Smart factories utilize advanced digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to create highly flexible, efficient, and interconnected production systems. Cellular manufacturing organizes equipment and workstations into compact cells focused on specific product families, optimizing workflow and reducing waste. Discover how these innovative approaches transform manufacturing performance and drive industry 4.0 advancements.
Why it is important
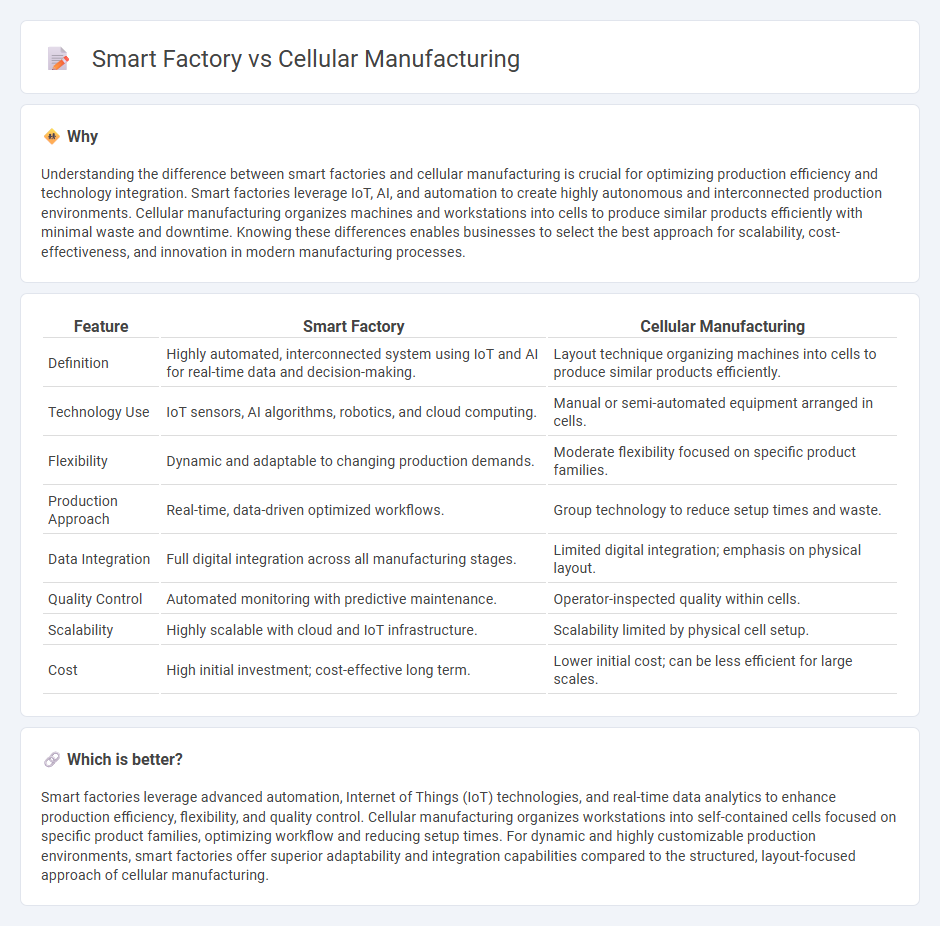
Understanding the difference between smart factories and cellular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and technology integration. Smart factories leverage IoT, AI, and automation to create highly autonomous and interconnected production environments. Cellular manufacturing organizes machines and workstations into cells to produce similar products efficiently with minimal waste and downtime. Knowing these differences enables businesses to select the best approach for scalability, cost-effectiveness, and innovation in modern manufacturing processes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Factory | Cellular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Highly automated, interconnected system using IoT and AI for real-time data and decision-making. | Layout technique organizing machines into cells to produce similar products efficiently. |
| Technology Use | IoT sensors, AI algorithms, robotics, and cloud computing. | Manual or semi-automated equipment arranged in cells. |
| Flexibility | Dynamic and adaptable to changing production demands. | Moderate flexibility focused on specific product families. |
| Production Approach | Real-time, data-driven optimized workflows. | Group technology to reduce setup times and waste. |
| Data Integration | Full digital integration across all manufacturing stages. | Limited digital integration; emphasis on physical layout. |
| Quality Control | Automated monitoring with predictive maintenance. | Operator-inspected quality within cells. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with cloud and IoT infrastructure. | Scalability limited by physical cell setup. |
| Cost | High initial investment; cost-effective long term. | Lower initial cost; can be less efficient for large scales. |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage advanced automation, Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, and real-time data analytics to enhance production efficiency, flexibility, and quality control. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into self-contained cells focused on specific product families, optimizing workflow and reducing setup times. For dynamic and highly customizable production environments, smart factories offer superior adaptability and integration capabilities compared to the structured, layout-focused approach of cellular manufacturing.
Connection
Smart factories integrate advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics to optimize production processes, while cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into small, self-contained units focused on specific product families. These approaches connect as cellular manufacturing enhances flexibility and efficiency within smart factories by enabling real-time data exchange and adaptive control across cells. Together, they drive higher productivity, reduce lead times, and improve resource utilization in modern manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Cellular Manufacturing:
Cellular manufacturing organizes production into small, self-contained units called cells, each dedicated to a specific set of tasks, enhancing efficiency and reducing lead times. It emphasizes lean principles, minimizing waste by streamlining workflows and improving worker specialization within cells. Discover how cellular manufacturing can transform your production processes and boost operational performance.
Work Cells
Cellular manufacturing organizes production into dedicated work cells that group machines and operators for specific tasks, enhancing flow and reducing lead times by minimizing movement and wait. Smart factories integrate IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics within these work cells to optimize operations, improve flexibility, and enable predictive maintenance. Explore how merging work cells with smart technologies drives manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Lean Production
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into cells to minimize waste and improve workflow, aligning closely with Lean Production principles by reducing lead times and inventory levels. Smart factories integrate advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to optimize processes, enhance real-time decision making, and drive continuous improvement in Lean environments. Explore how these approaches transform manufacturing for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Cellular Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide - Cellular manufacturing is a production system combining processes into unified cells to create efficient production flows with assigned resources and continuous performance monitoring.
Cellular manufacturing - Cellular manufacturing organizes work into multiple cells, often U-shaped, that consolidate various tasks in sequence to reduce waste, improve flexibility, shorten lead times, and boost productivity in lean manufacturing.
What Is Cellular Manufacturing? - Cellular manufacturing arranges workstations and equipment into self-sufficient cells where workers are cross-trained; it enhances communication, reduces work-in-process and space requirements, and improves product quality across industries such as automotive and electronics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com