Smart factories leverage interconnected machinery and real-time data analytics to enhance production efficiency and flexibility. Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling simulation, monitoring, and predictive maintenance to optimize manufacturing processes. Explore how integrating smart factories with digital twins revolutionizes industrial operations and drives innovation.
Why it is important
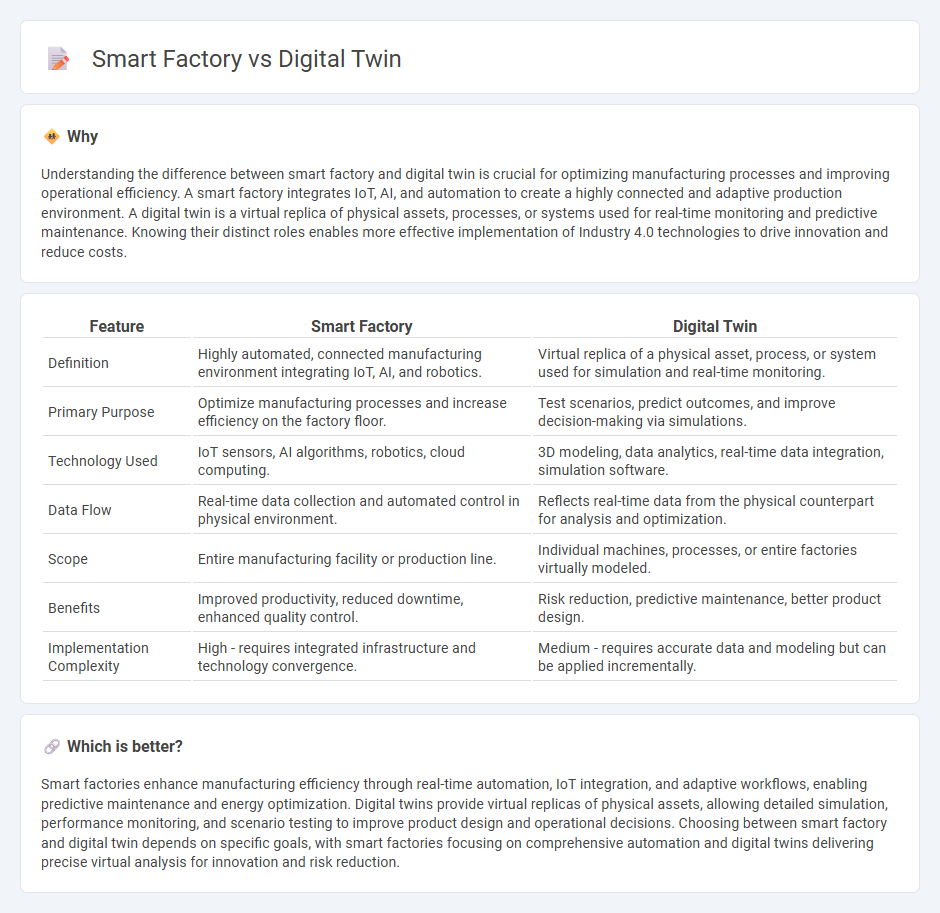
Understanding the difference between smart factory and digital twin is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and improving operational efficiency. A smart factory integrates IoT, AI, and automation to create a highly connected and adaptive production environment. A digital twin is a virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems used for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Knowing their distinct roles enables more effective implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies to drive innovation and reduce costs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Factory | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Highly automated, connected manufacturing environment integrating IoT, AI, and robotics. | Virtual replica of a physical asset, process, or system used for simulation and real-time monitoring. |
| Primary Purpose | Optimize manufacturing processes and increase efficiency on the factory floor. | Test scenarios, predict outcomes, and improve decision-making via simulations. |
| Technology Used | IoT sensors, AI algorithms, robotics, cloud computing. | 3D modeling, data analytics, real-time data integration, simulation software. |
| Data Flow | Real-time data collection and automated control in physical environment. | Reflects real-time data from the physical counterpart for analysis and optimization. |
| Scope | Entire manufacturing facility or production line. | Individual machines, processes, or entire factories virtually modeled. |
| Benefits | Improved productivity, reduced downtime, enhanced quality control. | Risk reduction, predictive maintenance, better product design. |
| Implementation Complexity | High - requires integrated infrastructure and technology convergence. | Medium - requires accurate data and modeling but can be applied incrementally. |
Which is better?
Smart factories enhance manufacturing efficiency through real-time automation, IoT integration, and adaptive workflows, enabling predictive maintenance and energy optimization. Digital twins provide virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing detailed simulation, performance monitoring, and scenario testing to improve product design and operational decisions. Choosing between smart factory and digital twin depends on specific goals, with smart factories focusing on comprehensive automation and digital twins delivering precise virtual analysis for innovation and risk reduction.
Connection
Smart factories integrate IoT sensors, automation, and data analytics to optimize production processes in real-time, while digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets or systems for simulation and predictive maintenance. The connection lies in digital twins providing a dynamic, data-driven model that smart factories use to monitor performance, reduce downtime, and enhance quality control. This synergy enables continuous improvement and agile decision-making in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Virtual Simulation
Virtual simulation in digital twins enables real-time replication of physical assets and processes, allowing precise monitoring, analysis, and predictive maintenance. Smart factories leverage virtual simulation to optimize production workflows, reduce downtime, and enhance operational efficiency through integrated IoT sensors and AI-driven insights. Explore the transformative impact of virtual simulation on manufacturing by diving deeper into digital twins and smart factory applications.
Real-time Data Integration
Digital twin technology enables real-time data integration by creating dynamic virtual models that reflect the physical processes and assets of a smart factory. Smart factories leverage these digital twins to optimize production efficiency, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management through continuous data synchronization. Explore the detailed differences and applications of real-time data integration in digital twins versus smart factories to enhance industrial innovation.
Cyber-Physical Systems
Digital twins create real-time virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling precise monitoring and predictive maintenance within Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS). Smart factories leverage these CPS to integrate automation, IoT sensors, and data analytics for optimized manufacturing processes and enhanced operational efficiency. Explore how digital twins and smart factories converge to revolutionize Cyber-Physical Systems and industrial innovation.
Source and External Links
What Is a Digital Twin? - A digital twin is a virtual representation of an object or system that accurately reflects a physical object, continuously updated in real time from sensor data to simulate, analyze, and optimize the physical counterpart's performance throughout its lifecycle.
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated, data-driven virtual model of real-world entities and processes, synchronizing real-time and historical data to enable continuous improvement, decision-making, and predictive simulation with high fidelity interaction.
Digital twin - A digital twin is a digital counterpart of a physical product, system, or process used for simulation, monitoring, testing, and maintenance, originally developed by NASA and increasingly applied across manufacturing to improve production processes and predictive maintenance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com