The Industrial Internet focuses on integrating advanced analytics, machine learning, and sensor data into large-scale industrial systems to optimize manufacturing processes and equipment performance. IoT (Internet of Things) encompasses a broader range of connected consumer and industrial devices that gather and exchange data via the internet for improved automation and convenience. Explore the distinctions to understand how each technology drives innovation in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Industrial Internet and IoT is crucial in manufacturing because the Industrial Internet focuses on integrating advanced analytics, machine learning, and industrial equipment for optimized production processes. IoT broadly connects everyday devices for data exchange, while Industrial Internet specifically targets industrial systems, ensuring higher reliability and security standards essential for manufacturing environments. Knowing this distinction helps manufacturers implement appropriate technologies that improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and enable predictive maintenance. Accurate application of Industrial Internet solutions drives competitive advantage through smarter, data-driven manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Internet | IoT (Internet of Things) |
|---|---|---|
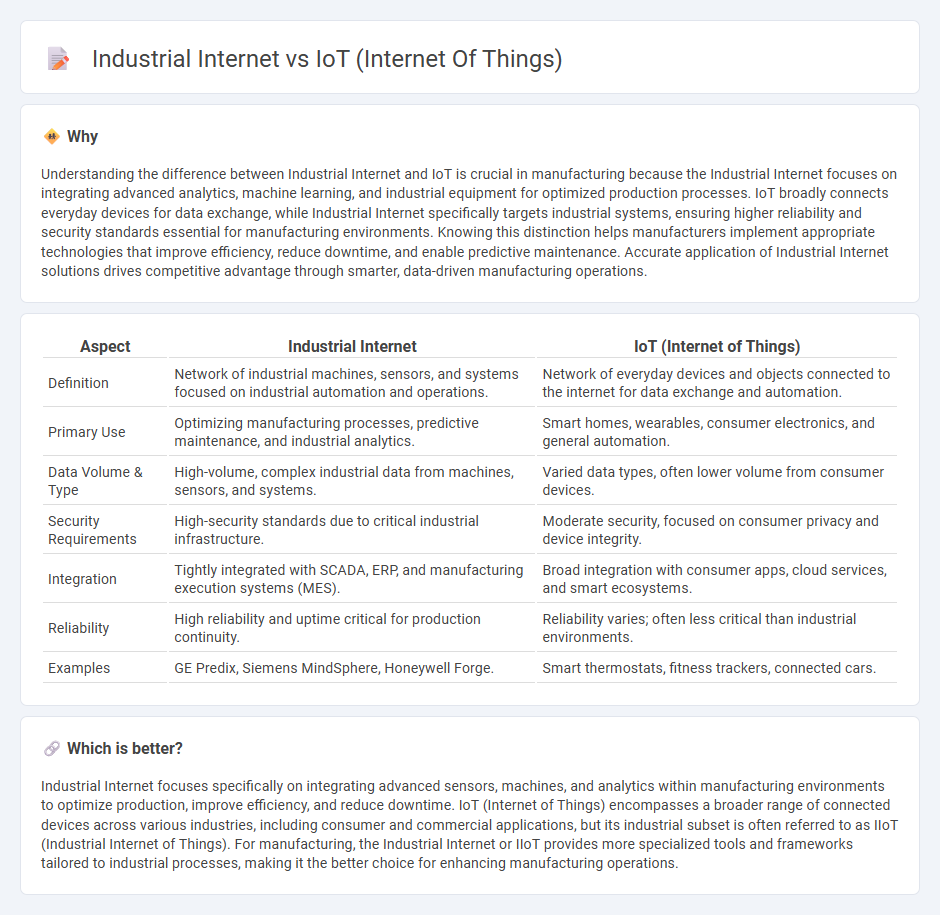
| Definition | Network of industrial machines, sensors, and systems focused on industrial automation and operations. | Network of everyday devices and objects connected to the internet for data exchange and automation. |
| Primary Use | Optimizing manufacturing processes, predictive maintenance, and industrial analytics. | Smart homes, wearables, consumer electronics, and general automation. |
| Data Volume & Type | High-volume, complex industrial data from machines, sensors, and systems. | Varied data types, often lower volume from consumer devices. |
| Security Requirements | High-security standards due to critical industrial infrastructure. | Moderate security, focused on consumer privacy and device integrity. |
| Integration | Tightly integrated with SCADA, ERP, and manufacturing execution systems (MES). | Broad integration with consumer apps, cloud services, and smart ecosystems. |
| Reliability | High reliability and uptime critical for production continuity. | Reliability varies; often less critical than industrial environments. |
| Examples | GE Predix, Siemens MindSphere, Honeywell Forge. | Smart thermostats, fitness trackers, connected cars. |
Which is better?
Industrial Internet focuses specifically on integrating advanced sensors, machines, and analytics within manufacturing environments to optimize production, improve efficiency, and reduce downtime. IoT (Internet of Things) encompasses a broader range of connected devices across various industries, including consumer and commercial applications, but its industrial subset is often referred to as IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things). For manufacturing, the Industrial Internet or IIoT provides more specialized tools and frameworks tailored to industrial processes, making it the better choice for enhancing manufacturing operations.
Connection
The Industrial Internet and IoT (Internet of Things) are interconnected as IoT devices collect real-time data from manufacturing equipment, enabling advanced analytics and automation on the Industrial Internet platform. This integration supports predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and enhances operational efficiency through seamless communication between machines and control systems. Manufacturing industries leverage these technologies to optimize production processes and improve supply chain management with data-driven insights.
Key Terms
Connectivity
The Internet of Things (IoT) encompasses a broad range of connected devices across consumer and commercial sectors, prioritizing seamless wireless connectivity and data exchange through protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee. The Industrial Internet, or Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), specifically targets industrial applications with a focus on robust, real-time connectivity using protocols such as MQTT, OPC-UA, and industrial Ethernet to ensure reliable machine-to-machine communication. Explore more about how these connectivity approaches transform operational efficiency and innovation in various industries.
Edge Computing
Edge computing in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) enhances real-time data processing by deploying computing resources closer to manufacturing equipment and sensors, reducing latency and improving operational efficiency. Unlike general IoT applications that often rely on centralized cloud servers, IIoT edge computing supports critical industrial processes requiring immediate analytics and decision-making on-site. Explore how edge computing transforms industrial automation and smart factories for deeper insights and optimized performance.
Data Integration
Data integration in IoT involves connecting diverse devices and systems to enable seamless data exchange and real-time analytics across consumer and enterprise environments. The Industrial Internet prioritizes robust, secure data integration frameworks that support mission-critical operations, predictive maintenance, and optimized manufacturing processes within industrial settings. Explore how advanced data integration techniques differentiate these domains and drive innovation in their respective ecosystems.
Source and External Links
What Is the Internet of Things? - The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects embedded with sensors and software that connect and exchange data over the internet, enabling seamless communication between people, processes, and things, including applications in Industry 4.0.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? - IoT refers to interconnected devices with sensors and network connectivity that collect and share data, ranging from smart home gadgets to complex industrial machinery, transforming industries like healthcare and manufacturing.
What is IoT? - Internet of Things Explained - IoT is the collective network of connected devices and communications technology that allows everyday objects to gather data and interact intelligently via the cloud, powered by advancements in computing chips and telecommunications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com