Smart factories integrate advanced IoT sensors, AI analytics, and real-time data to create adaptive manufacturing environments that optimize workflows and reduce downtime. Automated production lines focus on mechanizing specific tasks using robotics and control systems to increase efficiency and consistency in repetitive operations. Explore how these innovations transform industrial processes and improve productivity in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a smart factory and an automated production line is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and innovation. A smart factory integrates IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics for adaptive, autonomous decision-making, while automated production lines primarily focus on mechanized tasks with limited flexibility. This distinction helps manufacturers invest strategically in technology that aligns with their goals for scalability, customization, and predictive maintenance. Knowledge of these differences enhances competitive advantage by enabling tailored digital transformation strategies in the Industry 4.0 era.
Comparison Table
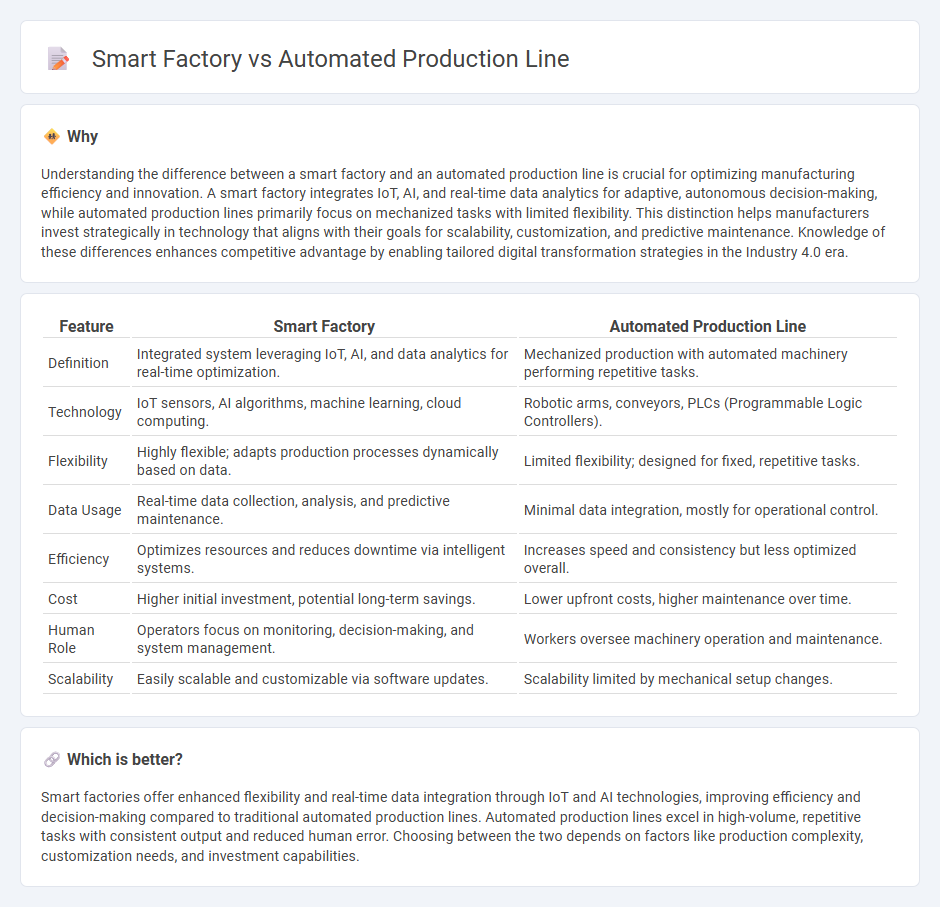
| Feature | Smart Factory | Automated Production Line |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated system leveraging IoT, AI, and data analytics for real-time optimization. | Mechanized production with automated machinery performing repetitive tasks. |
| Technology | IoT sensors, AI algorithms, machine learning, cloud computing. | Robotic arms, conveyors, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers). |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; adapts production processes dynamically based on data. | Limited flexibility; designed for fixed, repetitive tasks. |
| Data Usage | Real-time data collection, analysis, and predictive maintenance. | Minimal data integration, mostly for operational control. |
| Efficiency | Optimizes resources and reduces downtime via intelligent systems. | Increases speed and consistency but less optimized overall. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, potential long-term savings. | Lower upfront costs, higher maintenance over time. |
| Human Role | Operators focus on monitoring, decision-making, and system management. | Workers oversee machinery operation and maintenance. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable and customizable via software updates. | Scalability limited by mechanical setup changes. |
Which is better?
Smart factories offer enhanced flexibility and real-time data integration through IoT and AI technologies, improving efficiency and decision-making compared to traditional automated production lines. Automated production lines excel in high-volume, repetitive tasks with consistent output and reduced human error. Choosing between the two depends on factors like production complexity, customization needs, and investment capabilities.
Connection
Smart factories integrate automated production lines through advanced IoT sensors and AI-driven systems, enabling real-time data collection and process optimization. Automated production lines use robotics and machine learning algorithms to execute manufacturing tasks with precision, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. This connection fosters adaptive manufacturing environments that improve productivity, reduce downtime, and support scalable production.
Key Terms
**Automated Production Line:**
Automated production lines utilize robotics and machinery to perform repetitive tasks with high precision and speed, significantly reducing human error and labor costs. These systems are designed for specific manufacturing processes, often lacking flexibility to adapt to variations or customization. Explore how integrating smart factory technologies can transform automation capabilities for enhanced efficiency and responsiveness.
Robotics
Automated production lines utilize robotics for repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency but often lack adaptability and real-time data processing. Smart factories integrate advanced robotics with IoT, AI, and machine learning, enabling dynamic decision-making and predictive maintenance to optimize manufacturing processes. Explore how next-generation robotics are transforming industrial automation by visiting our detailed insights.
Conveyor System
Automated production lines use conveyor systems primarily for repetitive, linear transportation of materials, optimizing speed and efficiency in predefined tasks. Smart factories integrate conveyor systems with IoT sensors and AI, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive routing to enhance flexibility and minimize downtime. Explore the advancements in conveyor systems that differentiate traditional automation from smart manufacturing innovations.
Source and External Links
Benefits of Automated Production Lines - Automated production lines reduce production costs and labor costs, minimize errors, and ensure output consistency and quality by using machines and automated systems.
How Production Line Automation is Transforming Manufacturing - Production line automation uses technology like robotics and software to automate tasks, improving efficiency and minimizing human intervention in manufacturing processes.
Automated Production Line - An automated production line is a manufacturing system featuring automated machines and equipment to produce efficiently and quickly, reducing errors and enhancing product quality.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com