Predictive maintenance leverages data analytics and IoT sensors to monitor equipment health, enabling timely interventions before failures occur. Corrective maintenance addresses issues only after equipment breakdowns, often leading to unplanned downtime and higher repair costs. Explore the benefits and implementation strategies of both methods to optimize manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between predictive maintenance and corrective maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing downtime costs. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and analytics to anticipate equipment failures, allowing scheduled interventions before breakdowns occur. Corrective maintenance addresses equipment issues only after failure, often leading to higher repair costs and production delays. This knowledge enables manufacturers to implement cost-effective strategies that enhance equipment lifespan and maintain consistent product quality.
Comparison Table
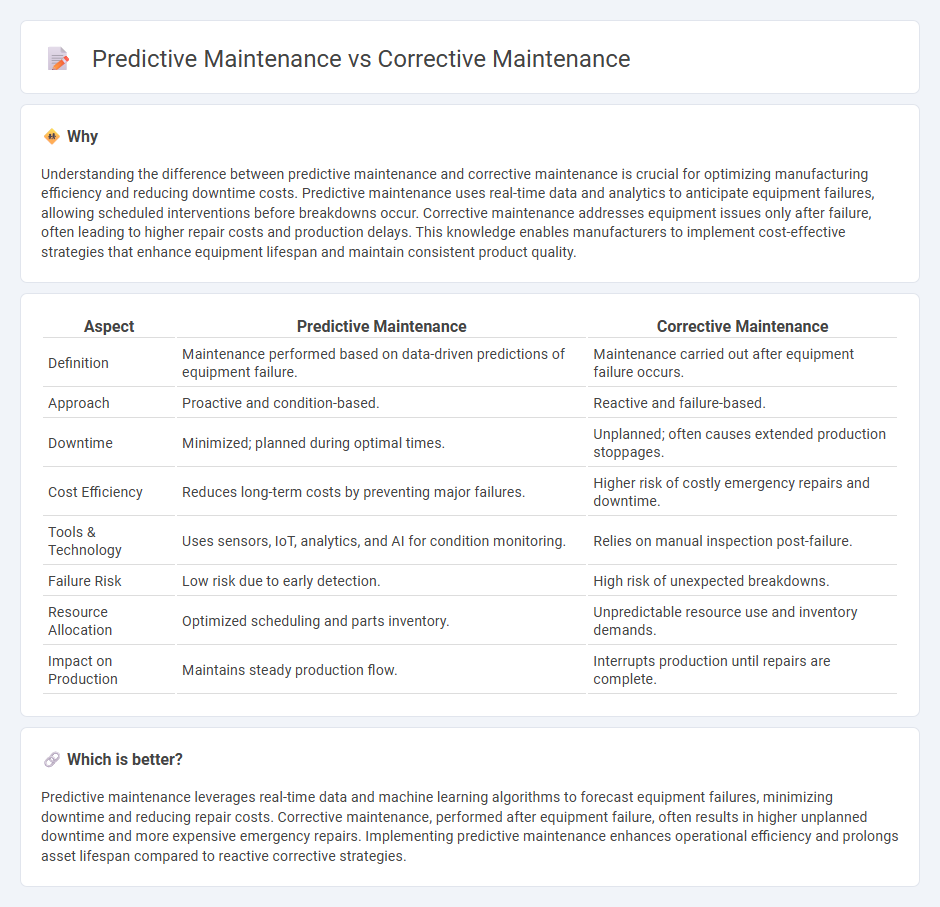
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Corrective Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance performed based on data-driven predictions of equipment failure. | Maintenance carried out after equipment failure occurs. |
| Approach | Proactive and condition-based. | Reactive and failure-based. |
| Downtime | Minimized; planned during optimal times. | Unplanned; often causes extended production stoppages. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces long-term costs by preventing major failures. | Higher risk of costly emergency repairs and downtime. |
| Tools & Technology | Uses sensors, IoT, analytics, and AI for condition monitoring. | Relies on manual inspection post-failure. |
| Failure Risk | Low risk due to early detection. | High risk of unexpected breakdowns. |
| Resource Allocation | Optimized scheduling and parts inventory. | Unpredictable resource use and inventory demands. |
| Impact on Production | Maintains steady production flow. | Interrupts production until repairs are complete. |
Which is better?
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures, minimizing downtime and reducing repair costs. Corrective maintenance, performed after equipment failure, often results in higher unplanned downtime and more expensive emergency repairs. Implementing predictive maintenance enhances operational efficiency and prolongs asset lifespan compared to reactive corrective strategies.
Connection
Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and IoT sensors to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely corrective maintenance actions that minimize downtime and repair costs. Corrective maintenance responds to unexpected breakdowns, and insights from these incidents help refine predictive algorithms for improved accuracy. This connection creates a feedback loop that enhances overall manufacturing efficiency and asset reliability.
Key Terms
Corrective Maintenance:
Corrective maintenance involves repairing equipment only after a failure occurs, minimizing upfront costs but potentially causing unexpected downtime and higher long-term expenses. It contrasts with predictive maintenance, which uses data analytics and condition monitoring to anticipate and prevent failures before they happen. Explore more about the advantages and challenges of corrective maintenance in industrial applications.
Breakdown
Corrective maintenance addresses equipment failures after a breakdown has occurred, often leading to unplanned downtime and higher repair costs. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and condition monitoring to anticipate and prevent breakdowns before they happen, optimizing asset reliability and reducing expenses. Explore detailed strategies and benefits of both maintenance approaches to enhance operational efficiency.
Repair
Corrective maintenance involves repairing equipment only after a failure occurs, often leading to unexpected downtime and higher repair costs. Predictive maintenance uses data analysis and sensor monitoring to anticipate and address potential issues before breakdowns, minimizing repair frequency and extending equipment lifespan. Explore how predictive maintenance can transform your repair strategy and reduce operational disruptions.
Source and External Links
What is Corrective Maintenance? Examples, Best Practices - Camcode - Corrective maintenance is performed to restore malfunctioning equipment to proper working order, can be deferred, scheduled, or predictive, and aims to minimize downtime and productivity loss by quickly fixing issues after failure or defect detection.
Corrective maintenance - Wikipedia - Corrective maintenance involves identifying, isolating, and rectifying faults to restore failed equipment to its operational condition, and can be immediate or deferred according to maintenance rules and standards like IEC 60050 and NF EN 13306.
What is Corrective Maintenance? Essential Guide and Best Practices - It is the process of repairing equipment after failure or defect detection, either as planned maintenance based on inspections or unplanned in response to unexpected breakdowns, with identification aided by inspections and performance monitoring.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com