Industrial symbiosis focuses on creating a network where waste or by-products from one manufacturing process serve as raw materials for another, enhancing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes producing goods through methods that minimize negative social and environmental effects while conserving energy and natural resources. Explore how these approaches contribute to a greener, more circular economy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between industrial symbiosis and sustainable manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact in production processes. Industrial symbiosis focuses on the collaboration between different industries to reuse waste materials, while sustainable manufacturing emphasizes eco-friendly practices within a single manufacturing system. Clear knowledge of these concepts enables businesses to implement more effective circular economy strategies and reduce carbon footprints. Distinguishing these approaches drives innovation and supports regulatory compliance in the manufacturing sector.
Comparison Table
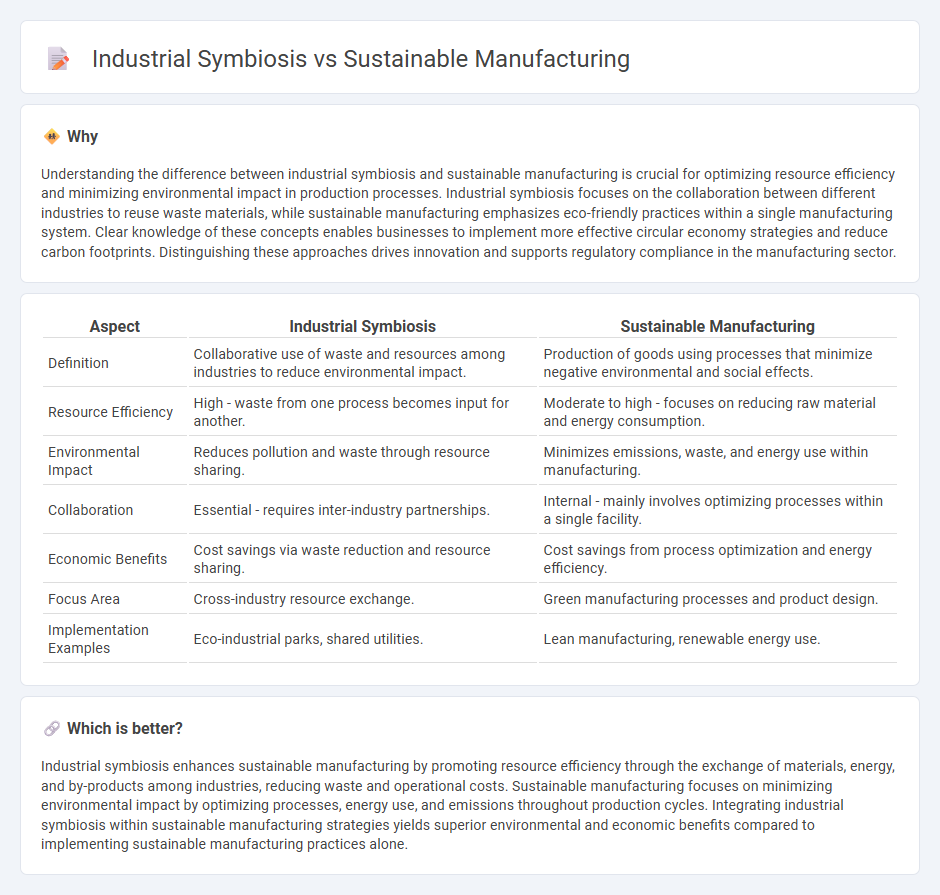
| Aspect | Industrial Symbiosis | Sustainable Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative use of waste and resources among industries to reduce environmental impact. | Production of goods using processes that minimize negative environmental and social effects. |
| Resource Efficiency | High - waste from one process becomes input for another. | Moderate to high - focuses on reducing raw material and energy consumption. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces pollution and waste through resource sharing. | Minimizes emissions, waste, and energy use within manufacturing. |
| Collaboration | Essential - requires inter-industry partnerships. | Internal - mainly involves optimizing processes within a single facility. |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings via waste reduction and resource sharing. | Cost savings from process optimization and energy efficiency. |
| Focus Area | Cross-industry resource exchange. | Green manufacturing processes and product design. |
| Implementation Examples | Eco-industrial parks, shared utilities. | Lean manufacturing, renewable energy use. |
Which is better?
Industrial symbiosis enhances sustainable manufacturing by promoting resource efficiency through the exchange of materials, energy, and by-products among industries, reducing waste and operational costs. Sustainable manufacturing focuses on minimizing environmental impact by optimizing processes, energy use, and emissions throughout production cycles. Integrating industrial symbiosis within sustainable manufacturing strategies yields superior environmental and economic benefits compared to implementing sustainable manufacturing practices alone.
Connection
Industrial symbiosis enhances sustainable manufacturing by optimizing resource efficiency through the exchange of materials, energy, and by-products among businesses. This collaboration minimizes waste generation, reduces environmental impact, and lowers operational costs in manufacturing processes. Integrating industrial symbiosis into sustainable manufacturing frameworks supports circular economy goals and promotes long-term ecological and economic resilience.
Key Terms
**Sustainable Manufacturing:**
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact through resource efficiency, waste minimization, and energy conservation during production processes. It integrates clean technologies and renewable energy to promote eco-friendly product life cycles. Explore deeper into sustainable manufacturing to understand its role in transforming global industrial practices.
Resource Efficiency
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes minimizing waste and energy use through optimized processes and renewable materials to enhance resource efficiency. Industrial symbiosis facilitates resource sharing between industries, where by-products or waste from one process serve as inputs for another, significantly reducing raw material consumption. Explore how integrating these strategies can maximize resource efficiency and environmental benefits.
Life Cycle Assessment
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact through efficient resource use, energy optimization, and waste minimization, assessed comprehensively via Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) to quantify carbon footprint, water consumption, and toxic emissions. Industrial symbiosis enables resource exchange between industries, facilitating waste reuse and by-product valorization, thereby enhancing overall sustainability performance as revealed by comparative LCA studies. Explore detailed LCA methodologies to understand the nuanced benefits and trade-offs between these strategies in advancing circular economy goals.
Source and External Links
Manufacturing - Sustainability Guide - Sustainable manufacturing involves optimized processes that minimize environmental impact, conserve energy and natural resources, enhance product lifecycle management, and emphasize remanufacturing, reparability, and industrial symbiosis for improved sustainability.
5 Ways Manufacturers Can Become More Sustainable - Genius ERP - Key strategies for sustainable manufacturing include reducing energy consumption, adopting renewable energy sources, using recyclable materials, implementing lean manufacturing to eliminate waste, and partnering with sustainable suppliers to promote eco-friendly practices throughout the supply chain.
Sustainable Manufacturing | US EPA - Sustainable manufacturing creates products through economically sound processes that minimize environmental impacts and conserve resources while enhancing safety and providing business benefits such as reduced costs, improved brand reputation, and increased competitiveness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com