Hyperautomation integrates advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) to enhance manufacturing efficiency by automating complex workflows beyond repetitive tasks. Robotic process automation focuses on automating rule-based, repetitive processes to reduce human error and increase speed in manufacturing operations. Explore how these automation innovations revolutionize production lines and drive operational excellence.
Why it is important
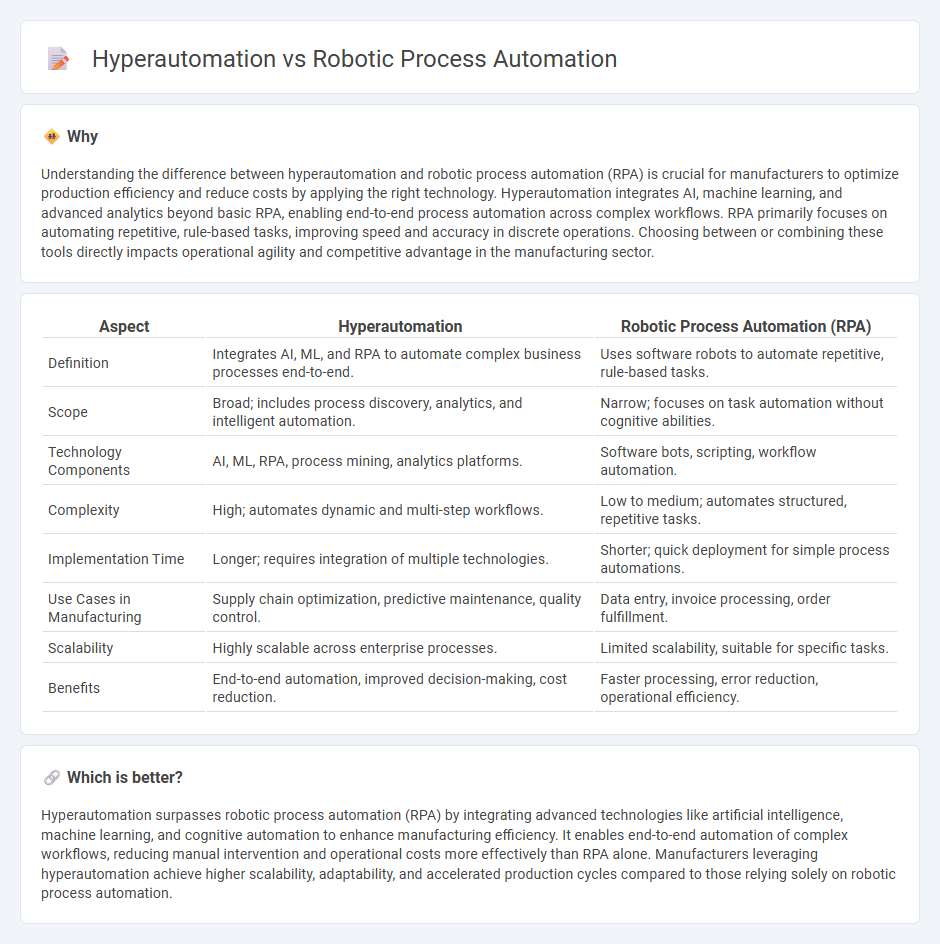
Understanding the difference between hyperautomation and robotic process automation (RPA) is crucial for manufacturers to optimize production efficiency and reduce costs by applying the right technology. Hyperautomation integrates AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics beyond basic RPA, enabling end-to-end process automation across complex workflows. RPA primarily focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, improving speed and accuracy in discrete operations. Choosing between or combining these tools directly impacts operational agility and competitive advantage in the manufacturing sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Hyperautomation | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates AI, ML, and RPA to automate complex business processes end-to-end. | Uses software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. |
| Scope | Broad; includes process discovery, analytics, and intelligent automation. | Narrow; focuses on task automation without cognitive abilities. |
| Technology Components | AI, ML, RPA, process mining, analytics platforms. | Software bots, scripting, workflow automation. |
| Complexity | High; automates dynamic and multi-step workflows. | Low to medium; automates structured, repetitive tasks. |
| Implementation Time | Longer; requires integration of multiple technologies. | Shorter; quick deployment for simple process automations. |
| Use Cases in Manufacturing | Supply chain optimization, predictive maintenance, quality control. | Data entry, invoice processing, order fulfillment. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable across enterprise processes. | Limited scalability, suitable for specific tasks. |
| Benefits | End-to-end automation, improved decision-making, cost reduction. | Faster processing, error reduction, operational efficiency. |
Which is better?
Hyperautomation surpasses robotic process automation (RPA) by integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cognitive automation to enhance manufacturing efficiency. It enables end-to-end automation of complex workflows, reducing manual intervention and operational costs more effectively than RPA alone. Manufacturers leveraging hyperautomation achieve higher scalability, adaptability, and accelerated production cycles compared to those relying solely on robotic process automation.
Connection
Hyperautomation integrates robotic process automation (RPA) with advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance manufacturing workflows by automating complex, repetitive tasks. RPA serves as the foundational layer, automating rule-based processes, while hyperautomation extends this capability by orchestrating multiple tools and systems for end-to-end process optimization. Together, they drive increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, and improved production scalability in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Robotics
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves using software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, streamlining workflows primarily through task-specific robots. Hyperautomation expands on RPA by integrating advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and process mining to automate complex business processes beyond simple tasks. Explore the evolving landscape of robotics to understand how these technologies transform automation efficacy and business productivity.
Artificial Intelligence
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based tasks, while Hyperautomation combines RPA with advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing to enable end-to-end process automation. AI enhances Hyperautomation by enabling cognitive capabilities like decision-making, predictive analytics, and adapting to unstructured data. Explore how integrating AI in Hyperautomation revolutionizes business efficiency and scalability.
Process Orchestration
Process orchestration in robotic process automation (RPA) focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks within individual workflows to improve efficiency and accuracy. Hyperautomation extends beyond RPA by integrating advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and process mining, enabling comprehensive process orchestration across complex business functions. Explore the differences to optimize your automation strategy effectively.
Source and External Links
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? - IBM - Robotic Process Automation is a technology using software robots to automate routine human tasks across various applications, combining rule-based software with AI capabilities to improve efficiency and digital transformation.
What is Robotic Process Automation - RPA Software - UiPath - RPA automates workflows by emulating human interaction with digital systems, reducing costs, human error, and freeing employees from mundane tasks to enhance productivity and customer experience.
RPA - Robotic Process Automation Software & Services - Xerox - RPA uses bots to automate repetitive, rule-based business processes such as document management, invoice processing, customer service, HR onboarding, and supply chain operations to improve efficiency and reduce errors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com