Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition by disassembling, repairing, and replacing components, significantly reducing waste and resource consumption compared to traditional manufacturing. Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes minimizing environmental impact through energy-efficient processes, renewable materials, and waste reduction throughout the entire product lifecycle. Explore the evolving strategies that drive efficiency and eco-friendly practices in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
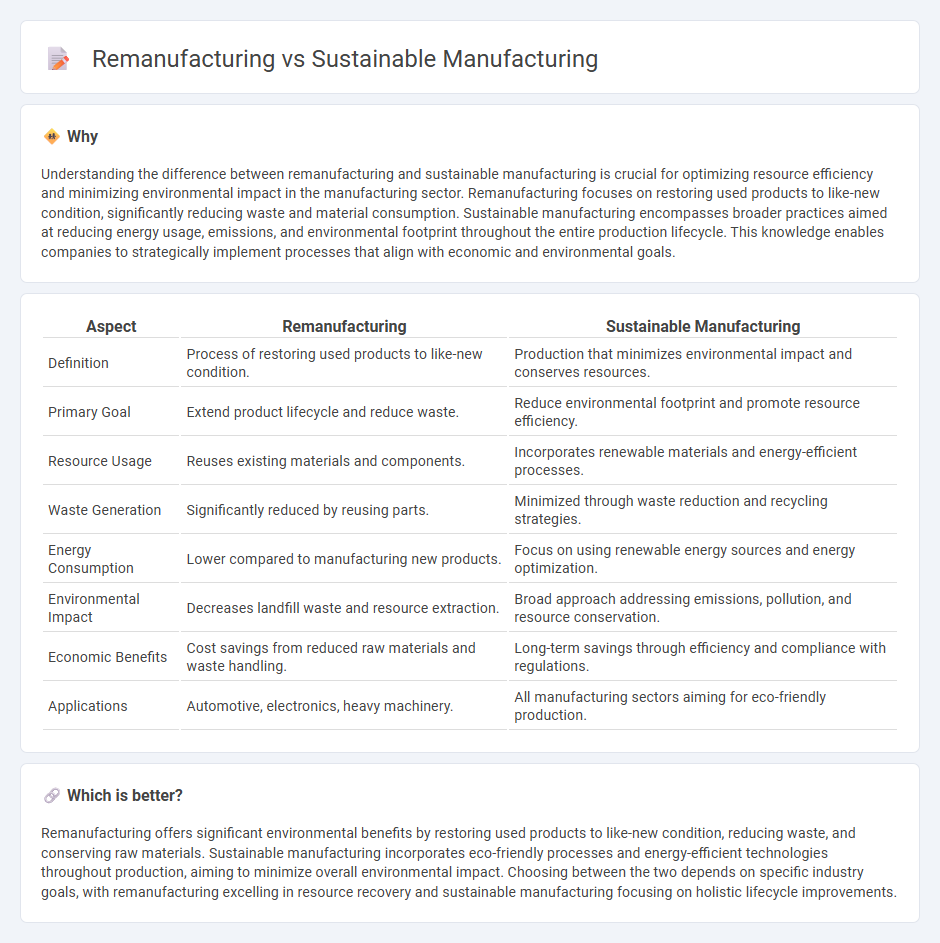
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and sustainable manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact in the manufacturing sector. Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition, significantly reducing waste and material consumption. Sustainable manufacturing encompasses broader practices aimed at reducing energy usage, emissions, and environmental footprint throughout the entire production lifecycle. This knowledge enables companies to strategically implement processes that align with economic and environmental goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Sustainable Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of restoring used products to like-new condition. | Production that minimizes environmental impact and conserves resources. |
| Primary Goal | Extend product lifecycle and reduce waste. | Reduce environmental footprint and promote resource efficiency. |
| Resource Usage | Reuses existing materials and components. | Incorporates renewable materials and energy-efficient processes. |
| Waste Generation | Significantly reduced by reusing parts. | Minimized through waste reduction and recycling strategies. |
| Energy Consumption | Lower compared to manufacturing new products. | Focus on using renewable energy sources and energy optimization. |
| Environmental Impact | Decreases landfill waste and resource extraction. | Broad approach addressing emissions, pollution, and resource conservation. |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings from reduced raw materials and waste handling. | Long-term savings through efficiency and compliance with regulations. |
| Applications | Automotive, electronics, heavy machinery. | All manufacturing sectors aiming for eco-friendly production. |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing offers significant environmental benefits by restoring used products to like-new condition, reducing waste, and conserving raw materials. Sustainable manufacturing incorporates eco-friendly processes and energy-efficient technologies throughout production, aiming to minimize overall environmental impact. Choosing between the two depends on specific industry goals, with remanufacturing excelling in resource recovery and sustainable manufacturing focusing on holistic lifecycle improvements.
Connection
Remanufacturing and sustainable manufacturing are connected through their shared goal of reducing waste and conserving resources by restoring used products to like-new condition, extending their lifecycle. This process minimizes raw material consumption and energy use compared to traditional manufacturing, lowering environmental impact. Companies implementing both strategies enhance circular economy practices and improve operational sustainability.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes minimizing environmental impact by optimizing energy use, reducing waste, and utilizing renewable resources throughout the production process. Remanufacturing specifically targets resource efficiency by restoring used products to like-new condition, significantly reducing raw material consumption and landfill waste. Explore the benefits of integrating these approaches to enhance circular economy practices and achieve greater resource conservation.
Closed-Loop Systems
Sustainable manufacturing minimizes environmental impact by integrating renewable resources, energy efficiency, and waste reduction, whereas remanufacturing specifically restores used products to like-new condition, extending product lifecycle within closed-loop systems. Closed-loop systems enable continuous resource recovery and material reuse, reducing raw material extraction and landfill waste, making both approaches crucial for circular economy goals. Explore how closed-loop strategies optimize sustainability through innovative manufacturing and remanufacturing practices.
Product Life Extension
Sustainable manufacturing reduces environmental impact by optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste throughout production processes, promoting durability and reparability to extend product life. Remanufacturing specifically focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition through disassembly, cleaning, and replacement of defective components, thereby significantly extending the lifecycle and conserving raw materials. Explore the benefits and strategies of extending product life through sustainable manufacturing and remanufacturing methods to advance circular economy goals.
Source and External Links
Manufacturing - Sustainability Guide - Sustainable manufacturing focuses on minimizing negative environmental impacts, conserving energy and natural resources, and optimizing processes for safety, efficiency, and closed-loop industrial practices.
Sustainable Manufacturing | US EPA - It involves creating products through economically sound processes that reduce environmental harm, conserve resources, and also deliver financial, operational, and reputational benefits to businesses.
Sustainable manufacturing | NIST - Manufacturers use international standards to map and improve the environmental aspects of their processes, leading to greater sustainability and efficiency throughout the product lifecycle.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com