Condition monitoring utilizes real-time data from sensors to predict equipment failures before they occur, improving production efficiency and reducing downtime. Reactive maintenance addresses equipment issues only after failures happen, often leading to unplanned outages and higher repair costs. Discover how condition monitoring can transform your manufacturing maintenance strategy for enhanced reliability and cost savings.
Why it is important
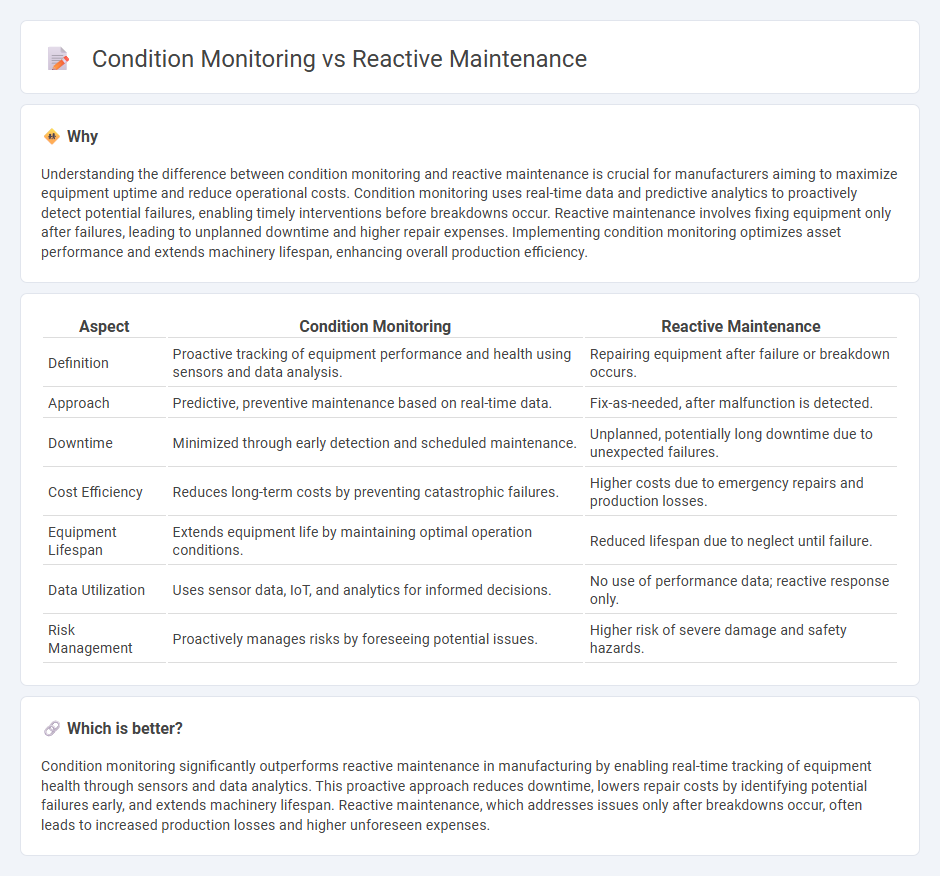
Understanding the difference between condition monitoring and reactive maintenance is crucial for manufacturers aiming to maximize equipment uptime and reduce operational costs. Condition monitoring uses real-time data and predictive analytics to proactively detect potential failures, enabling timely interventions before breakdowns occur. Reactive maintenance involves fixing equipment only after failures, leading to unplanned downtime and higher repair expenses. Implementing condition monitoring optimizes asset performance and extends machinery lifespan, enhancing overall production efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Condition Monitoring | Reactive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive tracking of equipment performance and health using sensors and data analysis. | Repairing equipment after failure or breakdown occurs. |
| Approach | Predictive, preventive maintenance based on real-time data. | Fix-as-needed, after malfunction is detected. |
| Downtime | Minimized through early detection and scheduled maintenance. | Unplanned, potentially long downtime due to unexpected failures. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces long-term costs by preventing catastrophic failures. | Higher costs due to emergency repairs and production losses. |
| Equipment Lifespan | Extends equipment life by maintaining optimal operation conditions. | Reduced lifespan due to neglect until failure. |
| Data Utilization | Uses sensor data, IoT, and analytics for informed decisions. | No use of performance data; reactive response only. |
| Risk Management | Proactively manages risks by foreseeing potential issues. | Higher risk of severe damage and safety hazards. |
Which is better?
Condition monitoring significantly outperforms reactive maintenance in manufacturing by enabling real-time tracking of equipment health through sensors and data analytics. This proactive approach reduces downtime, lowers repair costs by identifying potential failures early, and extends machinery lifespan. Reactive maintenance, which addresses issues only after breakdowns occur, often leads to increased production losses and higher unforeseen expenses.
Connection
Condition monitoring uses real-time data from sensors to assess equipment health, enabling early detection of faults and preventing unexpected breakdowns. Reactive maintenance occurs when repairs are performed after equipment failure, often resulting in higher downtime and costs. Integrating condition monitoring reduces reliance on reactive maintenance by identifying issues before they cause operational disruptions.
Key Terms
Downtime
Reactive maintenance addresses equipment downtime by fixing issues only after failure occurs, often leading to extended production halts and increased repair costs. Condition monitoring continuously tracks asset health through sensors and analytics, enabling predictive interventions that minimize unplanned downtime and optimize operational efficiency. Discover how integrating condition monitoring can transform maintenance strategies and reduce costly downtime.
Predictive analytics
Reactive maintenance addresses equipment failures after they occur, leading to unplanned downtime and increased repair costs. Condition monitoring continuously collects data on asset performance and health, enabling the use of predictive analytics to foresee potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively. Explore the benefits of integrating condition monitoring with predictive analytics to enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance expenses.
Failure detection
Reactive maintenance relies on identifying equipment failures after they occur, leading to unexpected downtime and higher repair costs. Condition monitoring uses real-time data from sensors and diagnostic tools to detect early signs of failure, enabling proactive interventions and optimizing asset lifespan. Explore how advanced failure detection techniques can enhance your maintenance strategy and reduce operational risks.
Source and External Links
Reactive Maintenance | What is Reactive Maintenance? - Reactive maintenance is the process of repairing assets after a breakdown or poor performance is observed, requiring lower initial costs and staffing but carrying risks of unplanned downtime for critical equipment.
What is Reactive Maintenance? - Reactive maintenance, also called corrective maintenance, is a strategy where repairs are performed only after an asset breaks down, making it suitable for low-cost, non-critical equipment that won't disrupt business operations if they fail.
What Is Reactive Maintenance? - This approach focuses on quickly restoring assets after a breakdown, often using a "run-to-failure" method, and is commonly used for equipment that does not significantly affect production or safety.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com