Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in manufacturing focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry, quality control, and machinery monitoring, enhancing efficiency at the operational level. Supply chain automation integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics to streamline end-to-end logistics, inventory management, and demand forecasting, optimizing the entire supply chain workflow. Discover how these automation technologies transform manufacturing processes by exploring their distinct roles and benefits.
Why it is important
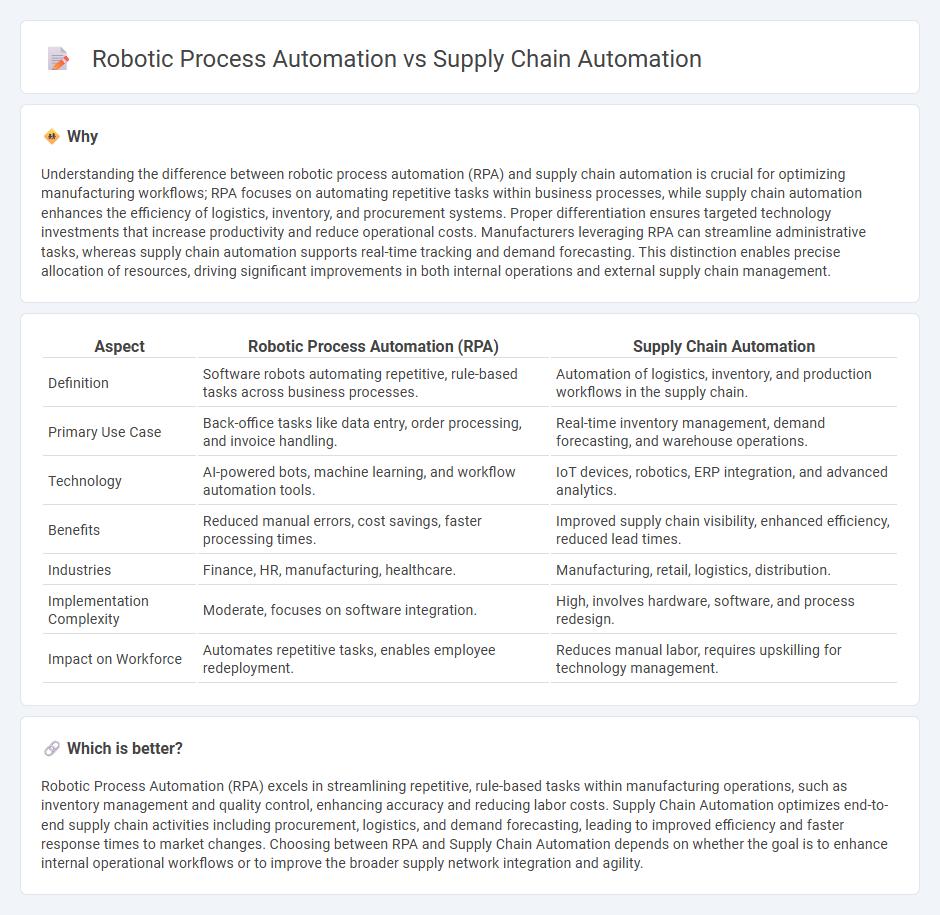
Understanding the difference between robotic process automation (RPA) and supply chain automation is crucial for optimizing manufacturing workflows; RPA focuses on automating repetitive tasks within business processes, while supply chain automation enhances the efficiency of logistics, inventory, and procurement systems. Proper differentiation ensures targeted technology investments that increase productivity and reduce operational costs. Manufacturers leveraging RPA can streamline administrative tasks, whereas supply chain automation supports real-time tracking and demand forecasting. This distinction enables precise allocation of resources, driving significant improvements in both internal operations and external supply chain management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Supply Chain Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automating repetitive, rule-based tasks across business processes. | Automation of logistics, inventory, and production workflows in the supply chain. |
| Primary Use Case | Back-office tasks like data entry, order processing, and invoice handling. | Real-time inventory management, demand forecasting, and warehouse operations. |
| Technology | AI-powered bots, machine learning, and workflow automation tools. | IoT devices, robotics, ERP integration, and advanced analytics. |
| Benefits | Reduced manual errors, cost savings, faster processing times. | Improved supply chain visibility, enhanced efficiency, reduced lead times. |
| Industries | Finance, HR, manufacturing, healthcare. | Manufacturing, retail, logistics, distribution. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate, focuses on software integration. | High, involves hardware, software, and process redesign. |
| Impact on Workforce | Automates repetitive tasks, enables employee redeployment. | Reduces manual labor, requires upskilling for technology management. |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in streamlining repetitive, rule-based tasks within manufacturing operations, such as inventory management and quality control, enhancing accuracy and reducing labor costs. Supply Chain Automation optimizes end-to-end supply chain activities including procurement, logistics, and demand forecasting, leading to improved efficiency and faster response times to market changes. Choosing between RPA and Supply Chain Automation depends on whether the goal is to enhance internal operational workflows or to improve the broader supply network integration and agility.
Connection
Robotic process automation (RPA) enhances supply chain automation by streamlining repetitive tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking, thereby increasing accuracy and efficiency. Integration of RPA with supply chain management systems enables real-time data analysis and faster decision-making, reducing operational costs and lead times. This connectivity promotes seamless collaboration across manufacturing stages, improving overall productivity and responsiveness to market demand.
Key Terms
Logistics Optimization
Supply chain automation integrates advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and machine learning to streamline procurement, inventory management, and distribution processes, enabling real-time visibility and demand forecasting. Robotic Process Automation (RPA), on the other hand, focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks like order processing, invoice handling, and shipment scheduling, reducing manual errors and operational costs. Explore how combining supply chain automation and RPA drives logistics optimization by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in your operations.
Workflow Integration
Supply chain automation integrates advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and machine learning to streamline logistics, inventory management, and demand forecasting, enhancing overall operational efficiency. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) specializes in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks within workflows, improving accuracy and speed in processes like order processing and invoicing. Explore how strategic workflow integration of both supply chain automation and RPA can transform business operations and competitiveness.
Digital Twin
Supply chain automation leverages digital twin technology to create real-time, virtual replicas of supply chain processes, enabling predictive analytics and proactive decision-making. Robotic process automation (RPA) automates repetitive tasks but lacks the dynamic modeling capabilities inherent in digital twins that simulate complex supply chain scenarios. Explore how integrating digital twins with supply chain automation can revolutionize operational efficiency and resilience.
Source and External Links
Procurement 101: Supply Chain Automation - How it works and why ... - Supply chain automation uses AI, robotics, and IoT technologies to automate decision-making and processes like predictive analytics, inventory optimization, and material transport, enhancing efficiency and 24/7 productivity.
What is Supply Chain Automation? - IBM - Supply chain automation employs AI, machine learning, RPA, and IoT to automate tasks with minimal human intervention, helping businesses manage disruptions, improve efficiency, and complement rather than replace human workers.
Supply Chain Automation: Benefits & Strategies for 2025 - ShipBob - Key supply chain processes like back-office operations and transportation can be automated using predictive analytics and route optimization, improving accuracy, reducing costs, and enhancing real-time visibility of goods movement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com