Machine vision enhances manufacturing accuracy by enabling automated inspection and quality control through image processing and pattern recognition. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) focuses on precision machining by controlling cutting tools with programmed instructions, optimizing production efficiency and repeatability. Explore the differences and advantages of machine vision and CNC technologies to elevate your manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
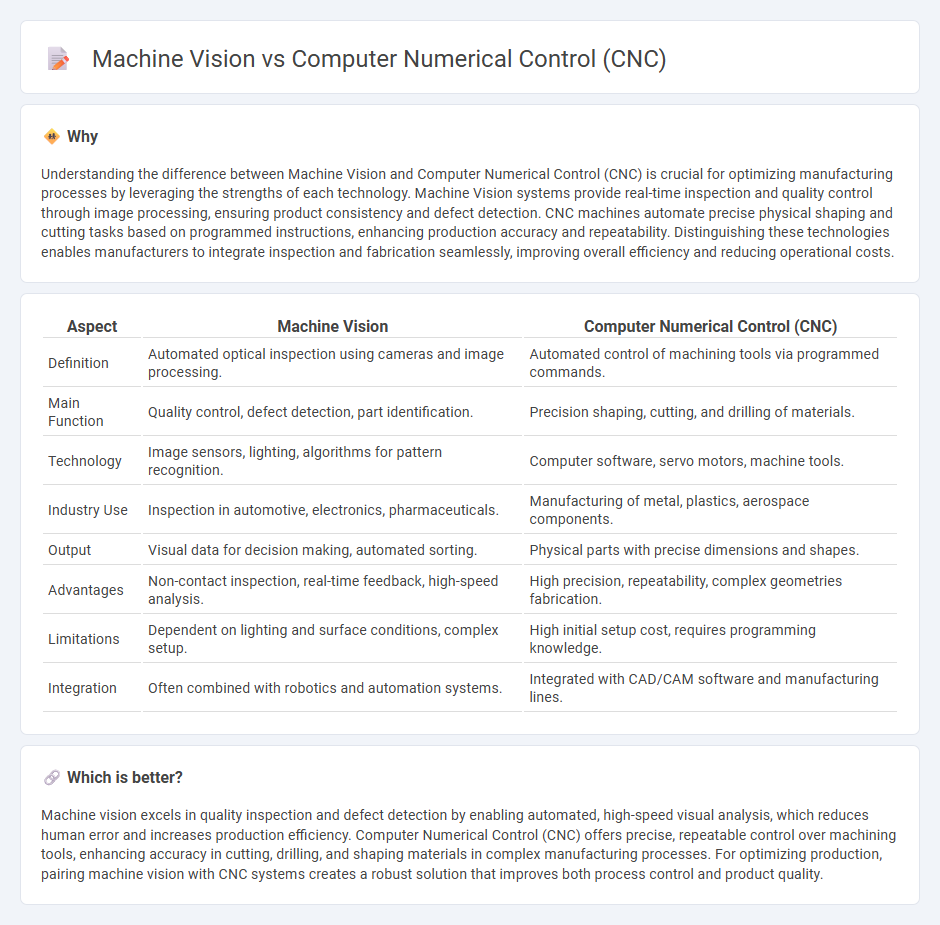
Understanding the difference between Machine Vision and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes by leveraging the strengths of each technology. Machine Vision systems provide real-time inspection and quality control through image processing, ensuring product consistency and defect detection. CNC machines automate precise physical shaping and cutting tasks based on programmed instructions, enhancing production accuracy and repeatability. Distinguishing these technologies enables manufacturers to integrate inspection and fabrication seamlessly, improving overall efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Machine Vision | Computer Numerical Control (CNC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated optical inspection using cameras and image processing. | Automated control of machining tools via programmed commands. |
| Main Function | Quality control, defect detection, part identification. | Precision shaping, cutting, and drilling of materials. |
| Technology | Image sensors, lighting, algorithms for pattern recognition. | Computer software, servo motors, machine tools. |
| Industry Use | Inspection in automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals. | Manufacturing of metal, plastics, aerospace components. |
| Output | Visual data for decision making, automated sorting. | Physical parts with precise dimensions and shapes. |
| Advantages | Non-contact inspection, real-time feedback, high-speed analysis. | High precision, repeatability, complex geometries fabrication. |
| Limitations | Dependent on lighting and surface conditions, complex setup. | High initial setup cost, requires programming knowledge. |
| Integration | Often combined with robotics and automation systems. | Integrated with CAD/CAM software and manufacturing lines. |
Which is better?
Machine vision excels in quality inspection and defect detection by enabling automated, high-speed visual analysis, which reduces human error and increases production efficiency. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) offers precise, repeatable control over machining tools, enhancing accuracy in cutting, drilling, and shaping materials in complex manufacturing processes. For optimizing production, pairing machine vision with CNC systems creates a robust solution that improves both process control and product quality.
Connection
Machine vision systems enhance Computer Numerical Control (CNC) operations by providing real-time visual feedback for precise machining. This integration allows CNC machines to automatically adjust cutting paths and detect defects, improving accuracy and reducing waste. The synergy between machine vision and CNC technology optimizes manufacturing efficiency and quality control.
Key Terms
G-code (CNC)
G-code serves as the essential programming language for Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines, directing precise tool movements and operations in manufacturing processes. Machine vision, in contrast, leverages advanced imaging and AI algorithms to inspect, guide, and enhance quality control without directly controlling machine tool paths. Explore the integral role of G-code in CNC machining and its complementary relationship with machine vision systems to optimize production efficiency.
Image Processing (Machine Vision)
Machine vision leverages advanced image processing algorithms to analyze visual data for quality inspection, defect detection, and automation, enhancing precision beyond traditional CNC controls. CNC controls primarily execute pre-programmed machining tasks without real-time visual feedback, whereas machine vision systems provide dynamic analysis and decision-making capabilities through high-resolution cameras and AI-driven image recognition. Explore in-depth how integrating machine vision with CNC systems revolutionizes manufacturing efficiency and accuracy.
Automation
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems automate precision machining by using programmed instructions to control machine tools, enhancing manufacturing accuracy and efficiency. Machine vision complements automation by enabling real-time quality inspection, defect detection, and guidance of robotic systems through advanced image processing algorithms. Explore how integrating CNC with machine vision transforms automated manufacturing workflows and boosts productivity.
Source and External Links
What is Computer Numerical Control (CNC)? - CNC is a manufacturing method that automates machine tools' control, movement, and precision through preprogrammed software, mainly using G-code and M-code to operate tools like mills, lathes, drills, and lasers with high accuracy.
Computer Numerical Control Certificate - CNC technology involves working with computer-controlled machines to manufacture highly precise parts for industries such as medical, aerospace, and automotive, using commands that control cutting, drilling, milling, and shaping various materials.
What is Computer Numerical Control (CNC) - CNC is an automated system that controls machine tooling with computer-interpreted coded instructions, enabling mass production of identical parts by executing programmed commands versus manual machining, which requires individual operator control.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com