Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines manufacturing workflows by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing accuracy, and reducing operational costs. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) focuses on maximizing equipment effectiveness through proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime, and fostering continuous improvement. Discover how integrating RPA and TPM can revolutionize manufacturing efficiency and productivity.
Why it is important
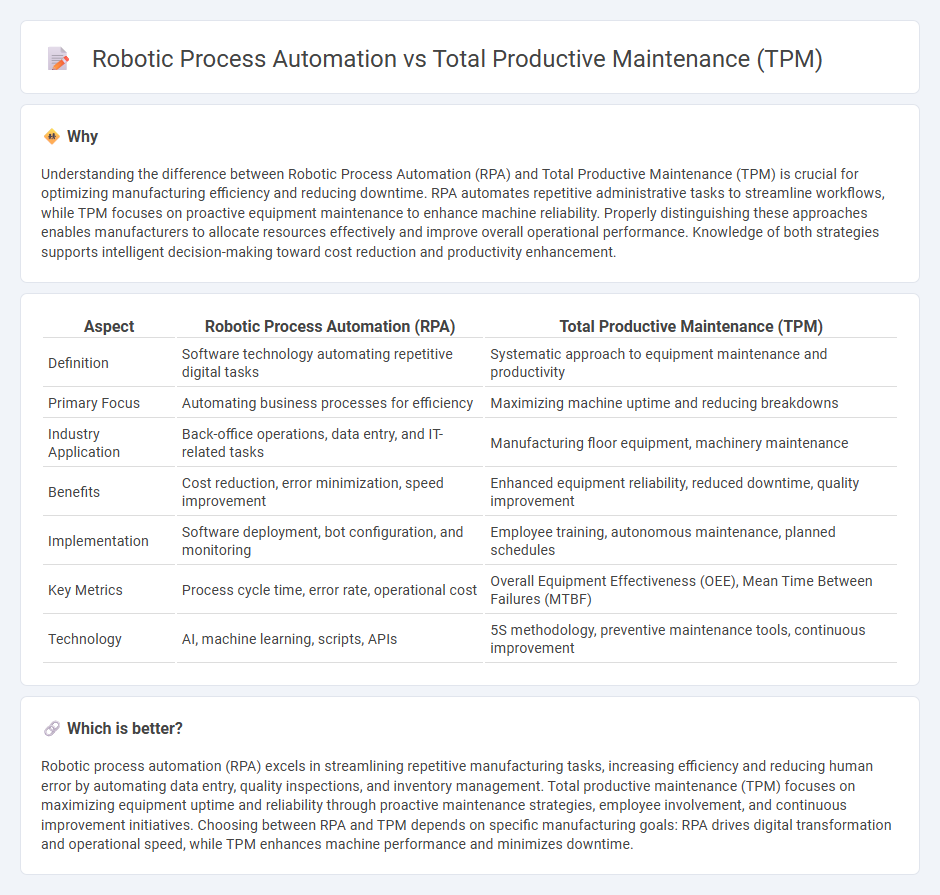
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing downtime. RPA automates repetitive administrative tasks to streamline workflows, while TPM focuses on proactive equipment maintenance to enhance machine reliability. Properly distinguishing these approaches enables manufacturers to allocate resources effectively and improve overall operational performance. Knowledge of both strategies supports intelligent decision-making toward cost reduction and productivity enhancement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software technology automating repetitive digital tasks | Systematic approach to equipment maintenance and productivity |
| Primary Focus | Automating business processes for efficiency | Maximizing machine uptime and reducing breakdowns |
| Industry Application | Back-office operations, data entry, and IT-related tasks | Manufacturing floor equipment, machinery maintenance |
| Benefits | Cost reduction, error minimization, speed improvement | Enhanced equipment reliability, reduced downtime, quality improvement |
| Implementation | Software deployment, bot configuration, and monitoring | Employee training, autonomous maintenance, planned schedules |
| Key Metrics | Process cycle time, error rate, operational cost | Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) |
| Technology | AI, machine learning, scripts, APIs | 5S methodology, preventive maintenance tools, continuous improvement |
Which is better?
Robotic process automation (RPA) excels in streamlining repetitive manufacturing tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing human error by automating data entry, quality inspections, and inventory management. Total productive maintenance (TPM) focuses on maximizing equipment uptime and reliability through proactive maintenance strategies, employee involvement, and continuous improvement initiatives. Choosing between RPA and TPM depends on specific manufacturing goals: RPA drives digital transformation and operational speed, while TPM enhances machine performance and minimizes downtime.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) by automating routine maintenance tasks and data collection, improving accuracy and efficiency in equipment management. RPA streamlines predictive maintenance workflows by analyzing sensor data to anticipate machine failures, thus supporting TPM's goal of maximizing equipment availability. Integrating RPA within TPM frameworks reduces downtime, optimizes resource allocation, and increases overall manufacturing productivity.
Key Terms
**Total Productive Maintenance (TPM):**
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a holistic approach to equipment maintenance that aims to maximize machine uptime and enhance production efficiency by involving all employees in proactive and preventive maintenance activities. TPM focuses on eliminating equipment downtime, reducing defects, and improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) through autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, and continuous improvement processes. Discover how TPM strategies transform operational reliability and production performance by exploring its core principles and implementation techniques.
Autonomous Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes Autonomous Maintenance, empowering operators to perform routine equipment upkeep, which reduces downtime and extends asset lifespan through proactive inspections and cleaning. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates digital workflows by mimicking human interactions with software, enhancing operational efficiency in data-intensive tasks rather than physical equipment care. Explore how integrating TPM's Autonomous Maintenance with RPA solutions can optimize overall productivity and asset management.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) enhances Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) by emphasizing proactive and preventive maintenance to minimize downtime, improve equipment reliability, and optimize performance. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) indirectly supports OEE by automating data collection and analysis, enabling real-time monitoring and faster decision-making. Explore how integrating TPM and RPA can significantly boost manufacturing efficiency and maximize asset utilization.
Source and External Links
TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) - Lean Manufacturing - Total Productive Maintenance is a holistic approach that emphasizes proactive and preventative maintenance by involving operators to maintain their equipment, aiming for perfect production with a safe, clean, and organized work environment based on 5S and eight supporting pillars.
TPM Meaning: Components, Benefits, & More - UpKeep - TPM seeks to maximize equipment effectiveness and eliminate losses through maintenance and safety management, framing maintenance as a strategic business advantage to reduce downtime and increase profit by applying a multi-process approach rooted in the 5S principles.
Total Productive Maintenance: An Overview - Reliable Plant - TPM involves using machines, employees, and processes collaboratively to prevent breakdowns, stops, defects, and accidents by empowering employees in equipment care and emphasizing proactive and preventive maintenance techniques for perfect production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com