Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive, rule-based tasks by using software robots to enhance operational efficiency in manufacturing workflows. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) improve material handling and logistics by navigating dynamic factory environments independently using sensors and AI. Explore how integrating RPA and AMRs can revolutionize manufacturing productivity and flexibility by clicking here.
Why it is important
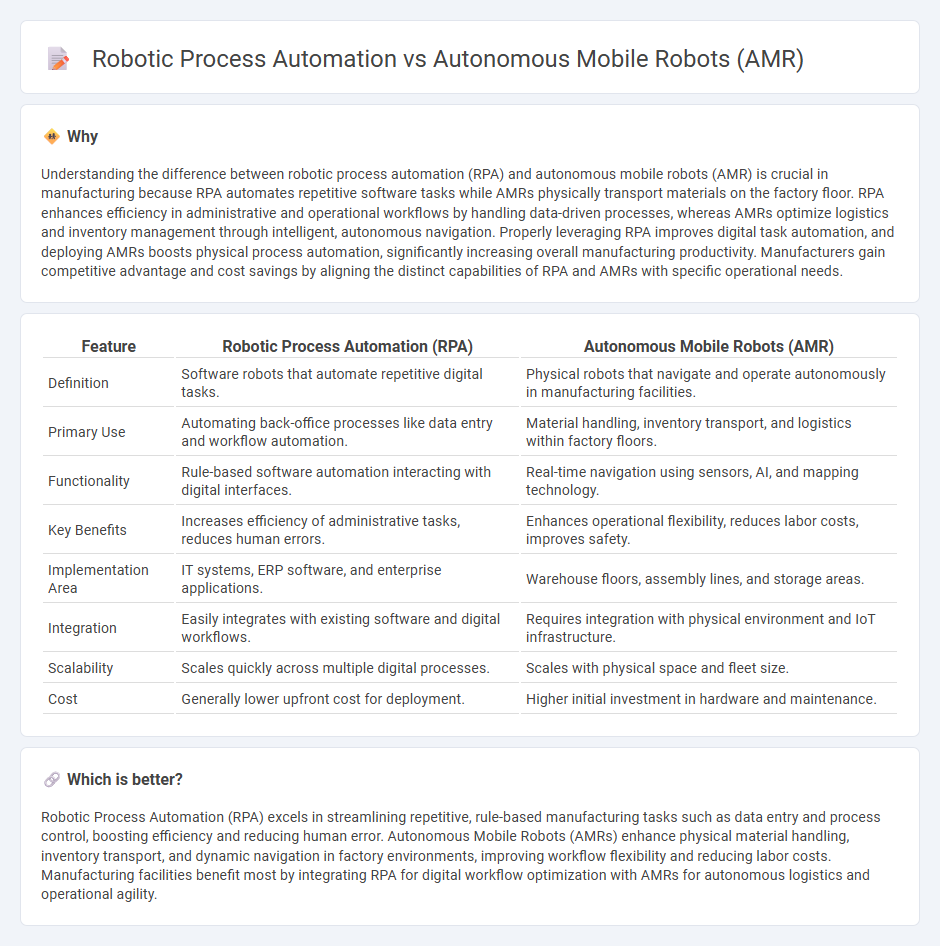
Understanding the difference between robotic process automation (RPA) and autonomous mobile robots (AMR) is crucial in manufacturing because RPA automates repetitive software tasks while AMRs physically transport materials on the factory floor. RPA enhances efficiency in administrative and operational workflows by handling data-driven processes, whereas AMRs optimize logistics and inventory management through intelligent, autonomous navigation. Properly leveraging RPA improves digital task automation, and deploying AMRs boosts physical process automation, significantly increasing overall manufacturing productivity. Manufacturers gain competitive advantage and cost savings by aligning the distinct capabilities of RPA and AMRs with specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots that automate repetitive digital tasks. | Physical robots that navigate and operate autonomously in manufacturing facilities. |
| Primary Use | Automating back-office processes like data entry and workflow automation. | Material handling, inventory transport, and logistics within factory floors. |
| Functionality | Rule-based software automation interacting with digital interfaces. | Real-time navigation using sensors, AI, and mapping technology. |
| Key Benefits | Increases efficiency of administrative tasks, reduces human errors. | Enhances operational flexibility, reduces labor costs, improves safety. |
| Implementation Area | IT systems, ERP software, and enterprise applications. | Warehouse floors, assembly lines, and storage areas. |
| Integration | Easily integrates with existing software and digital workflows. | Requires integration with physical environment and IoT infrastructure. |
| Scalability | Scales quickly across multiple digital processes. | Scales with physical space and fleet size. |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost for deployment. | Higher initial investment in hardware and maintenance. |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in streamlining repetitive, rule-based manufacturing tasks such as data entry and process control, boosting efficiency and reducing human error. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) enhance physical material handling, inventory transport, and dynamic navigation in factory environments, improving workflow flexibility and reducing labor costs. Manufacturing facilities benefit most by integrating RPA for digital workflow optimization with AMRs for autonomous logistics and operational agility.
Connection
Robotic process automation (RPA) streamlines manufacturing by automating repetitive digital tasks, while Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) handle physical material transport on the factory floor, enhancing operational efficiency. Integration of RPA with AMR systems enables seamless coordination between digital workflows and physical logistics, resulting in reduced cycle times and minimized human error. Together, they optimize production processes by synchronizing data-driven decision-making with dynamic, autonomous material handling.
Key Terms
Navigation (AMR)
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) use advanced sensor fusion, machine learning, and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) to navigate complex environments with real-time obstacle avoidance and dynamic path planning. Robotic process automation (RPA) focuses on task automation in digital workflows without physical navigation capabilities, relying on software algorithms to mimic human interactions with applications. Explore the latest advancements in AMR navigation technologies to understand their impact on operational efficiency.
Software Bots (RPA)
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are physical machines designed to navigate and perform tasks in dynamic environments using sensors and AI, while robotic process automation (RPA) involves software bots that execute repetitive, rule-based digital tasks within business applications. AMRs optimize warehouse logistics and manufacturing operations, enhancing efficiency through real-world interaction, whereas RPA streamlines back-office processes like data entry, invoice processing, and customer service automation. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how integrating AMR and RPA technologies can transform operational workflows.
Workflow Automation
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) enhance workflow automation by physically navigating environments to transport materials, improving operational efficiency in logistics and manufacturing sectors. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) optimizes digital workflows by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks within software applications, reducing human error and increasing processing speed. Explore detailed comparisons and use case benefits to understand how AMRs and RPA can be integrated for comprehensive workflow automation solutions.
Source and External Links
AMR vs AGV: Key Differences Explained - Mobile Industrial Robots - Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are intelligent, agile, and flexible robots using advanced sensors like 3D cameras and LiDAR, capable of dynamic navigation and obstacle avoidance in changing environments, unlike Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) that follow fixed paths.
Automated & Autonomous Mobile Robots | Robotnik(r) - Robotnik's AMRs autonomously perform tasks such as inspection, logistics, and quality control, adapting quickly to new environments using SLAM technology, providing versatile, scalable solutions across industries without needing complex reconfigurations.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) - ABB AMR/AGV robots - ABB's AMRs are sophisticated transport robots designed for diverse industrial sectors, featuring AI-powered navigation, high payload capacities, and flexible applications including production line automation and logistics, enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com