Industrial Internet leverages connected devices and data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes, enhance equipment efficiency, and enable predictive maintenance. Supply Chain Management coordinates the flow of materials, information, and finances from suppliers to customers, focusing on demand forecasting, inventory control, and logistics. Discover how integrating Industrial Internet with Supply Chain Management transforms operational performance and drives business growth.
Why it is important
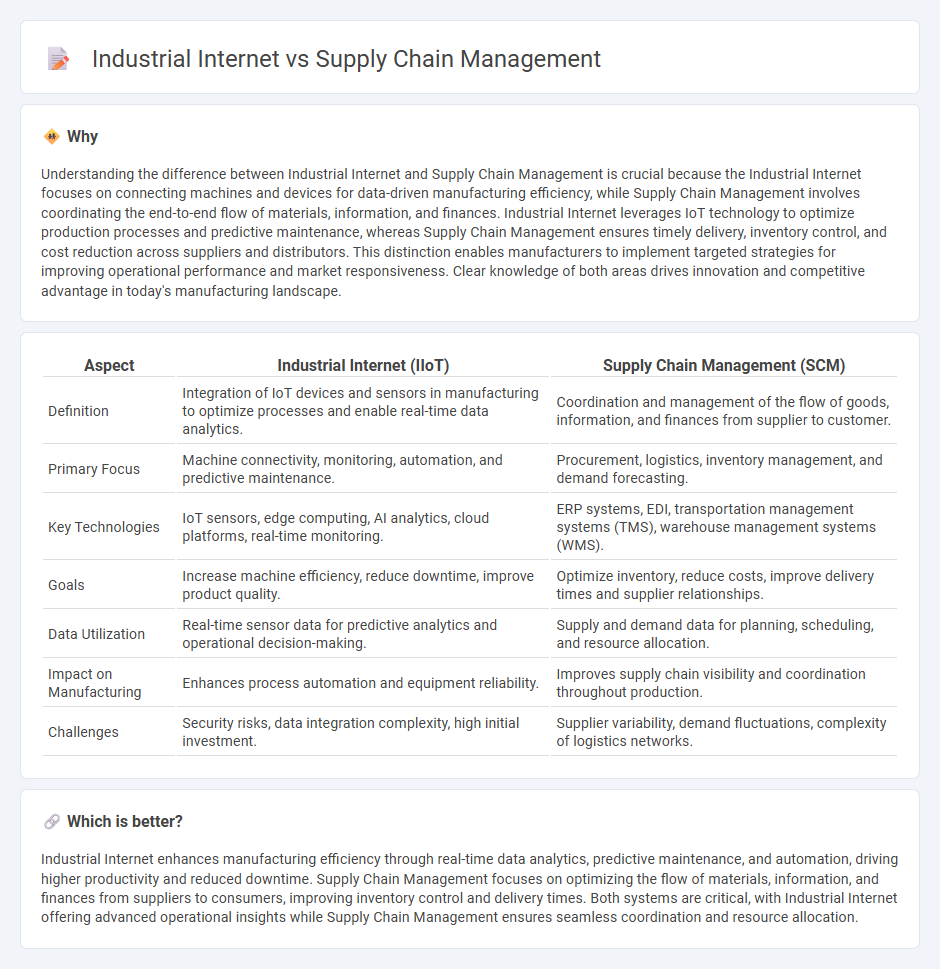
Understanding the difference between Industrial Internet and Supply Chain Management is crucial because the Industrial Internet focuses on connecting machines and devices for data-driven manufacturing efficiency, while Supply Chain Management involves coordinating the end-to-end flow of materials, information, and finances. Industrial Internet leverages IoT technology to optimize production processes and predictive maintenance, whereas Supply Chain Management ensures timely delivery, inventory control, and cost reduction across suppliers and distributors. This distinction enables manufacturers to implement targeted strategies for improving operational performance and market responsiveness. Clear knowledge of both areas drives innovation and competitive advantage in today's manufacturing landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Internet (IIoT) | Supply Chain Management (SCM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of IoT devices and sensors in manufacturing to optimize processes and enable real-time data analytics. | Coordination and management of the flow of goods, information, and finances from supplier to customer. |
| Primary Focus | Machine connectivity, monitoring, automation, and predictive maintenance. | Procurement, logistics, inventory management, and demand forecasting. |
| Key Technologies | IoT sensors, edge computing, AI analytics, cloud platforms, real-time monitoring. | ERP systems, EDI, transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management systems (WMS). |
| Goals | Increase machine efficiency, reduce downtime, improve product quality. | Optimize inventory, reduce costs, improve delivery times and supplier relationships. |
| Data Utilization | Real-time sensor data for predictive analytics and operational decision-making. | Supply and demand data for planning, scheduling, and resource allocation. |
| Impact on Manufacturing | Enhances process automation and equipment reliability. | Improves supply chain visibility and coordination throughout production. |
| Challenges | Security risks, data integration complexity, high initial investment. | Supplier variability, demand fluctuations, complexity of logistics networks. |
Which is better?
Industrial Internet enhances manufacturing efficiency through real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and automation, driving higher productivity and reduced downtime. Supply Chain Management focuses on optimizing the flow of materials, information, and finances from suppliers to consumers, improving inventory control and delivery times. Both systems are critical, with Industrial Internet offering advanced operational insights while Supply Chain Management ensures seamless coordination and resource allocation.
Connection
The Industrial Internet enhances Supply Chain Management by enabling real-time data collection and analysis through connected sensors and devices across manufacturing processes. This connectivity improves inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Integration of Industrial Internet technologies leads to increased supply chain transparency and agility, optimizing production schedules and delivery logistics.
Key Terms
**Supply Chain Management:**
Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves overseeing the flow of goods, information, and finances from raw materials to end customers, optimizing efficiency and reducing costs. It integrates procurement, production, logistics, and distribution to ensure timely delivery and inventory control. Explore how advanced SCM strategies can transform operational performance and drive business growth.
Logistics
Supply Chain Management (SCM) integrates planning, sourcing, production, and logistics to optimize the end-to-end flow of goods and information. The Industrial Internet enhances logistics by leveraging IoT devices, real-time data analytics, and predictive maintenance to improve shipment tracking, warehouse efficiency, and fleet management. Explore how combining SCM strategies with Industrial Internet technologies revolutionizes logistics operations for greater accuracy and cost savings.
Procurement
Supply Chain Management (SCM) enhances procurement efficiency by integrating demand forecasting, supplier collaboration, and inventory optimization to reduce costs and improve delivery times. The Industrial Internet leverages IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and automation to provide transparency and predictive maintenance, enabling proactive procurement decisions and minimizing supply disruptions. Explore detailed insights on how combining SCM strategies with Industrial Internet technologies can revolutionize procurement processes.
Source and External Links
What is Supply Chain Management? Roles, Salaries, and ... - Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves coordinating and overseeing activities from production to delivery of goods or services, focusing on planning, sourcing, organizing, delivering, and managing the entire supply chain efficiently to avoid delays and optimize performance.
What Is Supply Chain Management? - SCM is the coordination of the complete production flow from raw materials sourcing to delivering finished products, aiming to optimize the complex global network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers for cost and time efficiency.
What is SCM (Supply Chain Management) - SCM manages the flow of goods, data, and finances related to a product/service from raw material procurement to final delivery, integrating functions across procurement, product lifecycle, logistics, and global trade through advanced digital systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com