Remanufacturing involves completely rebuilding a product to meet original specifications using a combination of reused, repaired, and new parts, ensuring like-new performance and extended lifecycle. Repair focuses on fixing specific faults or damages to restore functionality without fully restoring the product to its original state. Explore the key differences and benefits of remanufacturing versus repair to optimize manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and repair is crucial in manufacturing because remanufacturing involves restoring products to like-new condition, ensuring longer lifecycle and consistent quality, while repair only fixes specific faults without guaranteeing full system restoration. This knowledge enables manufacturers to optimize costs, improve sustainability by reducing waste, and set accurate pricing strategies. It also helps in meeting regulatory standards and customer expectations for product reliability and performance. Manufacturers leveraging remanufacturing can enhance brand reputation by promoting eco-friendly practices and reducing carbon footprint.
Comparison Table
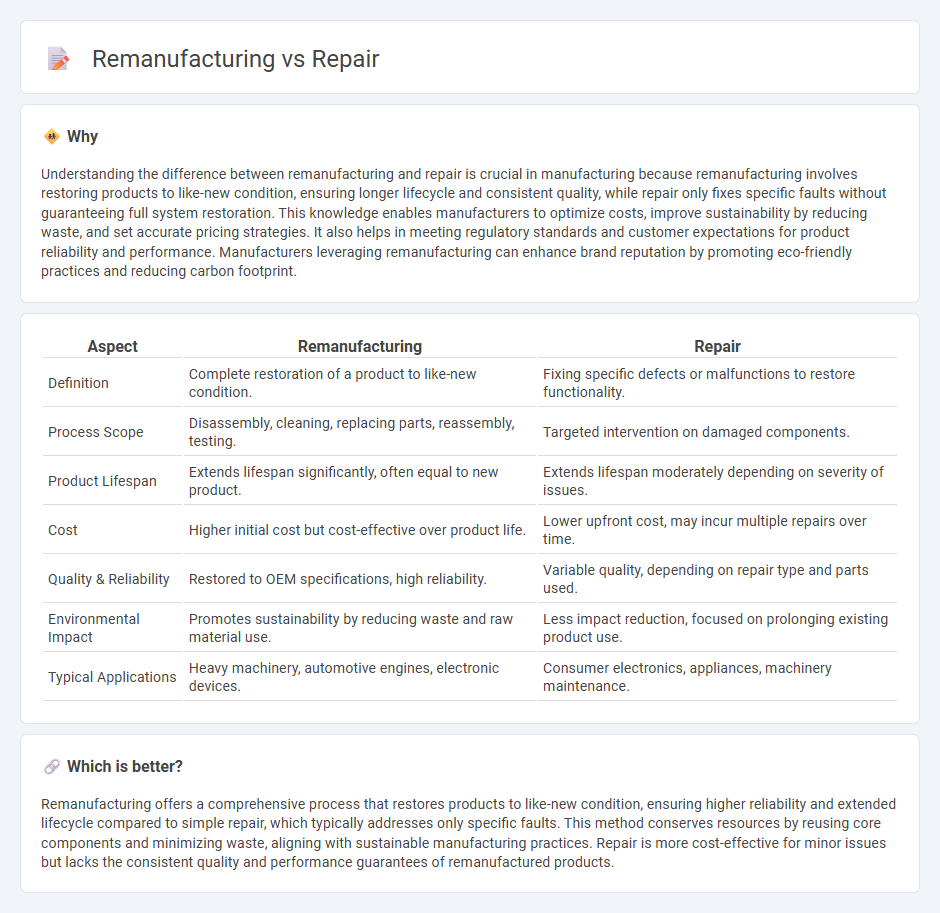
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete restoration of a product to like-new condition. | Fixing specific defects or malfunctions to restore functionality. |
| Process Scope | Disassembly, cleaning, replacing parts, reassembly, testing. | Targeted intervention on damaged components. |
| Product Lifespan | Extends lifespan significantly, often equal to new product. | Extends lifespan moderately depending on severity of issues. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but cost-effective over product life. | Lower upfront cost, may incur multiple repairs over time. |
| Quality & Reliability | Restored to OEM specifications, high reliability. | Variable quality, depending on repair type and parts used. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainability by reducing waste and raw material use. | Less impact reduction, focused on prolonging existing product use. |
| Typical Applications | Heavy machinery, automotive engines, electronic devices. | Consumer electronics, appliances, machinery maintenance. |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing offers a comprehensive process that restores products to like-new condition, ensuring higher reliability and extended lifecycle compared to simple repair, which typically addresses only specific faults. This method conserves resources by reusing core components and minimizing waste, aligning with sustainable manufacturing practices. Repair is more cost-effective for minor issues but lacks the consistent quality and performance guarantees of remanufactured products.
Connection
Remanufacturing and repair are interconnected processes that extend product life cycles by restoring used or defective products to like-new condition, reducing waste and conserving resources. Both practices rely on detailed inspections, component replacement, and quality testing to ensure performance and reliability comparable to new products. Integrating remanufacturing and repair within manufacturing operations supports sustainable production and drives cost efficiency by minimizing raw material consumption.
Key Terms
Restoration
Repair restores functionality by fixing specific parts or issues, often resulting in a shorter lifespan and limited warranty. Remanufacturing involves complete disassembly, cleaning, and replacement of worn components, producing a product equivalent to new in performance and durability. Explore more insights on how restoration methods impact product life cycle and environmental benefits.
Reconditioning
Reconditioning in repair involves restoring a product to its original working condition, often through cleaning, part replacement, and minor adjustments, whereas remanufacturing typically requires complete disassembly, inspection, and rebuilding to meet original factory specifications. Reconditioning extends the lifespan of equipment by addressing wear and tear without the extensive overhaul seen in remanufacturing, making it a cost-effective and sustainable maintenance option. Explore the detailed processes and benefits of reconditioning to understand its role in product lifecycle management.
Component Replacement
Repair involves fixing or replacing only the damaged parts of a component, aiming to restore its original function with minimal intervention. Remanufacturing entails a comprehensive process where parts are replaced or rebuilt to meet or exceed original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications, often resulting in a product that is like new. Explore more about how component replacement impacts cost, reliability, and sustainability in both repair and remanufacturing processes.
Source and External Links
REPAIR | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - To repair means to put something damaged or broken back into good condition or make it work again, such as repairing shoes, electrical equipment, or damaged tissue.
950 Synonyms & Antonyms for REPAIR | Thesaurus.com - Repair also means to fix or restore something, with synonyms including mend, refurbish, remedy, renovate, and rebuild, capturing the idea of restoration or fixing.
The Repair Association - The Repair Association advocates for the right to repair by fighting manufacturer restrictions on parts, tools, and instructions that lock out independent repair shops and drive repair costs artificially high.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com