models to create virtual replicas of physical assets, facilitating predictive analysis and scenario testing based on IoT data inputs. Explore how integrating IoT and digital twin simulation models can revolutionize asset management and performance optimization.
Source and External Links
What Is the Internet of Things? - IoT refers to a network of physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and technology to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet, spanning from household items to industrial machines.
What is IoT? - Internet of Things Explained - IoT is the collective network of connected devices and the technology enabling communication between these devices and the cloud, allowing everyday objects like toothbrushes, cars, and machines to collect data and respond intelligently using embedded sensors.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? - IoT is a network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects equipped with sensors, software, and connectivity to collect and share data, enabling applications from smart homes to smart cities and industrial automation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com