Condition-based monitoring leverages real-time data from sensors to predict equipment failures, optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing downtime. Time-based maintenance relies on predetermined intervals regardless of actual equipment condition, potentially leading to unnecessary servicing or unexpected breakdowns. Explore the advantages of each approach to enhance your manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
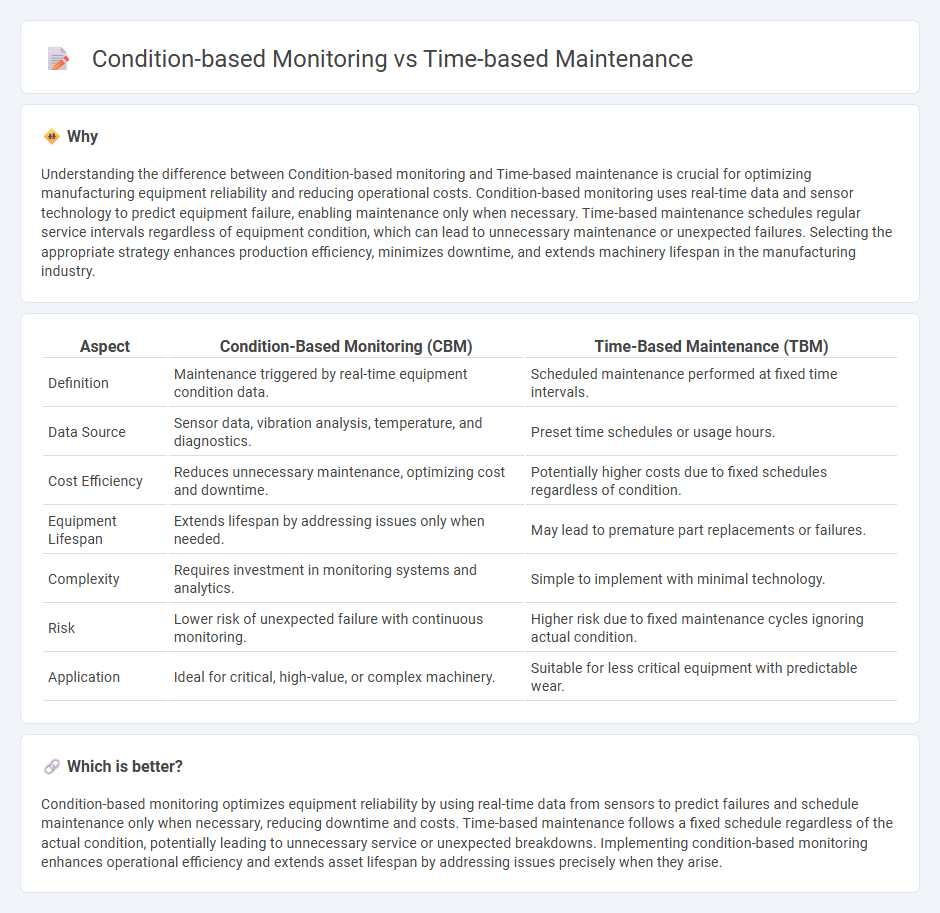
Understanding the difference between Condition-based monitoring and Time-based maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing equipment reliability and reducing operational costs. Condition-based monitoring uses real-time data and sensor technology to predict equipment failure, enabling maintenance only when necessary. Time-based maintenance schedules regular service intervals regardless of equipment condition, which can lead to unnecessary maintenance or unexpected failures. Selecting the appropriate strategy enhances production efficiency, minimizes downtime, and extends machinery lifespan in the manufacturing industry.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM) | Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance triggered by real-time equipment condition data. | Scheduled maintenance performed at fixed time intervals. |
| Data Source | Sensor data, vibration analysis, temperature, and diagnostics. | Preset time schedules or usage hours. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces unnecessary maintenance, optimizing cost and downtime. | Potentially higher costs due to fixed schedules regardless of condition. |
| Equipment Lifespan | Extends lifespan by addressing issues only when needed. | May lead to premature part replacements or failures. |
| Complexity | Requires investment in monitoring systems and analytics. | Simple to implement with minimal technology. |
| Risk | Lower risk of unexpected failure with continuous monitoring. | Higher risk due to fixed maintenance cycles ignoring actual condition. |
| Application | Ideal for critical, high-value, or complex machinery. | Suitable for less critical equipment with predictable wear. |
Which is better?
Condition-based monitoring optimizes equipment reliability by using real-time data from sensors to predict failures and schedule maintenance only when necessary, reducing downtime and costs. Time-based maintenance follows a fixed schedule regardless of the actual condition, potentially leading to unnecessary service or unexpected breakdowns. Implementing condition-based monitoring enhances operational efficiency and extends asset lifespan by addressing issues precisely when they arise.
Connection
Condition-based monitoring and time-based maintenance are interconnected strategies in manufacturing maintenance that optimize equipment reliability and lifespan. Condition-based monitoring relies on real-time data from sensors to identify equipment wear and predict failures, triggering maintenance only when necessary. Time-based maintenance schedules routine servicing at fixed intervals, but integrating it with condition-based monitoring enhances maintenance precision by adjusting tasks based on actual equipment condition and operational data.
Key Terms
Preventive Maintenance
Time-based maintenance schedules servicing activities at fixed intervals regardless of equipment condition, optimizing routine preventive maintenance efforts. Condition-based monitoring uses real-time data from sensors to predict and prevent failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs through targeted interventions. Explore deeper insights on how integrating these strategies can enhance your preventive maintenance program.
Predictive Maintenance
Time-based maintenance schedules equipment servicing at fixed intervals, often leading to unnecessary repairs or unexpected failures due to its lack of real-time data integration. Condition-based monitoring leverages sensors and IoT technology to track actual equipment health, enabling predictive maintenance that minimizes downtime and extends asset lifespan through timely interventions. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits to optimize your maintenance strategy effectively.
Real-time Sensors
Time-based maintenance schedules equipment servicing at fixed intervals regardless of actual condition, often leading to unnecessary downtime and higher costs. Condition-based monitoring leverages real-time sensors analyzing vibration, temperature, and pressure data to detect anomalies and predict failures more accurately. Discover how integrating advanced real-time sensor technology can optimize maintenance strategies and boost asset reliability.
Source and External Links
The complete guide to Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) - Time-Based Maintenance is a proactive strategy where equipment is serviced at predetermined intervals regardless of condition, aimed at preventing unexpected breakdowns and extending equipment life with benefits like predictability, extended life, and compliance.
What is Time-Based Maintenance? Definition and Examples - Time-based maintenance involves routine tasks at fixed intervals regardless of equipment condition, offering advantages such as easy implementation, predictable scheduling, and low training requirements but can result in unnecessary maintenance if done too frequently.
What Is Time-Based Maintenance? A Guide for ... - LLumin CMMS - Time-Based Maintenance schedules maintenance based on estimated equipment lifespan and statistical failure models like the bathtub curve, assuming predictable lifespan phases to help prevent breakdowns and extend equipment life.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com