Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products and processes that enable continuous reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling of materials to minimize waste and resource consumption. Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes the reduction of environmental impact through energy efficiency, waste reduction, and responsible sourcing throughout the production lifecycle. Explore the key differences and benefits of circular and sustainable manufacturing to enhance your production strategies.
Why it is important
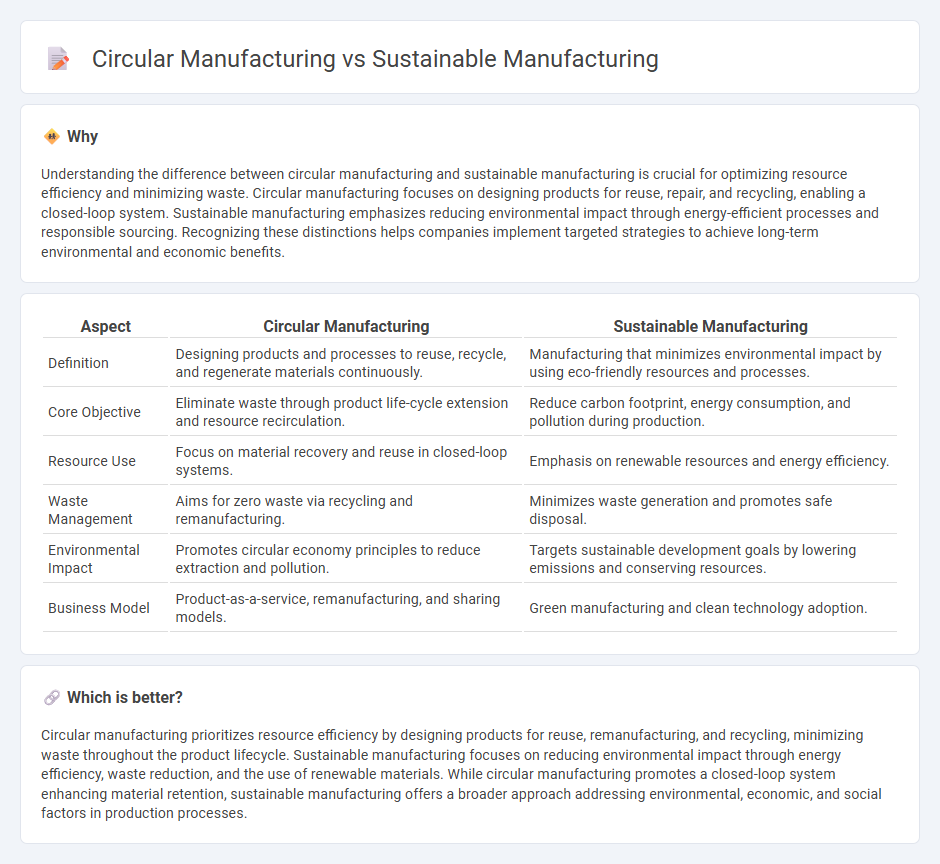
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and sustainable manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste. Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products for reuse, repair, and recycling, enabling a closed-loop system. Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact through energy-efficient processes and responsible sourcing. Recognizing these distinctions helps companies implement targeted strategies to achieve long-term environmental and economic benefits.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Sustainable Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Designing products and processes to reuse, recycle, and regenerate materials continuously. | Manufacturing that minimizes environmental impact by using eco-friendly resources and processes. |
| Core Objective | Eliminate waste through product life-cycle extension and resource recirculation. | Reduce carbon footprint, energy consumption, and pollution during production. |
| Resource Use | Focus on material recovery and reuse in closed-loop systems. | Emphasis on renewable resources and energy efficiency. |
| Waste Management | Aims for zero waste via recycling and remanufacturing. | Minimizes waste generation and promotes safe disposal. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes circular economy principles to reduce extraction and pollution. | Targets sustainable development goals by lowering emissions and conserving resources. |
| Business Model | Product-as-a-service, remanufacturing, and sharing models. | Green manufacturing and clean technology adoption. |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing prioritizes resource efficiency by designing products for reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, minimizing waste throughout the product lifecycle. Sustainable manufacturing focuses on reducing environmental impact through energy efficiency, waste reduction, and the use of renewable materials. While circular manufacturing promotes a closed-loop system enhancing material retention, sustainable manufacturing offers a broader approach addressing environmental, economic, and social factors in production processes.
Connection
Circular manufacturing and sustainable manufacturing are interconnected through their shared objective of minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency throughout the product lifecycle. Circular manufacturing emphasizes the continuous reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials to create closed-loop systems, reducing reliance on virgin resources. Sustainable manufacturing integrates environmental, economic, and social considerations to achieve long-term production processes that lower carbon emissions, conserve water, and reduce energy consumption, aligning closely with circular principles to promote eco-friendly industrial practices.
Key Terms
**Sustainable Manufacturing:**
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact by optimizing energy use, minimizing waste, and employing eco-friendly materials across production processes. It prioritizes lifecycle assessments to ensure products and processes contribute to long-term ecological balance without depleting natural resources. Discover how sustainable manufacturing strategies can drive innovation and resilience in your industry.
Resource Efficiency
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes minimizing environmental impact through energy-efficient processes and waste reduction, while circular manufacturing prioritizes resource efficiency by designing products for reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling within closed-loop systems. Both approaches aim to optimize raw material consumption, but circular manufacturing extends the lifecycle of materials, reducing dependency on virgin resources. Explore detailed strategies for enhancing resource efficiency in manufacturing to drive sustainability goals.
Emissions Reduction
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes reducing emissions by optimizing energy efficiency, minimizing waste, and using renewable resources throughout production processes. Circular manufacturing prioritizes emissions reduction by designing products for reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, effectively closing the material loop and preventing resource depletion. Explore the differences in strategies and technologies driving emissions reduction in both sustainable and circular manufacturing models.
Source and External Links
Sustainable Manufacturing - Optimizes processes to minimize environmental impact, conserve energy and resources, and enhance safety for employees and communities by focusing on the entire product lifecycle and closed-loop industrial systems.
5 Ways Manufacturers Can Become More Sustainable - Manufacturers reduce their environmental impact by lowering energy use, adopting renewable energy, using recyclable materials, implementing lean practices, and partnering with sustainable suppliers throughout the supply chain.
Sustainable Manufacturing | US EPA - Involves creating products through economically sound processes that conserve resources, minimize environmental harm, and deliver financial, operational, and reputational benefits for businesses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com