Lattice structure design enhances lightweight manufacturing by using periodic cellular configurations to achieve high strength-to-weight ratios and better energy absorption. Topology optimized structure design employs computational algorithms to distribute material efficiently within a given space, maximizing performance while minimizing weight and material usage. Explore the differences and advantages of these advanced design methodologies in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
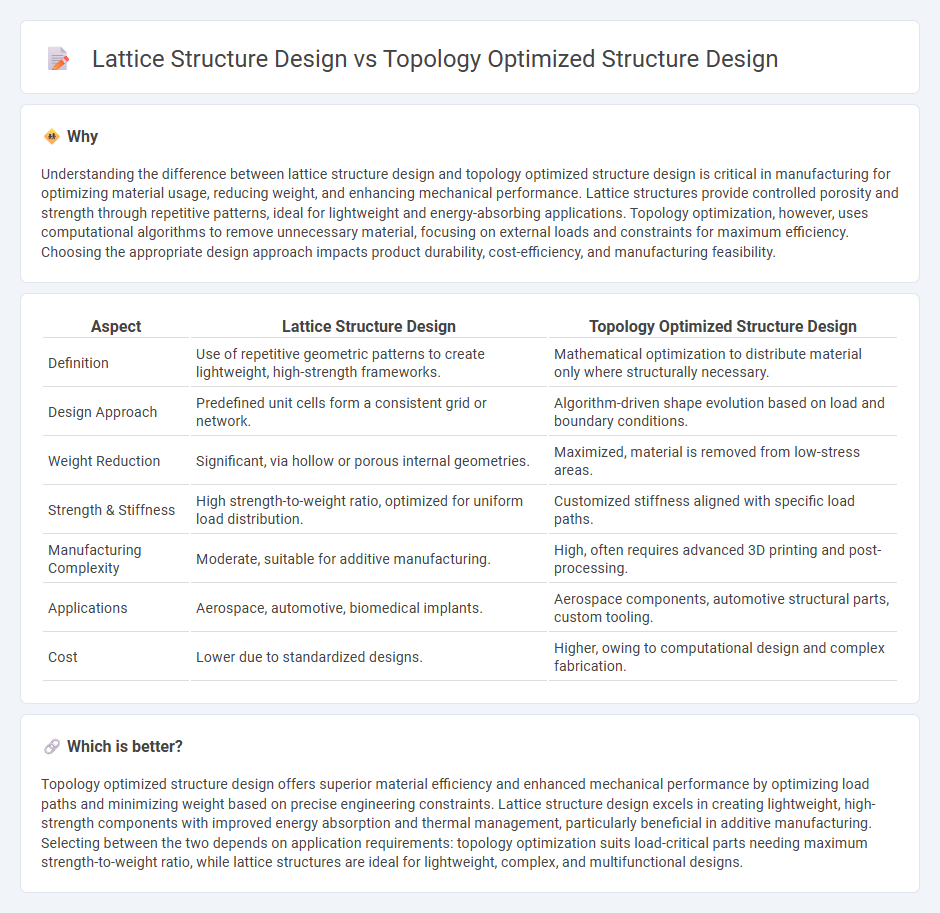
Understanding the difference between lattice structure design and topology optimized structure design is critical in manufacturing for optimizing material usage, reducing weight, and enhancing mechanical performance. Lattice structures provide controlled porosity and strength through repetitive patterns, ideal for lightweight and energy-absorbing applications. Topology optimization, however, uses computational algorithms to remove unnecessary material, focusing on external loads and constraints for maximum efficiency. Choosing the appropriate design approach impacts product durability, cost-efficiency, and manufacturing feasibility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lattice Structure Design | Topology Optimized Structure Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of repetitive geometric patterns to create lightweight, high-strength frameworks. | Mathematical optimization to distribute material only where structurally necessary. |
| Design Approach | Predefined unit cells form a consistent grid or network. | Algorithm-driven shape evolution based on load and boundary conditions. |
| Weight Reduction | Significant, via hollow or porous internal geometries. | Maximized, material is removed from low-stress areas. |
| Strength & Stiffness | High strength-to-weight ratio, optimized for uniform load distribution. | Customized stiffness aligned with specific load paths. |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Moderate, suitable for additive manufacturing. | High, often requires advanced 3D printing and post-processing. |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, biomedical implants. | Aerospace components, automotive structural parts, custom tooling. |
| Cost | Lower due to standardized designs. | Higher, owing to computational design and complex fabrication. |
Which is better?
Topology optimized structure design offers superior material efficiency and enhanced mechanical performance by optimizing load paths and minimizing weight based on precise engineering constraints. Lattice structure design excels in creating lightweight, high-strength components with improved energy absorption and thermal management, particularly beneficial in additive manufacturing. Selecting between the two depends on application requirements: topology optimization suits load-critical parts needing maximum strength-to-weight ratio, while lattice structures are ideal for lightweight, complex, and multifunctional designs.
Connection
Lattice structure design and topology optimized structure design are connected through their shared goal of enhancing material efficiency and mechanical performance in manufacturing by optimizing internal geometries. Lattice structures leverage periodic, lightweight frameworks to reduce weight while maintaining strength, which complements topology optimization that determines the optimal material distribution within a given design space. Integrating these approaches enables manufacturers to produce components with tailored stiffness, improved load-bearing capacity, and reduced material consumption, advancing additive manufacturing and lightweight engineering.
Key Terms
Material Distribution
Topology optimized structure design strategically distributes material within a specified design space to maximize performance while minimizing weight, focusing on optimal load paths and stress concentration areas. Lattice structure design employs repetitive, interconnected unit cells to create lightweight, high-strength materials with controlled porosity, often enhancing thermal and mechanical properties through geometrical patterns. Explore the advantages and applications of each method to determine the best approach for your material distribution needs.
Structural Efficiency
Topology optimized structure design maximizes structural efficiency by distributing material only where necessary to withstand loads, resulting in lightweight yet robust forms. Lattice structure design enhances strength-to-weight ratios through repetitive geometric patterns, improving mechanical performance and energy absorption. Explore how combining these methods can revolutionize material usage and structural performance in advanced engineering.
Geometric Complexity
Topology optimized structure design excels in reducing material usage by optimizing load paths, resulting in organic, highly complex geometries that enhance structural performance. Lattice structure design emphasizes repeating unit cells with controlled porosity, offering tailored mechanical properties and manufacturability, especially in additive manufacturing. Explore further insights into their geometric complexities and application-specific advantages to determine the ideal approach for your engineering needs.
Source and External Links
Topology Optimization 101: How to Use Algorithmic Models to ... - Topology optimization is a shape optimization method that uses algorithmic models to determine the optimal material layout within a user-defined space for a given set of loads, constraints, and objectives, typically using the finite element method to iterate and remove unnecessary material.
What is Topology Optimization? - Autodesk - Topology optimization is a mathematical technique that alters internal material distribution within a given design space by iteratively removing non-essential material to maximize performance criteria--such as strength or stiffness--while minimizing weight and material usage, resulting in complex, often non-intuitive structures.
Topology optimization - Wikipedia - Topology optimization is a free-form mathematical approach that optimizes material distribution for a given set of loads, boundary conditions, and constraints to achieve the best possible performance, commonly applied in concept design stages and increasingly used alongside additive manufacturing despite challenges in manufacturability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com