Lights-out manufacturing leverages fully automated, unmanned production processes that enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs by operating continuously without human intervention. Discrete manufacturing involves producing distinct items such as automobiles or electronics through complex assembly lines requiring skilled labor and manual oversight. Explore how these manufacturing methods transform industry practices and optimize production efficiency.
Why it is important
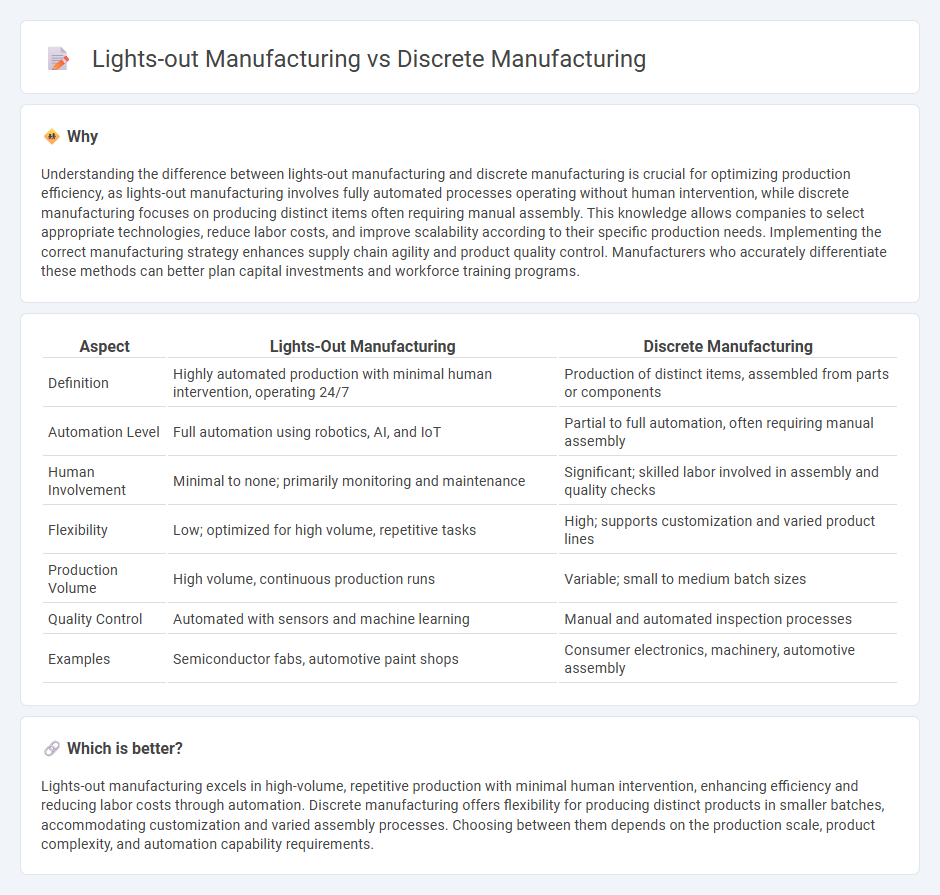
Understanding the difference between lights-out manufacturing and discrete manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency, as lights-out manufacturing involves fully automated processes operating without human intervention, while discrete manufacturing focuses on producing distinct items often requiring manual assembly. This knowledge allows companies to select appropriate technologies, reduce labor costs, and improve scalability according to their specific production needs. Implementing the correct manufacturing strategy enhances supply chain agility and product quality control. Manufacturers who accurately differentiate these methods can better plan capital investments and workforce training programs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights-Out Manufacturing | Discrete Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Highly automated production with minimal human intervention, operating 24/7 | Production of distinct items, assembled from parts or components |
| Automation Level | Full automation using robotics, AI, and IoT | Partial to full automation, often requiring manual assembly |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none; primarily monitoring and maintenance | Significant; skilled labor involved in assembly and quality checks |
| Flexibility | Low; optimized for high volume, repetitive tasks | High; supports customization and varied product lines |
| Production Volume | High volume, continuous production runs | Variable; small to medium batch sizes |
| Quality Control | Automated with sensors and machine learning | Manual and automated inspection processes |
| Examples | Semiconductor fabs, automotive paint shops | Consumer electronics, machinery, automotive assembly |
Which is better?
Lights-out manufacturing excels in high-volume, repetitive production with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs through automation. Discrete manufacturing offers flexibility for producing distinct products in smaller batches, accommodating customization and varied assembly processes. Choosing between them depends on the production scale, product complexity, and automation capability requirements.
Connection
Lights-out manufacturing integrates seamlessly with discrete manufacturing by enabling fully automated production processes without human intervention. This connection enhances efficiency, precision, and scalability in manufacturing discrete units such as automotive parts, electronics, and machinery components. Implementing lights-out strategies significantly reduces labor costs and downtime while improving quality control through constant machine monitoring and adaptive feedback systems.
Key Terms
Production Line
Discrete manufacturing involves assembling distinct products through sequential production lines with human oversight and manual interventions, while lights-out manufacturing operates fully automated production lines with minimal or no human presence, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Production lines in discrete manufacturing require quality checks, human decision-making, and flexibility to handle product variations, whereas lights-out production lines emphasize consistency, precision, and continuous operation enabled by robotics and AI-driven systems. Explore deeper insights into optimizing production line strategies for both manufacturing approaches.
Automation
Discrete manufacturing involves assembling distinct products such as automobiles, electronics, or appliances, relying heavily on skilled labor and flexible production lines. Lights-out manufacturing emphasizes fully automated processes with minimal or no human intervention, using advanced robotics, AI, and IoT technologies to achieve higher efficiency and 24/7 operation. Discover how automation transforms these production models to boost productivity and reduce costs.
Human Intervention
Discrete manufacturing involves significant human intervention for tasks like assembly, quality control, and customization, relying on skilled labor to ensure product precision. Lights-out manufacturing minimizes or eliminates human involvement by using fully automated systems and robotics to operate continuously without manual oversight. Explore how these approaches impact efficiency and labor dynamics in modern production environments.
Source and External Links
Discrete manufacturing - Wikipedia - Discrete manufacturing is the production of distinct, countable products like automobiles, furniture, and smartphones, often characterized by separate unit production with variable complexity and input materials.
Discrete vs. Process Manufacturing - How Do They Differ? - MRPeasy - Discrete manufacturing produces goods assembled from individual components and sub-assemblies along production lines, exemplified by car manufacturers creating finished vehicles from thousands of parts.
Discrete Manufacturing - Oracle Help Center - Discrete manufacturing involves producing specific quantities of single items using work orders and routings, suitable for make-to-stock or make-to-order environments, with examples including cars, furniture, and electronics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com