Cobotics integrates collaborative robots designed to work safely alongside humans, enhancing precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) automate production with adaptable machinery capable of handling various tasks, increasing responsiveness to market demands. Explore how cobotics and FMS transform modern manufacturing landscapes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cobotics and flexible manufacturing systems is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and worker safety. Cobotics involves collaborative robots designed to work alongside humans, enhancing precision and reducing labor-intensive tasks. Flexible manufacturing systems focus on automated processes that adapt to different product types, enabling rapid changes in production lines without extensive downtime. Knowing these distinctions helps manufacturers implement the most suitable technology for specific operational goals and cost management.
Comparison Table
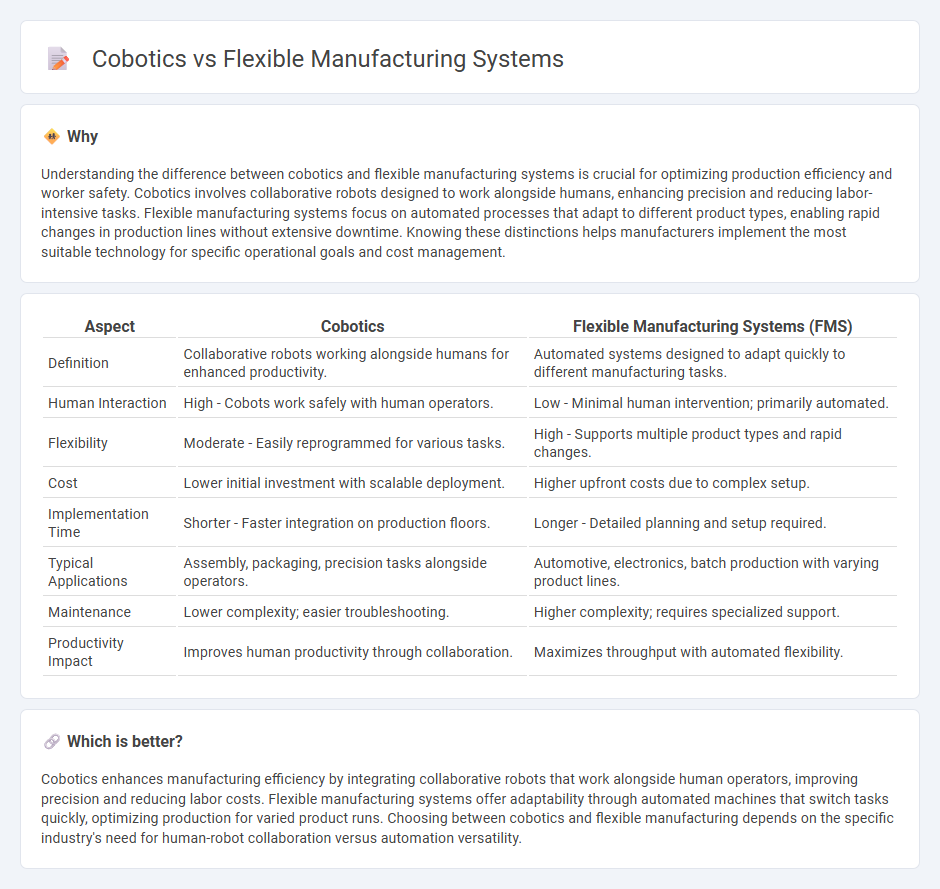
| Aspect | Cobotics | Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative robots working alongside humans for enhanced productivity. | Automated systems designed to adapt quickly to different manufacturing tasks. |
| Human Interaction | High - Cobots work safely with human operators. | Low - Minimal human intervention; primarily automated. |
| Flexibility | Moderate - Easily reprogrammed for various tasks. | High - Supports multiple product types and rapid changes. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment with scalable deployment. | Higher upfront costs due to complex setup. |
| Implementation Time | Shorter - Faster integration on production floors. | Longer - Detailed planning and setup required. |
| Typical Applications | Assembly, packaging, precision tasks alongside operators. | Automotive, electronics, batch production with varying product lines. |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity; easier troubleshooting. | Higher complexity; requires specialized support. |
| Productivity Impact | Improves human productivity through collaboration. | Maximizes throughput with automated flexibility. |
Which is better?
Cobotics enhances manufacturing efficiency by integrating collaborative robots that work alongside human operators, improving precision and reducing labor costs. Flexible manufacturing systems offer adaptability through automated machines that switch tasks quickly, optimizing production for varied product runs. Choosing between cobotics and flexible manufacturing depends on the specific industry's need for human-robot collaboration versus automation versatility.
Connection
Cobotics enhances flexible manufacturing systems by enabling collaborative robots to work safely alongside human operators, increasing adaptability and precision in production processes. Flexible manufacturing systems benefit from cobots' ability to quickly switch tasks and handle complex operations, optimizing workflow efficiency. This integration reduces downtime and improves scalability, driving innovation in smart factories.
Key Terms
Automation
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate programmable machines and robots to adapt quickly to product variations, maximizing automation efficiency and throughput. Cobotics, or collaborative robots, enhance automation by working safely alongside human operators, improving precision and flexibility in tasks without extensive reprogramming. Explore deeper insights into how automation evolves with FMS and cobotics to revolutionize production processes.
Human-robot collaboration
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate automated machinery with adaptable processes to optimize production efficiency, while cobotics centers on human-robot collaboration for shared task execution and safety. Cobots are designed to work alongside humans, enhancing dexterity and decision-making within manufacturing environments, contrasting with FMS's emphasis on automated, reprogrammable workflows. Explore the evolving landscape of human-robot collaboration by learning more about the complementary roles of FMS and cobotics in modern industry.
Reconfigurability
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) offer high reconfigurability through automated workstations and programmable logic controllers, enabling rapid adaptation to different product designs and volumes. Cobotics enhances reconfigurability by integrating collaborative robots that easily reprogram and redeploy alongside human operators, facilitating quick adjustments without extensive downtime. Explore the advantages of reconfigurability in these advanced manufacturing solutions to optimize your production processes.
Source and External Links
Flexible Manufacturing System - Wikipedia -- A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is an automation-based setup that can adapt to changes in product type, production sequence, or volume, typically combining work machines, material handling, and centralized computer control for efficient, adaptable manufacturing of small batch sizes.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) - Autodesk -- FMS are computer-controlled production systems designed to quickly adjust to new products, batch sizes, or manufacturing sequences by leveraging routing flexibility (changing operation order) and machine flexibility (using different machines for the same task).
What Are Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)? | Trevisan -- FMS types include engineered (for single-part, high-volume production), dedicated (limited product mix at high volume), sequential (fixed order part production), random (on-demand, mixed-product manufacturing), and modular (highly reconfigurable setups), each tailored to different manufacturing needs and flexibility levels.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com