Predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data and advanced analytics to anticipate equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs more effectively than traditional scheduled maintenance. Scheduled maintenance relies on predetermined intervals regardless of actual equipment condition, often leading to unnecessary servicing or unexpected breakdowns. Discover how integrating predictive maintenance can transform manufacturing efficiency and asset management.
Why it is important
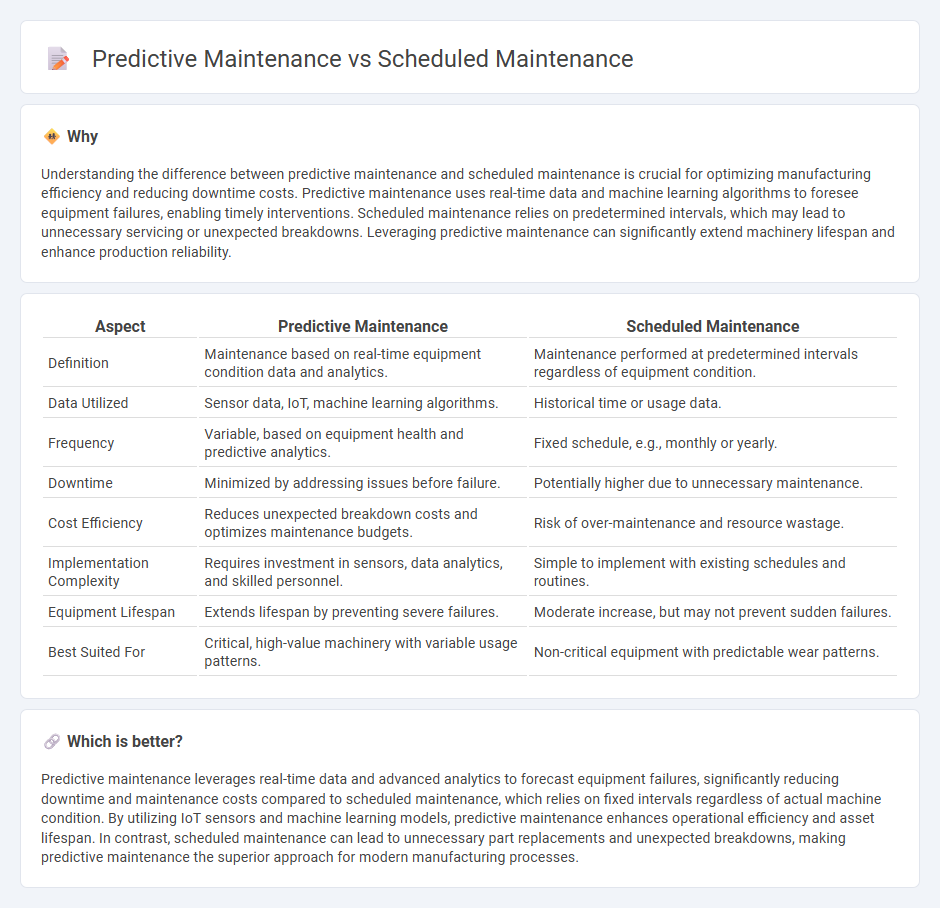
Understanding the difference between predictive maintenance and scheduled maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing downtime costs. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and machine learning algorithms to foresee equipment failures, enabling timely interventions. Scheduled maintenance relies on predetermined intervals, which may lead to unnecessary servicing or unexpected breakdowns. Leveraging predictive maintenance can significantly extend machinery lifespan and enhance production reliability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Scheduled Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance based on real-time equipment condition data and analytics. | Maintenance performed at predetermined intervals regardless of equipment condition. |
| Data Utilized | Sensor data, IoT, machine learning algorithms. | Historical time or usage data. |
| Frequency | Variable, based on equipment health and predictive analytics. | Fixed schedule, e.g., monthly or yearly. |
| Downtime | Minimized by addressing issues before failure. | Potentially higher due to unnecessary maintenance. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces unexpected breakdown costs and optimizes maintenance budgets. | Risk of over-maintenance and resource wastage. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires investment in sensors, data analytics, and skilled personnel. | Simple to implement with existing schedules and routines. |
| Equipment Lifespan | Extends lifespan by preventing severe failures. | Moderate increase, but may not prevent sudden failures. |
| Best Suited For | Critical, high-value machinery with variable usage patterns. | Non-critical equipment with predictable wear patterns. |
Which is better?
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs compared to scheduled maintenance, which relies on fixed intervals regardless of actual machine condition. By utilizing IoT sensors and machine learning models, predictive maintenance enhances operational efficiency and asset lifespan. In contrast, scheduled maintenance can lead to unnecessary part replacements and unexpected breakdowns, making predictive maintenance the superior approach for modern manufacturing processes.
Connection
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data analytics and IoT sensors to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, enhancing the efficiency of scheduled maintenance by informing optimal timing and scope. Scheduled maintenance ensures routine checks and repairs at predetermined intervals, but integrating predictive insights reduces unnecessary maintenance tasks and minimizes downtime. This synergy improves asset longevity, operational reliability, and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
**Scheduled Maintenance:**
Scheduled maintenance involves performing routine inspections and servicing tasks at predetermined intervals based on time or usage, ensuring consistent equipment reliability and minimizing unexpected breakdowns. This approach relies on historical data and manufacturer recommendations to prevent failures before they occur, optimizing maintenance resources and operational uptime. Discover more about how scheduled maintenance can enhance your asset management strategy.
Fixed Intervals
Scheduled maintenance follows fixed intervals based on predefined time frames or usage cycles, ensuring equipment undergoes routine checks regardless of condition. Predictive maintenance relies on real-time data and sensor analysis to forecast failures before they occur, minimizing unnecessary maintenance at fixed intervals. Explore how integrating sensor technology and data analytics can optimize your maintenance strategy beyond fixed schedules.
Preventive Tasks
Scheduled maintenance involves performing preventive tasks at predetermined intervals to reduce equipment failures and ensure reliability. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and condition monitoring technologies, such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging, to predict when preventive tasks should be executed based on actual equipment health. Discover how integrating predictive maintenance can optimize your preventive strategy and extend asset lifespan.
Source and External Links
What is Scheduled Maintenance? Examples, Benefits, and ... - Scheduled maintenance involves assigning maintenance tasks to a technician with a specific deadline, covering inspections, servicing, adjustments, and planned shutdowns, whether one-time or recurring, to reduce equipment failures and downtime.
What is Scheduled Maintenance? Meaning, Definition, ... - Scheduled maintenance refers to planned repair and service tasks performed within a set timeframe, including routine inspections, adjustments, regular servicing, and planned shutdowns, which can be recurring or triggered by specific needs.
What Is Scheduled Maintenance? Overview, Benefits, & More - Scheduled maintenance is any repair and upkeep work completed within a predetermined timeframe, detailing when and by whom tasks are performed, and can occur at regular intervals or in response to a work request.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com