Cobots, or collaborative robots, enhance manufacturing efficiency by working alongside human operators, improving precision and reducing repetitive strain injuries compared to manual labor. Unlike traditional manual processes, cobots can consistently perform complex tasks with minimal downtime and greater accuracy, which leads to increased production quality and throughput. Discover how integrating cobots can transform your manufacturing operations and optimize labor resources.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cobots and manual labor is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and workforce allocation. Cobots enhance precision, safety, and productivity by automating repetitive tasks, while manual labor provides adaptability and problem-solving skills in complex scenarios. Choosing the right balance reduces operational costs and improves product quality. Detailed assessment of task requirements and workforce capabilities drives effective integration of cobots in manufacturing processes.
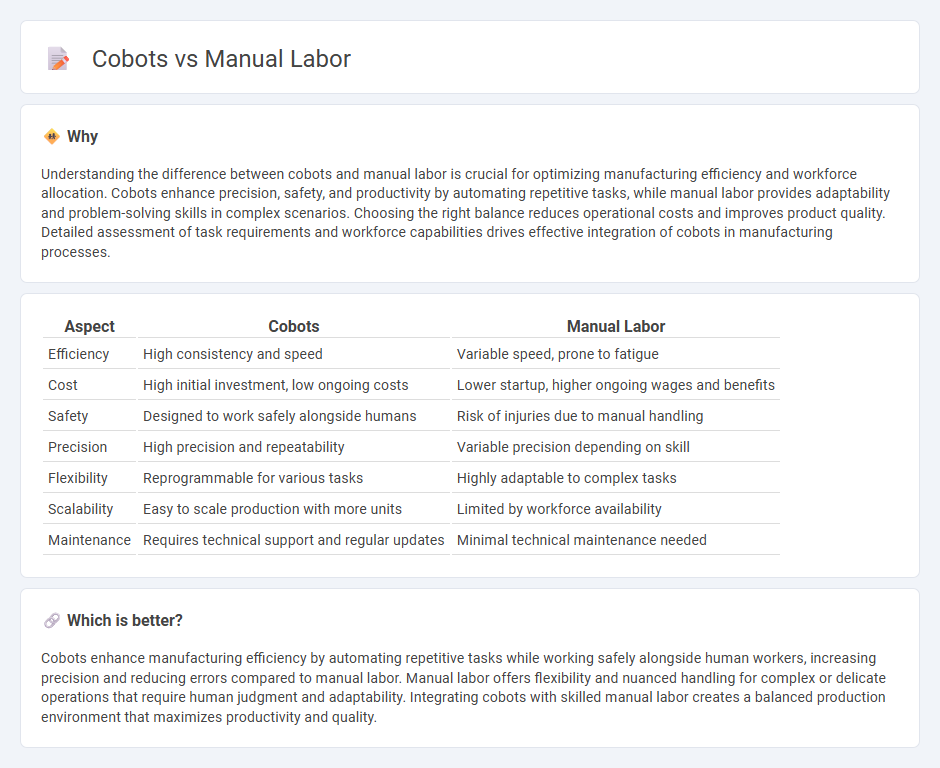
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cobots | Manual Labor |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High consistency and speed | Variable speed, prone to fatigue |
| Cost | High initial investment, low ongoing costs | Lower startup, higher ongoing wages and benefits |
| Safety | Designed to work safely alongside humans | Risk of injuries due to manual handling |
| Precision | High precision and repeatability | Variable precision depending on skill |
| Flexibility | Reprogrammable for various tasks | Highly adaptable to complex tasks |
| Scalability | Easy to scale production with more units | Limited by workforce availability |
| Maintenance | Requires technical support and regular updates | Minimal technical maintenance needed |
Which is better?
Cobots enhance manufacturing efficiency by automating repetitive tasks while working safely alongside human workers, increasing precision and reducing errors compared to manual labor. Manual labor offers flexibility and nuanced handling for complex or delicate operations that require human judgment and adaptability. Integrating cobots with skilled manual labor creates a balanced production environment that maximizes productivity and quality.
Connection
Cobots, or collaborative robots, enhance manufacturing efficiency by working alongside manual labor to automate repetitive and hazardous tasks, increasing productivity and safety. These robots adapt to human movements and workflows, allowing seamless human-robot collaboration without extensive reprogramming. Integrating cobots with skilled manual labor optimizes production lines, reduces errors, and improves overall operational flexibility in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Human-Robot Collaboration
Human-robot collaboration enhances productivity by combining manual labor's adaptability with cobots' precision and endurance. Cobots optimize repetitive tasks and reduce injury risks, while human workers contribute critical problem-solving and decision-making skills. Explore the benefits and future trends of integrating cobots into manual labor workflows for improved efficiency.
Ergonomics
Manual labor often exposes workers to repetitive strain injuries and musculoskeletal disorders due to sustained physical exertion and awkward postures. Cobots improve ergonomics by assisting with heavy lifting, repetitive tasks, and precision work, reducing physical stress and increasing workplace safety. Explore how integrating cobots can transform ergonomic outcomes and worker well-being in your facility.
Productivity
Manual labor often faces limitations in consistency and efficiency, impacting overall productivity in manufacturing environments. Collaborative robots (cobots) enhance productivity by automating repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and operating alongside workers safely to optimize workflow. Discover how integrating cobots can transform your production process for maximum output and efficiency.
Source and External Links
Benefits of Manual Labor: Preparing You For Your Career - Manual labor involves physical work often performed by blue-collar workers in industries like construction and agriculture, encompassing roles such as carpenters, electricians, factory workers, and farmers.
17 Manual Labor Jobs - Manual labor jobs require physical effort and include a wide spectrum from entry-level positions like housekeepers and landscapers to more technical roles that require certifications, including construction and emergency medical technicians.
Manual labour - Manual labor is the physical work done by humans as opposed to machines, historically associated with lower social status and often linked to socio-economic class distinctions in various societies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com