The industrial metaverse leverages immersive virtual environments and real-time data integration to enhance manufacturing processes beyond traditional smart factories, which primarily focus on automation and IoT-enabled operations. This virtual-physical convergence enables advanced simulations, remote collaboration, and predictive maintenance with higher precision and efficiency. Explore how the industrial metaverse is reshaping manufacturing innovation and operational excellence.
Why it is important
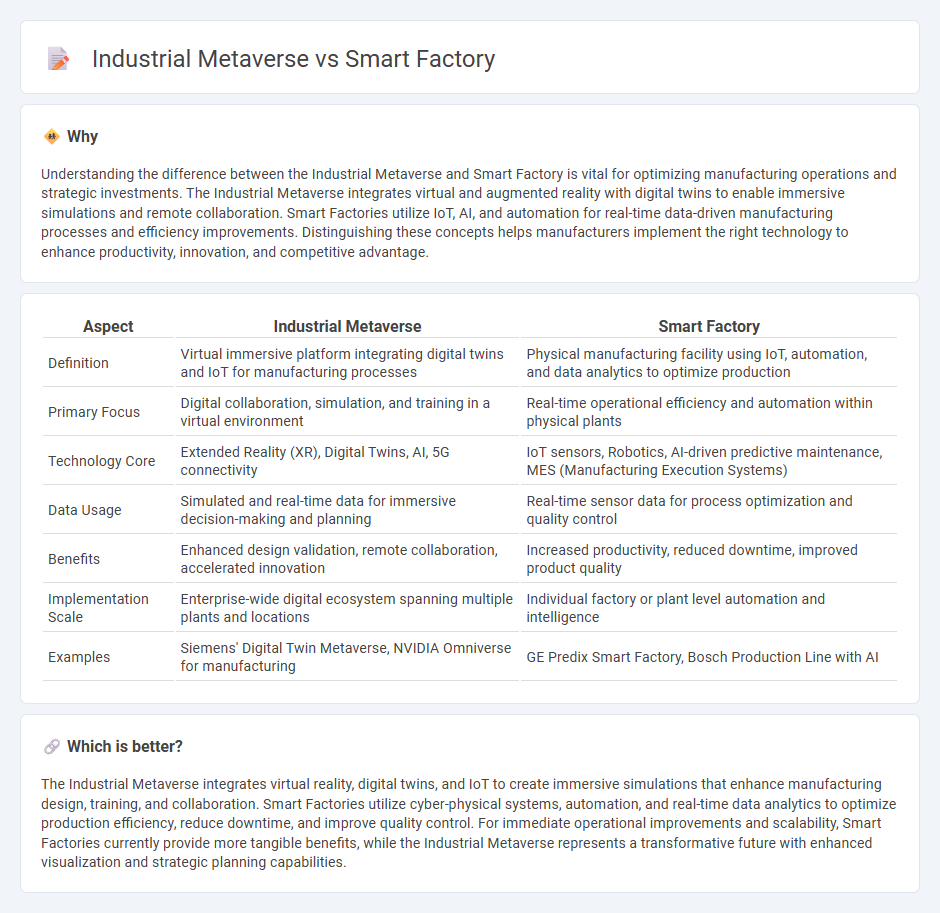
Understanding the difference between the Industrial Metaverse and Smart Factory is vital for optimizing manufacturing operations and strategic investments. The Industrial Metaverse integrates virtual and augmented reality with digital twins to enable immersive simulations and remote collaboration. Smart Factories utilize IoT, AI, and automation for real-time data-driven manufacturing processes and efficiency improvements. Distinguishing these concepts helps manufacturers implement the right technology to enhance productivity, innovation, and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Metaverse | Smart Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual immersive platform integrating digital twins and IoT for manufacturing processes | Physical manufacturing facility using IoT, automation, and data analytics to optimize production |
| Primary Focus | Digital collaboration, simulation, and training in a virtual environment | Real-time operational efficiency and automation within physical plants |
| Technology Core | Extended Reality (XR), Digital Twins, AI, 5G connectivity | IoT sensors, Robotics, AI-driven predictive maintenance, MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) |
| Data Usage | Simulated and real-time data for immersive decision-making and planning | Real-time sensor data for process optimization and quality control |
| Benefits | Enhanced design validation, remote collaboration, accelerated innovation | Increased productivity, reduced downtime, improved product quality |
| Implementation Scale | Enterprise-wide digital ecosystem spanning multiple plants and locations | Individual factory or plant level automation and intelligence |
| Examples | Siemens' Digital Twin Metaverse, NVIDIA Omniverse for manufacturing | GE Predix Smart Factory, Bosch Production Line with AI |
Which is better?
The Industrial Metaverse integrates virtual reality, digital twins, and IoT to create immersive simulations that enhance manufacturing design, training, and collaboration. Smart Factories utilize cyber-physical systems, automation, and real-time data analytics to optimize production efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve quality control. For immediate operational improvements and scalability, Smart Factories currently provide more tangible benefits, while the Industrial Metaverse represents a transformative future with enhanced visualization and strategic planning capabilities.
Connection
The Industrial Metaverse integrates virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and digital twins to create immersive simulations of manufacturing processes, enhancing real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance in smart factories. Smart factories leverage IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and automation to optimize production efficiency, while the Industrial Metaverse provides a collaborative platform for remote design, training, and problem-solving. Together, they enable seamless convergence of physical and digital manufacturing environments, driving innovation and operational excellence.
Key Terms
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
Smart Factories utilize Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) to integrate physical machinery with digital networks, enabling real-time data exchange and autonomous operations. Industrial Metaverse expands this concept by creating immersive digital twins of production environments, enhancing collaboration, simulation, and predictive maintenance through augmented reality and virtual reality technologies. Explore how CPS drives innovation in both Smart Factory frameworks and the Industrial Metaverse to transform manufacturing processes.
Digital Twin
Smart factories utilize digital twin technology to create virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance to optimize manufacturing processes. The industrial metaverse expands this concept into immersive digital environments where digital twins interact within interconnected ecosystems, facilitating collaborative design, simulation, and operational decision-making. Explore the transformative potential of digital twins in both smart factories and the industrial metaverse to drive industrial innovation.
Immersive Visualization
Smart Factory leverages IoT sensors, AI-driven automation, and real-time data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes, while the Industrial Metaverse integrates immersive visualization technologies such as AR, VR, and digital twins to create interactive, 3D environments for enhanced operational insight. Immersive visualization in the Industrial Metaverse enables remote collaboration, improved training, and predictive maintenance by simulating factory conditions and machinery behavior in a virtual space. Explore how these technologies redefine manufacturing efficiency and innovation for a deeper understanding.
Source and External Links
What is a smart factory? Understanding the future of manufacturing - A smart factory digitally integrates all manufacturing processes using sensors, AI, and cloud computing for continuous process improvement and forms a core part of Industry 4.0 with intelligent automation based on real-time data feedback.
Smart Factory Guide | L2L - A smart factory connects machines, people, and processes using digital technologies to improve efficiency, quality, safety, and costs by leveraging IIoT and data analytics within smart manufacturing frameworks aligned with Industry 4.0.
The Smart Factory @ Wichita | Deloitte US - Deloitte's Smart Factory experience in Wichita demonstrates how evolving smart factory technologies combine digital, physical, and experimental elements to drive innovation, competitiveness, and sustainable digital transformation in manufacturing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com