Industrial edge computing processes data locally on factory floors, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making capabilities essential for automation and predictive maintenance. Centralized computing relies on remote data centers, offering substantial processing power but often facing delays and bandwidth limitations. Discover how choosing between these computing models can optimize manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between industrial edge computing and centralized computing is crucial for optimizing manufacturing operations, as edge computing processes data locally on machines, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making. Centralized computing relies on remote data centers, which can introduce delays and increase bandwidth usage. Industrial edge computing enhances predictive maintenance by instantly analyzing sensor data, minimizing downtime and improving productivity. Choosing the right computing architecture directly impacts operational efficiency, cost management, and system reliability in manufacturing environments.
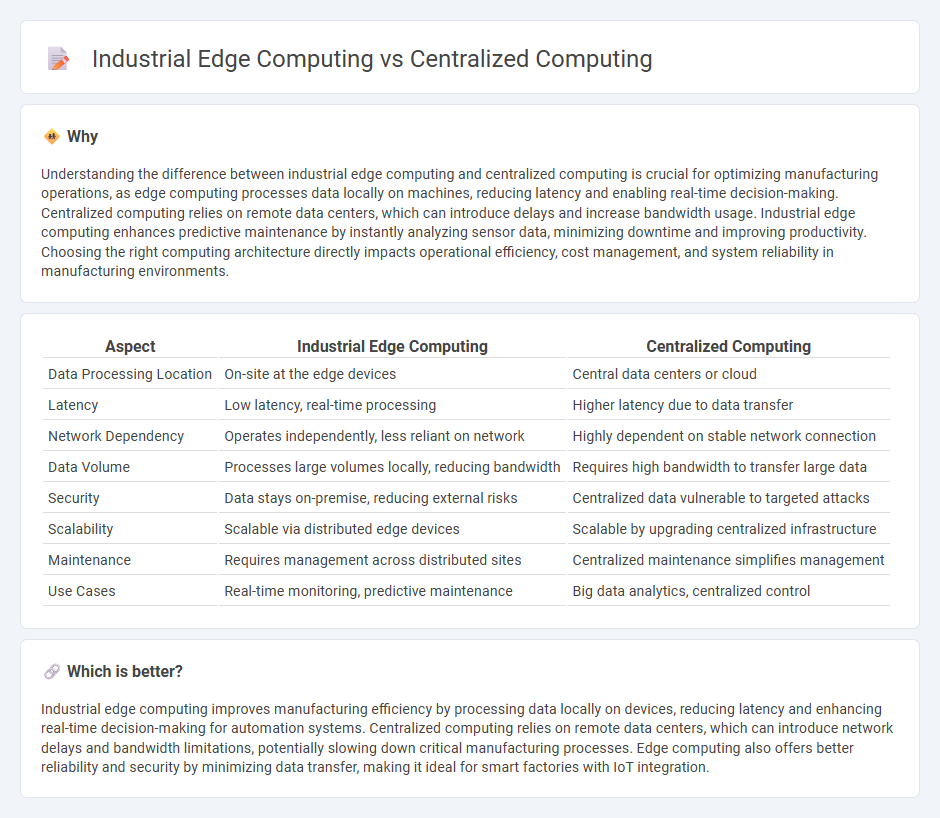
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Edge Computing | Centralized Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing Location | On-site at the edge devices | Central data centers or cloud |
| Latency | Low latency, real-time processing | Higher latency due to data transfer |
| Network Dependency | Operates independently, less reliant on network | Highly dependent on stable network connection |
| Data Volume | Processes large volumes locally, reducing bandwidth | Requires high bandwidth to transfer large data |
| Security | Data stays on-premise, reducing external risks | Centralized data vulnerable to targeted attacks |
| Scalability | Scalable via distributed edge devices | Scalable by upgrading centralized infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Requires management across distributed sites | Centralized maintenance simplifies management |
| Use Cases | Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance | Big data analytics, centralized control |
Which is better?
Industrial edge computing improves manufacturing efficiency by processing data locally on devices, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making for automation systems. Centralized computing relies on remote data centers, which can introduce network delays and bandwidth limitations, potentially slowing down critical manufacturing processes. Edge computing also offers better reliability and security by minimizing data transfer, making it ideal for smart factories with IoT integration.
Connection
Industrial edge computing processes data locally on manufacturing floors, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making for equipment monitoring and quality control. Centralized computing complements this by aggregating and analyzing large volumes of data collected from multiple edge devices to optimize production workflows and predictive maintenance strategies. The integration of both architectures ensures efficient data flow between local operations and enterprise-level analytics, enhancing overall manufacturing productivity and operational resilience.
Key Terms
Latency
Centralized computing relies on remote data centers, often causing increased latency due to longer data transmission distances, which can adversely impact real-time industrial applications. Industrial edge computing processes data locally at or near the source, significantly reducing latency and enhancing responsiveness for critical operations like predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring. Explore the advantages of industrial edge computing to optimize latency-sensitive processes in your industry.
Data Sovereignty
Centralized computing often raises data sovereignty concerns due to the storage and processing of sensitive industrial data in distant data centers governed by varying jurisdictional laws. Industrial edge computing addresses these issues by processing data locally on-site, ensuring compliance with regional data regulations and minimizing latency for real-time decision-making. Explore deeper insights on how edge computing protects your industrial data sovereignty and operational efficiency.
Real-time Processing
Centralized computing relies on remote data centers for processing, which can introduce latency hindering real-time industrial operations requiring immediate decision-making. Industrial edge computing processes data locally at or near the source, significantly reducing latency and enabling faster, more reliable real-time responses essential for automation and control systems. Explore how industrial edge computing transforms real-time processing by optimizing performance and efficiency in complex industrial environments.
Source and External Links
What is Centralized Computing? - Centralized computing is a system where all processing and data storage occur on a single central device or system, with clients connected to it and relying on it for computing needs, typically following a client-server architecture.
Centralized computing - Centralized computing involves performing all computing tasks at a central location with users accessing it via terminals, offering advantages like improved security and data accessibility but risking total system downtime if the central computer fails.
Centralized computing definition - Glossary - Centralized computing consolidates resources and data into one central system, simplifying maintenance and backups, commonly used in scenarios like government registries, mainframe banking, cloud storage, university systems, and hospital databases.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com